Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Benefits of AWS in modern Cloud over On-premises Method
Authors: Vivek Habib, Chirag Patil
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.43349
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
This research paper gives an overview of the benefits of AWS in the modern cloud over the On-premises methods that we use earlier before cloud computing is introduced. Cloud computing is performing well in today’s World and boosting the ability to use the internet more than ever. Cloud computing gradually developed a method to use the benefits of it in most of the organizations. It is very demanding in all businesses tasked with improving the quality of service, reducing costs as the organization pays for the service only what they consume based on the incoming and outgoing traffic.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Whether your excursion will guide you toward register power, information base capacity, content conveyance or other usefulness, the cloud conveys what you want to take your association to a higher degree of processing in the Amazon Web Services. The benefits of AWS in the modern cloud are huge. Data protection, regulatory compliance, quantifiability, flexibility, cost-effectiveness, multiple storages, auto-scaling, access to the data anytime, data-centric encryption, high-performance processing are a few benefits of AWS cloud. Let’s understand the importance of the AWS cloud in detail to get the best idea of it.
II. EXISTING SYSTEM
Whether an organization puts its applications in the cloud or whether it chooses to keep them on premises, information security will be central 100% of the time. Yet, for those organizations in exceptionally managed ventures, the choice could currently be made for them regarding whether to house their applications on premise. What's more, realizing your information is situated inside your in-house servers and IT foundation could likewise give more genuine serenity in any case.
On-premise programming expects that a venture buys a permit or a duplicate of the product to utilize it. Since the actual product is authorized and the whole occurrence of programming dwells inside an association's premises, there is for the most part more noteworthy insurance than with a distributed computing framework.
The disadvantage of on-premise conditions is that expenses related to overseeing and keeping up with all the arrangement involved can run dramatically higher than a distributed computing climate. An on-premise arrangement expects in-house server equipment, programming licenses, reconciliation abilities, and IT representatives available to help and oversee potential issues that might emerge. This doesn't factor in how much upkeep that an organization is answerable for when something breaks or doesn't work.
Cons of On-premises Servers
- Requires a capital interest in equipment and foundation.
- Requires space in your office for rack space or server room/storeroom, as well as devoted IT support.
- Might be more defenseless to information misfortune during calamity circumstances because of its in-house area. How regularly you take the information offsite will reflect how much information you'll lose in a crisis.
- No uptime ensures.
III. PROPOSED SYSTEM
Amazon Web Services or AWS as a condensing is a well-known Cloud Service Provider that enable on demand benefits like compute, storage, networking, security, databases, and so forth which can be gotten to through the web across the globe and the client isn't expected to manage or monitor these resources.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a flexible, secure and dependable cloud specialist organization and is the most sort after Cloud Computing and Hard expertise on the lookout. Amazon Web Services is a worldwide innovator as far as Public Cloud market share and gives cloud solutions in 245 unique nations across the globe. AWS provides us with more than 200 Cloud Computing services.
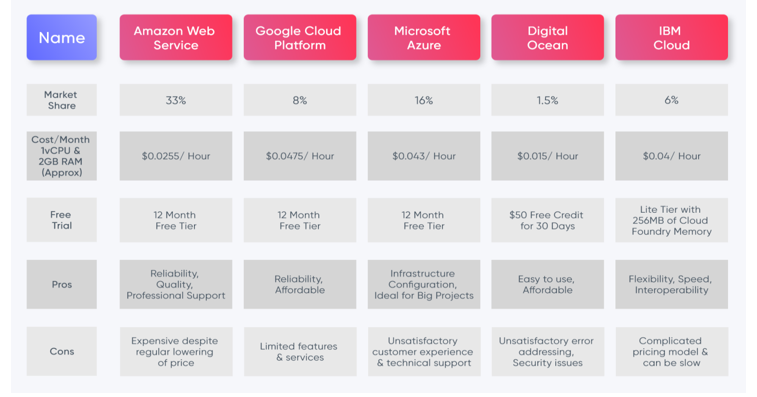
Below figure shows us that how AWS is used in modern cloud:
A. Compute Service
In cloud computing, the expression "compute" describes ideas and objects connected with software computation. It is a nonexclusive term used to reference handling power, memory, systems administration, stockpiling, and different assets expected for the computational progress of any program.
Amazon provides a number of compute services like EC2 instance, Amazon Elastic beanstalk, Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, AWS Lambda, AWS LightSail, AWS Fargate, etc. AWS helps to build and use the compute service in very cost-effective price, so that the customer pay only for the resource that he used. This is the good feature of AWS, because we know that on-premises we need to buy the server and even set up server, so it needs more time and is highly expensive.
