Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Assessing the vulnerabilities in databases and securing NoSQL Databases like MongoDB and Cassandra databases
Authors: Ms. Sumi M, Mr. Sreeraj C S
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.42999
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
On account of the rising amounts and the stand-out kinds of realities that need to be saved inside the Databases, offices, and organizations are quickly taking on NoSQL data sets to contend. Those data sets have been not planned with security as fundamentally important. NoSQL open-supply programming changed into In the primary high level to deal with unstructured measurements for the intention of business insight and Selection help. Throughout the long term, insurance highlights have been added to those data sets, but they are not quite as tough as they should be, and there\'s a degree for advancement as the complexity of the programmers has been expanding. In addition, the mapping less design of those data sets makes it more noteworthy intense to place into impact regular RDBMS like security capacities in those data sets. Famous NoSQL information bases are MongoDB and Apache Cassandra. Despite the fact that there are loads of examinations related to well-being weaknesses and tips to upgrade the security of NoSQL Databases, this exploration focuses especially on MongoDB and Cassandra data sets. This gander at goals to find and investigate all of the assurance weaknesses that MongoDB and Cassandra Databases have which can be specific to them and give you a stage through the advance manual that can help organizations to comfortable their records put away in these data sets. That is extremely urgent because of the reality the plan and weaknesses of each NoSQL data set are not quite the same as one another and thus require security hints which can be intended for them.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
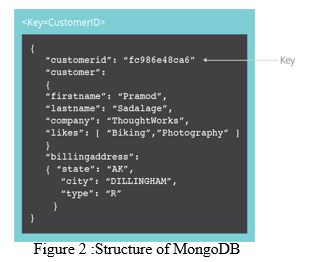
NoSQL (i.e., non-square or not simplest square) database is a database design, which is not based totally on the square (structure query language). Essentially, NoSQL databases aren't relational. They are designed with looser consistency fashions than RDBMS and commonly do no longer have a schema. NoSQL databases do now not rely upon schemas, tables, rows, or columns to prepare and retrieve facts. NoSQL databases are especially beneficial to store semi-established and unstructured information. NoSQL is being followed with the aid of corporations as a supplement to RDBMS to deal with new use cases because of the increasing volumes, velocity, variety (semi-structured and unstructured) of data that corporations want to save on an everyday foundation and the need for frequent updates and capabilities because the commercial enterprise necessities change on this digital and competitive economic system is becoming increasingly more difficult with the present traditional database control tools. A few examples of NoSQL databases are MongoDB, Cassandra, CouchDB, Redis, and HBase. Two of the top-rated NoSQL databases MongoDB and Cassandra no longer need to (Cooke, 2018). MongoDB is a record-oriented database, which means that the records are stored within the form of a report. Each database consists of collections, which in flip consist of files. Each document is composed of a different variety of fields, sizes, and content. Each document has an identity Area, that's used as a primary key. The structure of MongoDB is proven in the underneath discern. MongoDB does have a schema this is defined beforehand. The information (i.e., fields) can be created on the fly. MongoDB has its query language, which is called Mongo query language. The files in MongoDB are JSON-like, i.e., documents are represented in a binary-encoded format, that's called BSON (Binary JSON). BSON is an extension of the JSON model to offer ordered fields and extra statistics types. The default configuration of MongoDB permits full access to the database for everybody. MongoDB databases have a history of theft, and MongoDB servers have been held for ransom(McCallion, 2017). Since December of 2016, ransomware attacks had been happening on MongoDB databases, where attackers wipe off the database and ask for a ransom to get the information back. In 2018, the California Voter database, which contained data of over 19 million voters in California, changed exposed online because of an unsecured MongoDB database (Cimpanu, 2018). Apache Cassandra is a huge-column store database. It turn out to be evolved at FB at the start for inbox seek.
It emerge as designed to govern and control huge portions of facts throughout many servers. It could right away ingest similarly to technique very huge quantities of statistics. It's miles an allotted, decentralized, in particular scalable, to be had tuneable constant, and fault-tolerant database. It has the same nodes which may be clustered collectively in the manner to cast off bottlenecks and single factors of failure. Cassandra uses a peer-to-peer distribution model for the manner to distribute information. All nodes in Cassandra play an identical role, talking with every one-of-a-kind similarly no longer just like the grasp slave version. Cassandra database is being used by some of the most important corporations including Twitter, Cisco, eBay, Facebook, Netflix, and so on. CQL (Cassandra Query Language) is used to impeach the Cassandra database. Even though Cassandra has lots better protection than most NoSQL databases, some vulnerabilities can be exploited. For instance, the default configuration of some variations is susceptible to some distance-flung code execution. The security of those databases wants to be progressed because of the fact a few businesses additionally shop sensitive facts in the one's databases.
