Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Blind People Helping Hand
Authors: Neve Sujal Rajesh, Khairnar Megha Himmat, Gamane Amrisha Gokul, Prof. Sangale Sunil Hiraman
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.51014
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Blind people are facing many problems in their day-to-day life. They find it very difficult to read books as well as to recognize the object in front of them. From the survey of WHO,30 million peoples are permanently blind and 285 billion peoples with vision impairment. if you notice them, you can very well know about it they can’t walk without the help of other. one has to ask guidance to reach their destination. they have to face more struggles in their life daily life. Visually impaired people find difficulties detecting obstacles in front of them, during walking in the street, which makes it dangerous. A lots of blind people suffer in their own lives because of their vision loss. Vision is one of the five important senses in the human body. People with Vision loss have their own disability. Many countries around the world provide special assistance to these needed people to improve their life quality as good as possible. They provide them with special equipment for their disability to improve their daily life like voice message service, electronic stick that guide them while moving around and other specialized equipment. Blind people can\'t even walk without any aid. Many times they rely on others for help. Several technologies for the assistance of visually impaired people have been developed. This paper proposes a system for blind people. The proposed system aims to create a wearable visual aid for visually impaired people in which speech commands are accepted by the user. Its functionality addresses the identification of objects .This will help the visually impaired person to manage day-to-day activities through his/her surroundings. To help the blind people the visual world has to be transformed into the audio world with the potential to inform them about objects. Therefore, we propose to aid the visually impaired by introducing a system that is most feasible, compact, and cost effective. So, we implied a system that makes use of Raspberry Pi. Raspberry Pi is used to implement artificial vision using python language on the Open CV platform. The system consists of a webcam interfaced with raspberry pi. Pi Camera detects and find the type of object with the help of ultrasonic sensor. Ultrasonic sensor to detect the real time hurdles while walking on the roads. The ultrasonic sensor used in this project plays a vital role. It detects the object in front of this. When object is detected a indication sound is given to the user via earphone. While they hear this sound they can know an obstacle in front of them. The system is intended to provide Raspberry Pi. The proposed system detects an object around them and sends feedback in the form of speech, warning messages via earphone. This new system may solve some of major problems of blind persons that are still existing. The aim of all these systems is to help the user to detect object without the help of a second person. This system is to provide a low cost and efficient obstacle detection aid for blind which gives a sense of artificial vision by providing information about the environmental scenario of static and dynamic object around them, so that they can walk independently. This paper combines the functionality of Object detection. The objective is to develop user friendly application.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 253 million people live with visual impairment. 217 million of those have moderate to severe vision impairment and 37 million are blind. Traditionally, Tools like stick were used from decades to avoid obstacles. Keeping pet dogs or guide dogs were one of few techniques used by the visually impaired. Some took help of their family and friends for assistance. However, these techniques and tools had drawbacks. People with trained dogs needed money and time to feed and train the dogs. In today’s technologically advanced world the above techniques cannot suffice the needs of the visually impaired people. According to statistics from the World Health Organization (WHO), at least 285 million people are visually impaired or blindness. Blind people generally have to rely on white canes, guide dogs, screen-reading software, magnifiers, and glasses for navigation and surrounding object detection. Therefore, to help blind people, the visual world has to be transformed into the audio world with the potential to inform them about objects. In this paper, we propose a real-time object detection system to help visually impaired people in their daily life. This system consists of a Raspberry Pi. We propose a camera-based assistive speech output of object name to help blind persons detect object. The R-pi based object detection and reader comes as a proposed solution to enable visually impaired people to find difficulties in detecting obstacles and dangers in front of them during walking and to identify the world around. Blind people have high difficulty in doing their daily routines.
Due to low vision or blindness, they suffer from an inferiority complex and also it affects their economic conditions because of less efficiency in doing the work and the cost of the treatment. The major difficulty faced by blind people while navigating or traveling in the unknown surrounding. The ingenious device for blinds is an contraption which helps the blinds people to navigate with speed and confidence by detecting the nearby objects and obstacles using the help of pi camera, ultrasonic sensor and notify them with Speech warning sound along with voice alert. A portative user friendly device is flourished that can identify the obstacles in the path using ultrasonic sensors. If the obstacle is close then raspberry pi sends a signal to sound a and also sends the voice command through the earphones. The proposed system detects the obstacle images which are present in outdoor and indoor with the help of a camera. when any objects or obstacles come in range of an ultrasonic sensor and it make notify Speech warning messages activated when any obstacle is detected via earphone. Since the running of daily life of blind people is very difficult. This project helps them to run their life as usual. They can make this project as a gadget or a device in their hands which detects the obstacle. This project is more efficient than the existing system with cheaper and accurate one ease of use.