- Amazon EC2: Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) is a web organization that gives secure, resizable register limit in the cloud. It is planned to make web-scale handling less difficult for engineers. The clear web point of connection of Amazon EC2 licenses you to obtain and configuration limits with inconsequential scouring. It gives you limitless power of your figuring resources and permits you to run on Amazon's exhibited handling environment. Amazon EC2 diminishes the time expected to get and boot new server models (called Amazon EC2 events) to minutes, allowing you to quickly scale limit, both everywhere, as your figuring necessities change. Amazon EC2 changes the monetary parts of handling by allowing you to pay only for limits that you truly use. Amazon EC2 gives specialists and structure chiefs the gadgets to develop dissatisfaction adaptable applications and confine themselves from ordinary frustration circumstances.
Types of EC2:
- On-Demand Instances-With On-Demand occasions, you pay for register limit continuously or the second contingent upon which cases you run. No more extended term responsibilities or forthright installments are required. You can increment or diminish your register limit contingent upon the requests of your application and just compensation the predefined per hourly rates for the case you use.
- Spot Instances-Spot Instances are accessible at up to a 90% markdown contrasted with On-Demand costs and let you exploit unused Amazon EC2 limit in the AWS Cloud. You can altogether decrease the expense of running your applications, become your application's register limit and throughput for a similar spending plan, and empower new sorts of distributed computing applications.
- Reserved Instances-Reserved Instances give you a huge rebate (up to 72%) contrasted with On-Demand occurrence evaluating. You have the adaptability to change families, working framework types, and occupancies while profiting from Reserved Instance estimating when you utilize Convertible Reserved Instances.
- Savings Plans-Savings Plans are an adaptable valuing model that deals with low costs on EC2 and Fargate use, in return for a pledge to a reliable measure of use (estimated in $/hour) for a 1 or long term.
- Dedicated Hosts-A Dedicated Host is an actual EC2 server devoted for your utilization. Devoted Hosts can assist you with diminishing expenses by permitting you to utilize your current server-bound programming licenses, including Windows Server, SQL Server, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (dependent upon your permit terms), and can likewise assist you with meeting consistence necessities.
2. Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling: Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling assists you with keeping up with application accessibility and permits you to consequently add or eliminate EC2 cases as per conditions you characterize. You can utilize the armada, the board elements of Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, to keep up with the wellbeing and accessibility of your armada. You can likewise utilize the dynamic and prescient scaling highlights of Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling to add or eliminate EC2 examples. Dynamic scaling answers changing interest and prescient scaling consequently plans the right number of EC2 occasions in light of anticipated request. Dynamic scaling and prescient scaling can be utilized together proportionally quicker.
3. Amazon Lambda: AWS Lambda allows you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. You pay just for the process time you consume, there is no charge when your code isn't running. With Lambda, you can run code for basically any sort of use or backend administration all with zero organization. Simply transfer your code, and Lambda deals with everything expected to run and scale your code with high accessibility. You can set up your code to naturally set off from other AWS services, or you can call it straightforwardly from any web or versatile application.
4. Amazon Fargate: AWS Fargate is a figure motor for Amazon ECS that permits you to run holders without overseeing servers or bunches. With AWS Fargate, you never again need to arrange, design, and scale groups of virtual machines to run holders. This eliminates the need to pick server types, choose when to scale your groups, or streamline bunch pressing. AWS Fargate eliminates the requirement for you to communicate with or think about servers or clusters. Fargate allows you to focus on planning and building your applications as opposed to dealing with the foundation that runs them.
B. Networking Service
A capability that facilitates a network operation. It generally is provided by a server (which are often running one or a lot of services), supported network protocols running at the appliance layer within the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model of the network. Some examples area unit name system (DNS), dynamic host configuration protocol (DHCP), voice net protocol (VoIP), etc. AWS provides number of Networking service like VPC, AWS API Gateway, AWS Cloud Map, Amazon CloudFront, Elastic Load balancing, Amazon Route 53, etc. AWS helps us to setting up environment where we launch our virtual servers, database, storage, etc.
- Amazon VPC: Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) allows you to arrangement a sensibly separated segment of the AWS Cloud where you can send off AWS assets in a virtual organization that you characterize. You have unlimited oversight over your virtual systems administration climate, including choice of your own IP address range, production of subnets, and design of course tables and organization entryways. You can utilize both IPv4 and IPv6 in your VPC for secure and simple admittance to assets and applications.