A. Definition of Terms
NoSQL: Non-SQL [1]/non-relational/not solely SQL may be schema-less information wherever information is kept in forms apart from tabular relations not like relative databases.
- SQL: Structured command language may be an artificial language wont to manages information within the electronic database management system (RDBMS)
- RDBMS: Electronic database management system (RDBMS) may be a direct system that's supported the relative model.
- Confidentiality: Confidentiality suggests that the information is accessible solely to those that square measure approved to access it supported a collection of rules. It limits access to information.
- Integrity: Integrity suggests ensuring that the information is consistent, accurate, and trustworthy over its entire life cycle.
- Convenience: Availability ensures that approved folks have reliable access to the information at any respect times.
- JavaScript: JavaScript may be a high level, multi-paradigm, and taken artificial language, which is an important part of net applications because it permits interactive web content.
- PHP: Personal home page may be a scripting language on the server-side and used for net development. JSON: JavaScript object notation may be a file format derived from JavaScript and is language freelance. It transmits information objects that contain attribute-value pairs and an array of information varieties. It transmits them in human-readable text.
- NoSQL Injection: NoSQL injection may be a vulnerability within the NoSQL information that enables Associate in Nursing assailant to regulate the information queries with the assistance of unsafe user input. It is wont to modify information, amendment privileges, expose sensitive data, or take down the complete application.
- CSRF: Cross-site request forgery may be a sort of cyber-attack that tricks Associate in Nursing end-user into corporal punishment malicious actions on an internet application that they're attested in.
- DOS: A denial of service attack may be a sort of cyber-attack during which an Associate in Nursing assailant makes the system or network resource inaccessible to the supposed users by disrupting services either briefly or indefinitely.
- MD5: Message digest algorithmic rule may be a common hashing perform that produces a 128-bit hash worth. it's primarily wont to prove the integrity of the information.
- Reposeful API: RESTful API is Associate in Nursing API (Application program interface) that uses communications protocol requests to place, GET, POST, and DELETE information.
- Password Brute Force attacks: A secret brute force attack or brute force attack is an Associate in Nursing attack wherever the assailant submits an inventory of passwords and checks all of them consistently to search out the right one.
- Man within the Middle Attacks: a person within the middle attack may be a quite cyber-attack wherever Associate in Nursing assailant relays and alters the communication between 2 parties on the Q.T. whereas they believe they're human activity with one another.
- Authorization: Authorization may be a method that determines what permissions a user has, that determines what a user will see and do.
- Authentication: Authentication may be a method that confirms a user’s identity, primarily with the assistance of usernames and passwords so solely approved users have access to a system, resource, or data [19].
- Coding: Encryption may be a method of secret writing the message or information in such the simplest way that solely approved folks will access it employing a preset key.
- TLS/SSL: Transport layer security and Secure Sockets layer square measure science protocols that give security for communications over an electronic network (SSL may be a deprecated precursor of TLS.
- Plain-text: Plain text / Clear text is information that's clear with no coding or graphical illustration.
- POST: POST is an Associate in Nursing communications protocol-supported request technique utilized by the World Wide Web (World Wide Web). The request is for the webserver to just accept information that's coarctate within the body of the request message. it's primarily used once submitting a completed net kind or uploading a file.
- HTML: machine-readable text nomenclature is the customary nomenclature that's wont to produce web content and net applications.
- Cluster: In databases, clusters square measure a group of databases that connect along to produce a service.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
The schema of NoSQL databases is dynamic, in contrast to SQL databases that have a predefined schema. NoSQL databases provide high quantifiability, performance, low latency, and suppleness. These pieces of information use AN unstructured command language whose syntax differs from information to database. classified in keeping with however they store the info. There are primarily 5 differing types of NoSQL databases betting on however the info is held on (Vishwakarma, 2017). They are:
- Key-Value Store: Accustomed store keys and their associated paired values. due to its simplicity, the question is quick. Some use cases of key-value knowledgebases are: storing user session data, storing user preferences, storing cart knowledge, and maintaining schema-free user profiles. Some well-liked Key-Value-based NoSQL databases are generator and Riak. a number of the foremost well-liked firm’s victimization Key Value-based NoSQL databases are Twitter, Coinbase, and Pinterest.
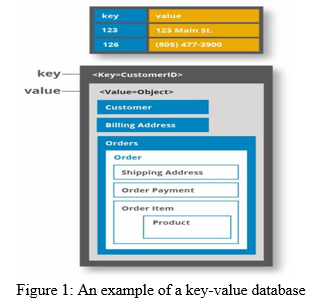
2. Document-based Store: A document store information (also called document-oriented information, combination information, or just document store or document information) may be a knowledge base that uses a document-oriented model to store data. Document store knowledgebases stores every record and its associated data at intervals of one document. every document contains semi-structured knowledge that may be queried against victimization varied questions and analytics tools of the DBMS.