II. PROBLEM STATEMENT
To make an efficient use of R-Pi . Provide solution with least hardware requirement. To develop an application that is cost efficient. Easy to use and accurate so that Visually Impaired People can adopt the application quickly. The major challenge with visually impaired people is difficulty in recognizing of objects. There are various issues they have to deal with, while performing various daily tasks. They are unable to recognize objects while performing day-to-day activities, depriving them from normal social life. One of the major problems faced by Blind people is detecting and recognizing an obstacle in their path. To Implement application for Blind People. The projects approach lies in developing a system based on Raspberry pi 3 , which is capable of detect objects & converting the text to speech and producing output in the form of audio signals to make the blind person aware of the object in front of him. We choose Pi 3 as our platform because it is a standard representative of embedded device and is widely being used for devising low cost-system.
III. LITERATURE REVIEW
Many researchers have contributed to this field. Various combinations of existing technologies have been used. Braille systems, screen magnifiers, etc. went through some developments but later faced technical issues.
- Ayat A. Nada, was proposed, Stick solution use different technologies like infrared, ultrasonic sensor and laser but they still have drawbacks. In the present study we introduce, light pressure, low-cost, adaptable, fast response and low power utilization. Smart stick based infrared technology. A combination of infrared sensors can reveal stair-cases and other obstacle presence in the user path, within a range of two meters. The tentative results carry out good accuracy and the stick is able to identify all of disincentives.
- S. Innet, N.Ritnoom was proposed that blind people use a white stick as a tool for directing them when they move or walk. In spite of, the white stick is helpful, it cannot give a high assurance that it can assure blind people away from all level of hurdles. Several researchers have been obessed in establishing electronic devices to protect blind people away from obstacles with a higher guarantee. This study introduces an hurdles restraint alternative by using an electronic stick that serves as a tool for blind people in walking. It exploits an infrared sensor for detecting hurdles along the roadway. With all level of hurdles, the infrared stick facilitates to identify all type of earthly available in the course such as concrete, wood, metal, glass, and human being. The outcome also shows that the stick detects obstacles in range of 80 cm which is the same as the length of white stick. The twig is designed to be small and light, so that blind people can carry it comfortably.
- Ross Girshick , we propose a Fast Region-based Convolutional Network method (Fast R-CNN) for object detection. Fast R-CNN frames on previous work to accurately distribute object proposals using deep convolutional networks. Correlated to previous work, Fast R-CNN uses several innovations to improve training and testing speed while also increasing detection accuracy. Fast R-CNN tracks the very deep VGG16 network 9x faster than R-CNN, is 213x faster at test-time, and achieves a higher mAP on PASCAL VOC 2012. Compared to SPP net, Fast R-CNN trains VGG16 3x faster, tests 10x faster, and is more accurate. Fast R-CNN is implemented in Python and C++.
- Multiple Distance Sensors Based Smart Stick for Visually Impaired People :Amit Kumar proposed this system. In this system a novel low-cost yet durable and accurate smart stick to assist visually impaired people while they walk in indoor/outdoor unstructured environments. There is a large group of people who have difficulties in their daily routine work due to losing their eyesight. Walking with confidence is one of them which may have different challenges in different environments/countries. We have considered the Indian context where outdoor environments are often clustered and noisy.
Keeping these challenges in mind, a new smart stick is developed which is capable of detecting obstacles of any height in front or slightly sideways of the person. The stick gives a fair idea about the distance and the location of obstacles through vibration in hand and audio in the ear of the person. The wireless connection has been set up using Bluetooth between theearphone and the stick. Different frequencies of the generated vibration and different tracks of the audio alert the person about the distance of the obstacle. Real-time experiments have been conducted in different environments by different people to observe the accuracy of the stick and results are quite encouraging.
5. In this system, an electronic aid to visually impaired people is designed which helps them to voyage to the destination like normal people. The aiding system is built into a walking stick that shall be carried by a visually impaired person. The aiding system acts like a reproduction vision. Sensors with most accurate outputs are used in this work. The intelligent algorithm is used in the software so that it is more user-friendly. A suitable walking stick is designed with all the stuff built-in. The canopy people will able to budge from one place to another lacking other help. If such a system is developed, it will act as a basic stand for the invention of more such devices for the canopy people in the potential which will be cost-effective. And as far as the localization is anxious it will be able to provide accurate information on the position of the canopy if in case they lost with help from the GPS. It will be a real boon for the blind. The developed prototype gives good results in detecting obstacles paced at distance in front of the user.These works report the designing of the multi-sensor blind stick. This will be useful for visually impaired peoples. The canopy stick consists of tricky features which detect obverse and top part of the obstacles, water stagnated/manholes on the ground. Due to these features it is the best tool for blind and visually impaired people for on foot on the road. It is unforced, cost-effective, configurable and simple to handle smart supervision systems. The system is planned implemented, tested and verified. The results indicate that the structure is expert and inimitable in its impending in specifying the source and space of the obstacles.