The following are the key concepts for VPCs:
- Virtual private cloud (VPC) - A virtual organization devoted to your AWS account.
- Subnet - A range of IP addresses in your VPC.
- CIDR block - Classless Inter-Domain Routing. An IP address allotment and course accumulation philosophy.
- Route table - A set of rules, called routes, that are utilized to figure out where organization traffic is coordinated.
- DHCP Option sets: Configuration data, (for example, domain name and domain name server) passed to EC2 instances when they are launch into VPC subnets.
- Internet Gateway - A gateway that you attach to your VPC to enable communication between assets in your VPC and the web.
- VPC endpoint - Enables you to privately connect your VPC to upheld AWS services and VPC endpoint services fueled by PrivateLink without requiring an internet gateway, NAT gadget, VPN connection, or AWS Direct Connect association
- NAT Gateway: An oversaw AWS administration that permits EC2 examples in private subnets to associate with the web, other VPCs, or on-premises organizations.
- Security groups: It is virtual firewall works at subnet level. For each security group, you can add rule that control the traffic based on protol and ports.
- Network ACLs: A Network ACL is an optional layer of security for your VPC that acts as a firewall for controlling traffic in and out of one or more subnet. NACL’s are stateless.
2. Route 53: Amazon Route 53 is a profoundly accessible and versatile cloud Domain Name System (DNS) web administration. It is intended to give engineers and organizations a very solid and financially savvy method for directing end clients to Internet applications by interpreting intelligible names, for example, www.example.com, into the numeric IP addresses, for example, 192.0.2.1, that PCs use to associate with one another. Amazon Route 53 is completely consistent with IPv6 also.
3. CloudFront: Amazon CloudFront is a web service that speed up distribution of your static and dynamic web content, for example, HTML, CSS, Js and picture documents, to your Users. CloudFront delivers your content through an overall organization of server farms called edge areas. At the point when a client demands content that you're presenting with CloudFront, the solicitation is steered to the edge area that gives the most reduced dormancy (time delay), so that content is delivered with the most possible performance.
4. Elastic Load Balancing: Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes your incoming traffic across multiple targets, for example, EC2 instance, containers, and IP addresses, in at least one Availability Zones. It monitors the health of its registered targets, and routes traffic just to the healthy targets. Elastic Load Balancing scales your load balancer as your incoming traffic changes over the time. It can automatically scale to by far most of responsibilities.
C. Databases Services
Database as a service (DBaaS) may be a cloud computing managed service providing that gives access to a info while not requiring the setup of physical hardware, the installation of computer code or the requirement to set up the info.
AWS provide multiple database services like Amazon RDS, Amazon Aurora, Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon ElasticCache, Amazon RedShift, etc. Using AWS database service we do not need to manage the database server because AWS take cares of that. It is very cheaper than the on-premises method, like purchase the database server and maintain that server, so take lots of resources and cost.
- Amazon RDS: Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) is a web service that makes it simpler to set up, work, and scale a relational database in the AWS Cloud. It gives cost-productive, resizable limit with regards to an industry-standard relational database and manages normal database organization tasks. Amazon RDS is accessible on a few information base case types - enhanced for memory, execution or I/O - and provides you with six recognizable Database’s engines to choose from, including Amazon Aurora, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, Oracle Database, and SQL Server. You can utilize the AWS Database Migration Service to easily relocate or recreate your current data sets to Amazon RDS.
- Amazon Aurora: Amazon Aurora is a MySQL and PostgreSQL compatible relational databases engine that combines the speed and availability of high-end databases with the simplicity and cost-e?ectiveness of open-source databases. Amazon Aurora is up to five times faster than standard MySQL databases and three times quicker than standard PostgreSQL data sets. It gives the security, accessibility, and dependability of business information bases at 1/tenth the expense. Amazon Aurora is completely overseen by Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS), which automates time-consuming administration tasks like hardware provisioning, database setup, patching, and backups.
- Amazon DynamoDB: Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL database service that provides quick and predictable performance with seamless scalability. DynamoDB allows you to offload the regulatory weights of working and scaling a distributed database so that you don't have to worry about hardware provisioning, configuration and setup, replication, software patching, or cluster scaling. DynamoDB also offers encryption at rest, which eliminates the operational burden and complexity engaged with protecting sensitive data. With DynamoDB, you can make database tables that can store and recover any amount of data and serve any level of request traffic. You can scale up or scale down your tables' throughput limit without downtime or performance degradation.