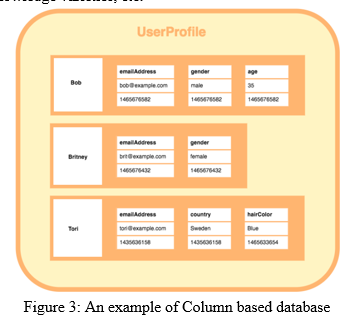
3. Column-based Store: A column store information may be a variety of information that stores knowledge employing a column orientated model. A column store information also can be cited as a: Column information. Some well-liked column-based NoSQL databases are prophetess and HBase. a number of the favored firms that use Column based mostly NoSQL databases are Facebook and Spotify [2]. The below diagram shows AN example of a column storing information. The columns in every row here are contained at intervals that individual row and every row will have a unique variety of columns and that they will be in a very different order and knowledge varieties, etc.
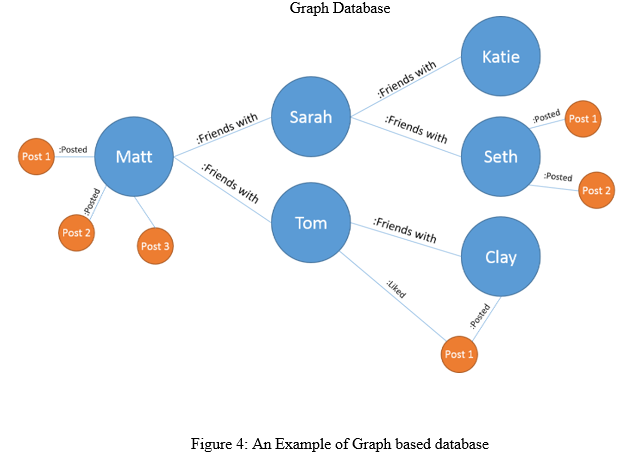
4. Graph-based Database: As its name suggests, graph information is shapely supported graphs. These graphs represent complicated, interconnected data in addition because the relationships at intervals it in a very clear approach, and they store this knowledge as an oversized, coherent knowledge set. The graphs are created from nodes – clearly labeled and acknowledgeable knowledge entities and objects – and edges. The latter involves the relationships between the objects. each element is depicted visually as points and contours. Edges every has a begin and finish purpose, whereas every node perpetually encompasses a bound variety of relationships to different nodes, whether or not incoming, outgoing, or planless.
A. Security Issues or Vulnerabilities in NoSQL Databases in General
- Because the NoSQL info is schema-free, it's troublesome to implement fine-grained access management or enforce role-based access control. This, combined with an absence of central control, makes it very difficult to enforce integrity constraints (Dindoliwala & Morena, 2017).
- Security should be obligatory within the middleware by the developers for NoSQL databases as there's no feature to implant security at intervals in the database (Dindoliwala & Morena, 2017).
- NoSQL databases have distributed nodes, that create an associate degree enlarged attack surface that produces it difficult to secure this knowledgebase. If one node is compromised, the whole system will be compromised. {in a during a in an exceedingly in a terribly} NoSQL info, data is shared between thousands of nodes. this suggests there would be multiple entry points related to every node, which will increase the chance of unauthorized access (Kadebu, Prudence, & Mapana, 2014) [3].
- NoSQL databases that use JavaScript and PHP on the server-side for the aim of enhancing database performance are at risk of question injection attacks (Shahriar & Haddad, 2017).
- NoSQL databases have very fewer security measures at intervals the database compared to ancient SQL knowledgebases. For example, ancient SQL databases have integral data integrity and cryptography features, whereas NoSQL databases store data in plain text and lack such inbuilt security features. External security mechanisms should be enforced to secure these databases (Dindoliwala & Morena, 2017).
- NoSQL databases are vulnerable to identification brute force attacks, replay attacks, and man within the middle attacks because of inefficient password storage mechanisms and authentication techniques (Dindoliwala & Morena, 2017).
- NoSQL databases primarily use REST as their communication protocol, which is prone to injection attacks, cross-site request forgery, and cross-site scripting attacks (Dindoliwala & Morena, 2017). (viii) NoSQL databases lack authentication mechanisms that will} be enforced across all the nodes of the cluster. These authentication mechanisms work on an area node level (Shahriar & Haddad, 2017).
- In NoSQL databases, authorization is applied on a per-database level and not on a group level. Also, authorization is applied at higher levels instead of lower levels (Dadapeer et al., 2016) [18].
- As NoSQL databases may contain sensitive data, the inefficient security mechanisms make the info at risk of corporate executive attacks as well. this can be created a lot of problems the fact that almost all NoSQL databases lack smart logging, auditing, and log analysis mechanisms (Dadapeer et al., 2016).
- Tons of NoSQL databases lack network transport layer cryptography over the TLS/SSL on each server and client-side. This results in insecure communication between the server and also the purchasers (Shahriar & Haddad, 2017).
- In key-value NoSQL databases, it's important to protect the key. As NoSQL databases are schema-free, there's no want to find the schema, associate degree makes it straightforward for an aggressor to search out or decipher the key victimization key brute-forcing attack (Chahal et al., 2017).
B. Security Issues or Vulnerabilities in MongoDB
- Authentication may be enabled in standalone mode, but when the usage of sharded mode in MongoDB, authentication isn't supported. The authentication furnished in standalone mode uses a key this is hashed in MD5 before it's far saved inside the key record. This is notably cozy, but if the attacker cracks the MD5, he/she will crack the key if they get a keep of the key record. The agency version for MongoDB does offer an additional provider for Kerberos, however, the authentication is not supported in sharded mode (Noiumkar & Chomsiri, 2014) [17].
- MongoDB uses a binary wire-degree protocol for patron interfaces on TCP port 27017, and the function RESTful is used for handling the server on port 28017. No information encryption is executed for those ports, which means the customer-server communication is not comfortable (Noiumkar & Chomsiri, 2014).
- The internal scripting language used in MongoDB is JavaScript, which is not an easy scripting language and is prone to a scripting injection assault (Aviv et al., 2015) [4].
- MongoDB uses JSON format for data and queries. Although the JSON format is considered more secure than SQL in terms of performing an injection attack, it enables new types of injection attacks. It is vulnerable to PHP array injection, JavaScript injection, and cross-site request forgery attacks due to HTTP REST API exposure (Aviv et al., 2015).
- MongoDB has a feature of disclosing HTTP relaxation API, which shall we the customer programs to query the database. This option makes the database susceptible to CSRF assaults that permit bypassing firewalls and different outside perimeter defences by way of the attacker. In a secured network, when the database exposes relaxation API, anyone with gets entry to the network can query the database the usage of HTTP, which shall we queries to be initiated from the browser. This is a huge vulnerability as an attacker can inject an internet site with an HTML shape, and spearfishing may be used by an attacker controlling a malicious internet site to trick a worker of a corporation into browsing on that website. If the employee does that, the HTML form may be submitted with an action URL of an internal MongoDB database. The movement will succeed as the employee has access to the network from within (Aviv et al., 2015).
- MongoDB does now no longer have the ability to automatically encrypt documents that are written to the database. They are saved in plain text. This way that if a hacker is capable of getting into the system, he or she will effortlessly examine those documents (Dadapeer et al., 2016).
- In MongoDB, authorization is disabled. The authorization is provided on a keeping with-database degree, and it follows a position-primarily based method. Moreover, the roles are confined to three (Shahriar & Haddad, 2017).
- MongoDB’s internal hypertext transfer protocol server doesn't support SSL for shopper node communication, which implies the shopper communications don't seem to be secure unless the enterprise edition is employed or the complete MongoDB is recompiled with the “-sl” possibility (Shahriar & Haddad, 2017) [16].
- MongoDB model two.Four.Zero-2.4.4 features a vulnerability of an uninitialized pointer, that permits AN assaulter to hold out a denial of service attack (Chahal et al., 2017).
- MongoDB will no longer have any facilities for auditing movements which might be dead within the info. for each instance of MongoDB, there is, however, an AN hypertext transfer protocol console that shows data roughly the machine and also the purchasers that be a part of. this can be of no use though if authorization is disabled (Shahriar & Haddad, 2017).
a. PHP Array Injection: MongoDB databases are prone to PHP array injections as a result of PHP features a constitutional associative arrays feature that enables associate in nursing assaulter to send malicious payloads Aviv et al 2015 explain let’s take associate in nursing example of an online application that works with a PHP backend that encodes requests in JSON format this format is then wont to question the MongoDB knowledge store.
b. javascript Injection: Some operations in MongoDB are prone and permit associates in nursing assaulter to run discretionary javascript expressions in space of the user input at the server variety of these operators are where map-reduce establishment and devil whereas the assault string is evaluated concatenated or parsed into NoSQL API calls the NoSQL injection attacks is also completed the in that operator is above all inclined as a result of it operates as a filter at intervals the sql question it might absorb progressive javascript options in an end eavor to strain the facts the assaulter will bypass discretionary code into the wherein operator as a part of the question [15].
C. Security Problems or Vulnerabilities in Cassandra
- Cassandra will now not have a day out a mechanism for inactive connections even though there are inactive connections Cassandra will now not close to the connections for those customers that a vulnerability for a denial of supplier associate in nursing assaulter can be capable of creating fake association makes an attempt that consumes resources and makes the server unobtainable for the fresh customer connections noiumkar chomsiri 2014.