D. Storage Services
Storage as a service (STaaS) could be a information storage business model wherever a supplier rents storage resources to a client through a subscription. STaaS saves you cash through in operation expenditure (OpEx) agility—you solely obtain the storage you would like once you would like it.
AWS provides fast and scalable option to store their data in their storage service like Amazon S3, Amazon EFS, Amazon EBS, etc.
- Amazon EFS: Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) gives a basic, serverless, set-and-forget elastic file system for use with AWS Cloud services. It is worked to scale on request to petabytes without disturbing applications, developing and contracting naturally as you add and eliminate documents, wiping out the need to arrangement and oversee ability to oblige development. Amazon EFS has a straightforward web administrations interface that permits you to make and arrange record frameworks rapidly and without any problem. The assistance deals with all the record stockpiling framework for you, implying that you can stay away from the intricacy of sending, fixing, and keeping up with complex document framework arrangements. Amazon EFS supports the Network File System version 4 (NFSv4.1 and NFSv4.0) protocol, so the applications and tools that you use today work seamlessly with Amazon EFS. Multiple compute instances, like Amazon EC2, Amazon ECS, and AWS Lambda, can access an Amazon EFS file system at the same time, providing a common data source for workloads and applications running on more than one compute instance or server.
- Amazon EBS: Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) gives block level capacity volumes to use with EC2 occasions. EBS volumes act like crude, unformatted block gadgets. You can mount these volumes as gadgets on your cases. EBS volumes that are connected to an occurrence are uncovered as capacity volumes that persevere freely from the existence of the example. You can make a document framework on top of these volumes, or use them in any capacity you would utilize a block device (like a hard drive). You can dynamically change the configuration of a volume attached to an instance. Using Amazon EBS, you can pay for what you use and how much you use. It is more cheaper than the On-premises methods.
- Amazon S3: Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. Customers of all sizes and industries can use Amazon S3 to store and protect any amount of data for a range of use cases, such as data lakes, websites, mobile applications, backup and restore, archive, enterprise applications, IoT devices, and big data analytics. Amazon S3 provides management features so that you can optimize, organize, and configure access to your data to meet your specific business, organizational, and compliance requirements.
Advantages of S3:
- Create Buckets: Firstly, we create a bucket and provide a name to the bucket. Buckets are the containers in S3 that stores the data. Buckets must have a unique name to generate a unique DNS address.
- Storing data in buckets: Bucket can be used to store an infinite amount of data. You can upload the files as much you want into an Amazon S3 bucket, i.e., there is no maximum limit to store the files. Each object can contain upto 5 TB of data. Each object can be stored and retrieved by using a unique developer assigned-key.
- Download data: You can also download your data from a bucket and can also give permission to others to download the same data. You can download the data at any time whenever you want.
- Permissions: You can also grant or deny access to others who want to download or upload the data from your Amazon S3 bucket. Authentication mechanism keeps the data secure from unauthorized access.
- Standard interfaces: S3 is used with the standard interfaces REST and SOAP interfaces which are designed in such a way that they can work with any development toolkit.
- Security: Amazon S3 offers security features by protecting unauthorized users from accessing your data.
IV. KEY DIFFERENCES OF ON-PREMISE VERSUS CLOUD
A. Arrangement
On Premises: In an on-premises climate, assets are sent in-house and inside an endeavor's IT foundation. An undertaking is liable for keeping up with the arrangement and all its connected cycles.
Cloud: While there are various types of distributed computing (like public cloud, private cloud, and a mixture cloud), in a public distributed computing climate, assets are facilitated in the vicinity of the specialist organization however endeavors can get to those assets and use however much they need at some random time.
B. Cost
On Premises: For ventures that send programming on premises, they are liable for the continuous expenses of the server equipment, power utilization, and space.
Cloud: Enterprises that choose for utilize a distributed computing model just need to pay for the assets that they use, with none of the support and upkeep costs, and the cost changes up or down contingent upon how much is consumed.
C. Control
On Premises: In an on-premises climate, undertakings hold every one of their information and are completely in charge of what befalls it, no matter what. Organizations in profoundly directed businesses with additional protection concerns are bound to wonder whether or not to jump into the cloud before others in light of this explanation.
Cloud: In a distributed computing climate, the topic of responsibility for is one that many organizations - and merchants besides, have battled with. Information and encryption keys dwell inside your outsider supplier, so if the unforeseen occurs and there is personal time, you perhaps not be able to get to that information.