- Cassandra makes use of Cassandra question language cl but it miles vulnerable to injection very like sql adapter et al 2016 [5].
- passwords saved in Cassandra makes use of the md5 hash the md5 hashing rule may be a basic methodology that won’t cryptographically comfortable enough adapter et al 2016.
- Cassandra will not supply cryptography for communications that take region between the information and its customers if an associate in nursing assaulter makes an attempt to watch the network guests then he can be able to get all of the records that are being transmitted within the community it’s conjointly clean for the assaulter to induce the credentials of the users for the rationale that username and parole of the patron are transmitted within the network as plain text adapter et al 2016.
- the facts kept in Cassandra are not encrypted in the open-supply model the facts are not encoded for the rationale that there’s no machine-controlled mechanism in Cassandra to encrypt the records documents so if an associate in nursing assaulter accesses the facts heshe can instantly extract the facts for the rationale that facts is in plain matter content adapter et al 2016 [14].
- Cassandra features a weak authentication there’s no authentication and authorization between the shopper and also the Cassandra cluster by default once a malicious user with access to the network bypasses the shopper authentications then the user will extract knowledge Shahriar Haddad 2017.
- Cassandra has associate in nursing authentication mechanism said as authenticate its implementations which could be default implementation and simple authenticator adapter et al 2016 the default implementation turns off the information authentication demand and also the simple authenticator permits you to installation an inventory of users and connected passwords the employment of a flat-report the passwords will each be kept in plain-text or hashes victimization the md5 hashing set of rules the protection issues with those are
a. Even though at the passwords are saved as md5 hashes the communications among the information and also the purchasers contain causing the parole in undeniable-textual content associate in nursing assaulter which will sniff the community will effortlessly discover the parole for authentication
b. the md5 hashing set of rules isn’t thought of secure any longer as a result of the offered rainbow tables and pre-calculated lists online that might suit a hash to the associated simple-text [13].
8. Cassandra has associate in nursing authorization mechanism said as authority that comes into play while there is also a study or compose each column or while a keyspace is changed authority has 2 implementations that are a skip-via and simple authority the skip- through implementation offers complete permissions to any or all customers and simple authority uses a flat-record that features a listing of usernames and also the associated permissions adapter et al 2016 the protection issues with those are:
a. The authorization is enforced simplest on existing column families and as a result for new accessorial columns and column families, there’s no safety.
b. Simple authority doesn’t reload the flat-record once each gets entry to this suggests that that the Cassandra manner needs to be restarted sooner than changing the powerful permissions.
c. The permissions which could be granted to a shopper are primarily based completely on the flat document saved on the cluster member to that the link is attached and afterward if the documents for all cluster members at intervals the cluster aren’t synchronal its able to be a protection issue.
III. METHODOLOGY
To solve the problem, I will use the following steps:
- Step 1: Establish and analyse all the protection vulnerabilities of MongoDB and prophetess databases.
- Step 2: List the protection concerns for every info and write the associated standing for that the most concerns would be knowledge files authentication authorization auditing injection attacks and client-server communication the associated standing would make a case for what safety features are obtainable aren’t obtainable or aren’t strong enough etc the subsequent is associate degree example of what it looks like [12].
Considerations and Statuses
|
Consideration |
Status |
|
Data files |
Not encrypted |
|
Client-Server communication |
Not encrypted |
|
Authentication |
The available feature is not robust enough |
|
Authorization |
The available feature is not robust enough |
|
Auditing |
Not available |
|
Injection attacks |
possible |
Table 1: An example of Considerations and Statuses
3. Step 3: To support the concerns and therefore the statuses, I’ll come back up with a step by step recommendations that lists the steps that developers will follow in tiny corporations and organizations to secure the ASCII text file versions of MongoDB and Cassandra databases.
A. Data Presentation
The concerns and also the associated statuses that were known to induce the breadth of safety features in MongoDB and prophetess databases area unit are explained below. These concerns and statuses area units were later employed in the study to gauge the protection of those databases.
- Data Files: Data files area unit software system files that area unit wont to store knowledge among information or a computing system. Data files got to be properly secured with encoding to stop data felony AND intentional corruption by an attacker.
Statuses
a. Encrypted: Knowledge the info the information} within the data files is encoded by changing plain text to ciphertext
b. Not Encrypted: Knowledge the info the information} within the data files isn't encoded, which suggests it’s kept in plain text. Therefore if an associate degree offender gets his/her hands on the info, they'll build malicious use of the knowledge.
2. Client-Server Communication: Client-Server communication may be a method wherever purchasers (a program) send requests for services or resources to the server (another program), and therefore the server responds to the consumer requests (Sullivan, 2019) [11]. In most cases, there square measure multiple purchasers and one server. Securing the communications between purchasers and servers is extremely vital as a result of client-server communications additionally involve the exchange of credentials once authentication is going down. If the communications aren't encrypted, associate degree offenders observing the network traffic will get a hold of the knowledge and use it for malicious functions. Also, the purchasers and servers ought to be attested by employing a protocol like TLS (Transport layer security) to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of the knowledge that's changed.
Statuses
a. Encrypted: The info that's changed between the purchasers and therefore the Server is encrypted.
b. Not Encrypted: The info that's changed between the purchasers and therefore the Server isn't encrypted.
3. Authentication: Authentication is the method of confirming that solely a certified person is given access to the info (Chahal et al., 2017). A weak authentication mechanism will expose the info to replay attacks or man-in-the-middle attacks.
Statuses
a. The offered feature is robust: The offered authentication feature is robust and is extremely onerous to bypass
b. The offered feature isn't sturdy enough: The offered authentication feature is weak and is simple to bypass and is prone to attacks.
4. Authorization: Authorization may be a method of permitting users to access the info by looking at their role (Chahal et al., 2017). An absence of authorization options compromises the application security associate degree and maybe a loophole for hostile access from an offender [6].
Statuses
a. The offered feature is robust: The offered authorization feature is robust and is extremely onerous to bypass
b. The offered feature isn't sturdy enough: The offered authorization feature isn't sturdy enough.
5. Auditing: knowledge auditing may be a method designed to let associate degree administrators perceive World Health Organization checked out what and whether World Health Organization had modified what once (Yehuda, 2018). It provides some way to log user activity occurring on info. several corporations and organizations have internal security policies and external mandates that need auditing. Hence, auditing may be an important tool that will be wont to investigate what happened if an associate degree attack were to happen.
Statuses
a. Available: Auditing options square measure offered within the ASCII text file version.
b. Not Offered: Auditing options aren't available within the ASCII text file version.
6. Injection Attacks: NoSQL injection may be a security vulnerability wherever associate degree offender makes malicious use of user input to require management of the info queries, that successively compromises the databases. victimization of this system, associate degree offenders will expose the unauthorized data, build changes to the info, increase the privileges, or take down the full application.
Statuses
a. Possible: The info isn't secure against injection attacks.
b. Very Difficult: The info is well secured against injection attacks.
B. Data Analysis
A qualitative technique was wont to analyze all the vulnerabilities and are available up with a collection of concerns and statuses that best describe the safety problems with open supply versions of MongoDB and prophetess databases [10]. These concerns and statuses were analyzed in an exceedingly qualitative manner to come back up with a step by step recommendations that will be wont to secure the ASCII text file versions of those databases.
IV. RESULT ANALYSIS
After following the methodology discussed, I came up with the following considerations and statuses for NoSQL databases like Cassandra and MongoDB databases:
A. Consideration and Statuses
Cassandra’s Considerations and Statuses
|
Consideration |
Status |
|
Data files |
Records in storage aren’t automatically encrypted. It's far saved in plain textual content via default. |
|
Authorization |
The available characteristic isn't always sturdy or sufficient. The authority interface allows complete permissions to all users and the Simple Authority uses a flat File and is now not a maintained File throughout the cluster. |
|
Client-Server communication |
Now not encrypted. An attacker can monitor the database traffic to peer all communication. |
|
Authentication |
The available function isn't robust enough. The authentication is becoming off via default. With the use of SimpleAuthenticator, users, and passwords may be set with a flat file with a password in MD5 hash, however, the password continues to be transmitted in undeniable textual content via the Client interface. |
|
Injection attacks |
Possible. Cassandra query language is a parsed language vulnerable to injection assaults. |
|
Auditing |
Not available. Inline auditing is not supported. |
Table 2: A list of Cassandra’s Considerations and Statuses [9].
B. MongoDB
MongoDB’s Considerations and Statuses
|
Consideration |
Status |
|
Client-Server communication |
Not encrypted. An attacker can monitor the database traffic to see all communication. |
|
Authentication |
The available feature is not robust enough in standalone mode. In the Sharded mode, authentication is not supported. |
|
Authorization |
The available feature is not robust enough. A basic role-based access control model is supported, but the access control is enforced at an inappropriate granularity level. |
|
Data files |
Data in storage is not automatically encrypted. It is stored in plain text by default. |
|
Injection attacks |
Possible. The internal scripting language is JavaScript, which is an interpreted language with a potential for injection attacks. |
|
Auditing |
Not available in the open-source version |
Table 3: A list of MongoDB’s considerations and statuses
Based totally on the above protection considerations and statuses for each database, I got here up with the under step by step hints for securing the open-supply variations of MongoDB and Cassandra databases:
C. Step By step Recommendations
- MongoDB
a. Step 1: The get right of entry to manage isn't always enabled by using default in MongoDB. Whilst initializing the MongoDB shell, the –auth keyword may be used to permit authorization. Putting in authorization reduces the risk of account breaches. To create customers with roles, the subsequent command can be used [7]:
Use admin
Db. createUser(
{
User: “sindhu”,
Pwd: “securepassword”,
roles: [{role:”useAdminAnyDatabase”,db:”admin”}]
}
)
b. Step 2: In most cases, hackers first experiment with the default port numbers earlier than they attack (Paramathmuni, 2018). Subsequently, alternate the default port numbers in the MongoDB configuration record: mongo. Config.