D. Security
On Premises: Companies that have additional touchy data, for example, government and banking businesses should have a specific degree of safety and protection that an on-premises climate give. Notwithstanding the guarantee of the cloud, security is the essential worry for some businesses, so an on-premises climate, in spite of a portion of its disadvantages and sticker price, seems OK.
Cloud: Security concerns remain the main hindrance to distributed computing sending. There have been many advertised cloud breaks, and IT offices all over the planet are concerned. From individual data of workers, for example, login qualifications to a deficiency of protected innovation, the security dangers are genuine.
E. Consistence
On Premises: Many organizations these days work under some type of administrative control, no matter what the business. Maybe the most well-known one is the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) for private wellbeing data, however there are numerous others, including the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA), which contains nitty gritty understudy records, and other government and industry guidelines. For organizations that are dependent upon such guidelines, they really must stay consistent and know where their information is consistently.
Cloud: Enterprises that in all actuality do pick a distributed computing model should take care of any outstanding concerns and guarantee that their outsider supplier depends on code and truth be told agreeable with each of the different administrative orders inside their industry. Touchy information should be gotten, and clients, accomplices, and representatives should have their protection guaranteed.
Conclusion
In AWS cloud you pay as you use. In another cloud platform, regardless of whether the services are utilized, installment should be finished all. That is the development of the AWS cloud and makes this unique in relation to some other providers.
References
[1] G. Aldering, G. Adam, P. Antilogus, P. Astier, R. Bacon,S. Bongard, C. Bonnaud, Y. Copin, D. Hardin, F. Henault, D.A. Howell, J. Lemonnier, J. Levy, S.C. Loken, P.E. Nugent,R. Pain, A. Pecontal, E. Pecontal, S. Perlmutter,R.M. Quimby, K. Schahmaneche, G. Smadja and W.M.Wood-Vasey, Overview of the Nearby Supernova Factory, in: TheSociety of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference, J.A. Tyson and S. Wolff, eds, Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, Vol. 4836, SPIE, Bellingham, WA, 2002, pp. 61–72. [2] Amazon Web Services, http://aws.amazon.com/ [3] Amazon EC2, http://aws.amazon.com/ec2/ [4] Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/ec2/userguide/what-is-amazon-ec2-auto-scaling.html [5] AWS Lambda, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/welcome.html [6] AWS Fargate, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonECS/latest/userguide/what-is-fargate.html [7] Amazon VPC, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/what-is-amazon-vpc.html [8] Amazon Route 53, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/Route53/latest/DeveloperGuide/Welcome.html [9] Amazon CloudFront, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudFront/latest/DeveloperGuide/Introduction.html [10] Amazon ELB, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/userguide/what-is-load-balancing.html [11] Amazon S3, http://aws.amazon.com/ebs/s3/ [12] Amazon DynamoDB, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/amazondynamodb/latest/developerguide/Introduction.html [13] Amazon RDS, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/Welcome.html [14] Amazon Aurora, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/AuroraUserGuide/CHAP_AuroraOverview.html [15] Amazon EFS, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/efs/latest/ug/whatisefs.html [16] Amazon EBS, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/AmazonEBS.html [17] Amazon S3, https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/userguide/Welcome.html [18] E. Angerson, Z. Bai, J. Dongarra, A. Greenbaum, A. McKenney, J. Du Croz, S. Hammarling, J. Demmel, C. Bischof and D. Sorensen, LAPACK: a portable linear algebra library for highperformance computers, in: Proceedings of Supercomputing’ 90, IEEE, New York, NY, 2002, pp. 2–11. [19] C. Aragon, S. Poon, G. Aldering, R. Thomas and R. Quimby, using visual analytics to develop situation awareness in astrophysics, Information Visualization 8(1) (2009), 30–41. [20] M. Armbrust, A. Fox, R. Griffith, A. Joseph, R. Katz, A. Konwinski,G. Lee, D. Patterson, A. Rabkin, I. Stoica et al., Above the clouds: a Berkeley view of cloud computing, Technical Report UCB/EECS-2009-28, EECS Department, University of California, Berkeley, CA, 2009. [21] CFITSIO, http://heasarc.nasa.gov/docs/software/fitsio/fitsio.html [22] http://www.klientsolutech.com/importance-of-cloud-computing-worldwide [23] https://www.itproportal.com/2013/05/02/top-10-tips-why-you-should-use-the-cloud-andhow-to-do-it-securely/.
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Vivek Habib, Chirag Patil. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET43349
Publish Date : 2022-05-26
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