c. Step 3: Authentication can be enabled by navigating to the #safety segment inside the MongoDB configuration report “Mongod. Conf”. Remove the “#” in the front of safety to allow it.
Security:
Authorization: “enabled”
Restart MongoDB now
To test the authentication, the show DBS command can be used. If the authentication

d. Step 4: computerized scripts can stumble on MongoDB instances that aren't included by way of a firewall. Verify the popularity of the firewall using the command:
sudo ufw status
If the status says inactive, activate it using the following command:
host$ sudo ufw enable
Also, make allow SSH using the command:
host$ sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
The output should indicate that only OpenSSH is allowed:
e. Step 5: If far off get right of entry to desires to be allowed, we will limit that access to a selected host for the default port 27107 the usage of the following command: host$ sudo ufw allow from client_ip_address to any port 27107 For each additional client who needs access, re-run this command using the IP address.
f. Step 6: A replication key file can be enabled to robotically enable authentication and ensure information encryption. With the usage of this method, the simplest hosts that have this file installed will be capable of being a part of the reproduction set. A key file may be generated using any desired technique. Once it's miles generated, copy the key file to the duplicate set individuals, permit the access manipulation and begin the replica set for you to permit the replication key file, add the following to the MongoDB configuration report (mongo. Conf):
Security:
Keyfile: <path to keyfile>
g. Step 7: although auditing functions are to be had in some versions of MongoDB, there are none to be had for the open-source model. Additionally, there's no third-birthday party device that can be hooked up inside the MongoDB open-supply version to generate audit logs. This may be a development inside the future in which MongoDB releases auditing capabilities for the open-supply model, or a third-celebration device is evolved that may generate audit logs for the open-source model of MongoDB.
h. Step 8: That allows you to save any injection assaults, a RESTful API can be developed that connects to the database with a constrained account most effectively. Further, the records enter can be sanitized, and robust authentication may be used. Additionally, permit the most effective direct connections from the API and network or machine firewalls that may be used to dam all the local customer communications.
2. Cassandra
a. Step 1: Cassandra does now not mechanically encrypt the statistics. We can permit inter-node encryption by navigating to the server_encryption_option section in Cassandra.YAML. The default for internode_encryption is set as none. Alternate this to either rack, dc, or all.
b. Step 2: We can also allow the client to Node Encryption by using navigating to the client_encryption_options section in Cassandra. YAML. The 2 number one alternatives for permitting encryption right here are “enabled” and “non-compulsory”.
If both are set as false, the client connections are unencrypted.
If both are set as true, the same port supports both encrypted and unencrypted connections.
If enabled is set as true and optional is set to false, all the client connections are then secured. Choose this option for better security.
c. Step 3: In Cassandra. Yaml file, flip the authentication choice from Allow All Authenticator (default authentication which does not perform any authentication exams and calls for no credentials) to Password Authenticator, which can be used to permit username and password authentication.
Authenticator: Password Authenticator
Restart the node after this.
d. Step 4: To prevent any security breaches, change the default superuser, which is ‘Cassandra’ to another superuser:
CREATE ROLE <new_super_user> WITH PASSWORD = ‘<provide a strong password here>’
AND SUPERUSER = true
AND LOGIN = true;
e. Step 5: Authorization can be enabled by using converting the authorizer putting inside the Cassandra.Yaml report. Using default, its miles are set as AllowAuthorizer. This setting offers all permissions to all the roles. Trade this to CassandraAuthorizer, which allows for complete permissions control.
Authorizer: CassandraAuthorizer
Once authorization is turned on, statements such as GRANT PERMISSION,
REVOKE PERMISSION, etc. can be used to set the access privileges for the clients.
Restart the node after this.
f. Step 6: As auditing functions are most effective to be had for the business enterprise versions, a 3rd-party tool along with credit may be hooked up to get the auditing functionality for the open-supply model of Apache Cassandra. Depending on the version of Cassandra, a well-suited audit model may be installed. EcAudit calls for a JVM that is Java 8 well suited. To start the setup, placed the audit jar report within the listing: $CASSANDRA_Home/lib/ listing on the way to permit the plug-in, the following settings need to be modified in Cassandra.Yaml report [8]:
Authenticator: com.ericson.bss.cassandra.ecaudit.auth.AuditAuthenticator
Authorizer: com.ericson.bss.cassandra.ecaudit.auth.AuditAuthorizer
Role manager: com.ericson.bss.cassandra.ecaudit.auth.AudiRoleManager
All the audit logs are stored in the audit.yaml file in Cassandra’s configuration directory.
V. SCOPE OF FUTURE RESEARCH
The research paintings that were done for this look may be expanded in addition to helping make the open-source variations of NoSQL databases such as MongoDB and Cassandra greater robust in safety like their RDBMS counterparts.
Conclusion
This examination affords and discusses a comprehensive list of vulnerabilities of NoSQL databases in widespread and vulnerabilities that might be unique to MongoDB and Cassandra databases. The examination also identifies and describes a set of safety issues for every database and provides suggestions that may be used to comfortable the MongoDB and Cassandra databases.
References
[1] Zahid, A., Masood, R., & Shibli, M. A. (2014). Security of sharded NoSQL databases: A comparative analysis. 2014 Conference on Information Assurance and Cyber Security (CIACS). doi:10.1109/ciacs.2014.6861323 [2] Yehuda, Yaniv. (2018, March 21). Database Audits: Why You Need Them and What Tool is to Use. Retrieved from www3.dbmaestro.com, website:https://www3.dbmaestro.com/blog/database-audits-why-you-need-them-what-tools-to- use [3] Vishwakarma, R. (2017, May 16). The Different Types of NoSQL Databases. [4] Sullivan, J. (2019, April). client-server model (client-server architecture). Retrieved from searchnetworking.techtarget.com website: Retrieved from search networking.techtarget.com [5] Shahriar, H., & Haddad, H. M. (2017). Security Vulnerabilities of NoSQL and SQL Databases for MOOC Applications. International Journal of Digital Society (IJDS), 8(1), 1244-1250. [6] Sadalage, P. (2014, October 3). NoSQL Databases: An Overview. [7] R, Rajmohan., & S, P Priyadharshini. (2017). Analysis of Database Security Model Against NOSQL Injection. l Journal of Scientific Research in Computer Science, 2(2). [8] Saran, R., M, Sai Baba., S, Jayanthi., & E, Soundararanjan. (2015). Storing of Unstructured data into MongoDB using Consistent Hashing Algorithm. International Journal of Emerging Technologies in Engineering Research,3(3). [9] Paramathmuni, P. (2018, October 31). MongoDB security tips. (2018, October 31). Retrieved from developer.rackspace.com [10] Cooke, A. (2018, May 08). Top Rated NoSQL Databases for 2018 I TrustRadius. Retrieved from https://www.trustradius.com/buyer-blog/top-rated-nosql-databases-2018/ [11] Okman, L., Gal-Oz, N., Gonen, Y., Gudes, E., & Abramov, J. (2011). Security Issues in NoSQL Databases. 2011IEEE 10th International Conference on Trust, Security, and Privacy in Computing and Communications. doi:10.1109/trustcom.2011.70 [12] Noiumkar, P., & Chomsiri, T. (2014). A comparison of the level of security in the Top 5 Open-source NoSQL databases. 2014 The 9th International Conference on Information Technology and Applications. [13] McCallion, J. (2017). 26,000 unsecured MongoDB servers were hit by ransomware. (2017, September 06). [14] Hou, B., Qian, K., Li, L., Shi, Y., Tao, L., & Liu, J. (2016). MongoDB NoSQL Injection Analysis and Detection. 2016 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Cyber Security and Cloud Computing (CSCloud). doi:10.1109/cscloud.2016.57 [15] Ghazi, Y., Masood, R., Rauf, A., Shibli, M. A., & Hassan, O. (2016). DB-SECaaS: A cloud-based protection system for document-oriented NoSQL databases. EURASIP Journal on Information Security,2016(1). doi:10.1186/s13635-016-0040-5 [16] Dindoliwala, V. J., & Morena, R. D. (2017). Survey on Security Mechanisms In NoSQLDatabases. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science,8(5). [17] Cimpanu, C. (2018, August 07). California Voter Database Compromised in MongoDB Incident. [18] Ahmadian, M. (2017). Secure query processing in cloud NoSQL. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics (ICCE). doi:10.1109/icce.2017.7889242. [19] Amreen, & Dadapeer. (2016). A survey on robust security mechanisms for NoSQL databases. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering,4(4), 7662-7666. doi:10.15680/IJIRCCE.2016.0404265.
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Ms. Sumi M, Mr. Sreeraj C S. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET42999
Publish Date : 2022-05-20
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