6. Navigation assistance for visually impaired (NAVI) refers to systems that can assist or guide people with vision loss, ranging from partially sighted to blind, using sound commands. In this paper, a new system for NAVI is presented based on visual and range information. Instead of using several sensors, we choose one device, a consumer RGB-D camera, and take advantage of both range and visual information. In particular, the main contribution is the combination of depth information with image intensities, resulting in the robust expansion of the range-based floor segmentation. On one hand, depth information, which is reliable but limited to a short-range, is enhanced with the long-range visual information. On the other hand, the difficult and prone-to-error image processing is eased and improved with depth information. The proposed system detects and classifies the main structural elements of the scene providing the user with obstacle-free paths to navigate safely across unknown scenarios. The proposed system has been tested on a wide variety of scenarios and data sets, giving successful results and showing that the system is robust and works in challenging indoor environments.
7. Laviniu Tepelea, Loan Gavrilut & Alexandru Gacsadi proposed the assistance system. In the system toassist people with visual impairments, the smartphone proves to be very useful, but it requires sensory modules external to the phone to detect obstacles and find a safe way. The Android application we have made, offers not only a travel guide, but also other daily assistive functions such as reading a poster or article, making phone calls, findingthe date, time, and battery level. The special interface created for the blind has proved its efficiency, and the communication of the relevant information verbally transmitted through the TTS to the earphones to one ear leads to a correct understanding of the message and leaves the user the opportunity to receive other useful information from the environment. External platforms communicate data from sensors to the phone via Bluetooth and Wi-Fi where sensorial data fusion is made, and at the appropriate time, the relevant information is communicated to the user, warning of the existence of an obstacle at a certain level. The accelerator sensor can detect when the person with visual impairment is falling, and a phone call to a favorite number is made, for example, the emergency service, and the light sensor detects the need to move from outdoor guidance to indoor guidance and vice versa. Experimental tests made with the assistive system have proven its usefulness, but they have also revealed that further testing is needed to find the optimum obstacle detection distance, both inside buildings and in the outdoor environment. In the future, more powerful and cheaper smartphones will be made, which will lead to more effective assistance. Finally, this aiding system for visually impaired, based on a smartphone, but also using other small external sensory modules, proves to be a viable, portable, low-cost, small-scale solution. More important, it does not require many hours of training.
8. Kabalan Chaccour & Georges Badr proposed this system, In this system a novel design for an indoor navigation system for visually impaired and blind people. The proposed approach has a simple architecture that allows the subject to be fully independent in his home or work. The system provides navigation assistance and obstacle avoidance functionalities in indoor premises algorithms.
Unlike other systems in the related work, the subject needs only to hold his smartphone during his displacement and doesn't require any particular skills to be operated. The complexity of the system resides in the computer vision processing algorithm seamlessly to the user. Future development is planned for the system expansion to add more functionality. On the application level, we are working to automatically run the application when motion is sensed from the subject (chair rise, walking, etc.). It can also revert to its sleep mode in static conditions to minimize the battery consumption. Battery level can also be communicated loudly through voice messages to avoid critical situations. The application may also offer gait analysis for elderly and visually impaired subjects and may prevent the subject from a potential fall. On the remote processing system level, enhanced image processing algorithms may be implemented to detect specific objects in the environment. The time between voice messages must be adequately chosen to avoid flooding the ears and disturbance. These issues will be addressed in future research activities.
9. This system presents a smart guiding device for visually impaired users, which can help them move safely and efficiently in a complicated indoor environment. The depth image and the multi-sensor fusion based algorithms solve the problems of small and transparent obstacle avoiding. Three main auditory cues for the blind users were developed and tested in different scenarios, and results show that the beep sound-based guiding instructions are the most efficient and well-adapted. For weak sighted users, visual enhancement based on the AR technique was adopted to integrate the traversable direction into the binocular images and it helps the users to walk more quickly and safely. The computation is fast enough for the detection and display of obstacles. Experimental results show that the proposed smart guiding glasses can improve the traveling experience of the visually impaired people. The sensors used in this system are simple and at low cost, making it possible to be widely used in the consumer market.
10. ZoranZivkovic et.al proposes Improved Adaptive Gaussian Mixture Model for Background Subtraction Background subtraction is a common computer vision task. We analyze the usual pixel-level approach. We develop an efficient adaptive algorithm using Gaussian mixture probability density. Recursive equations are used to constantly update the parameters and but also to simultaneously select the appropriate number of components for each pixel.
IV. PROPOSED SYSTEM
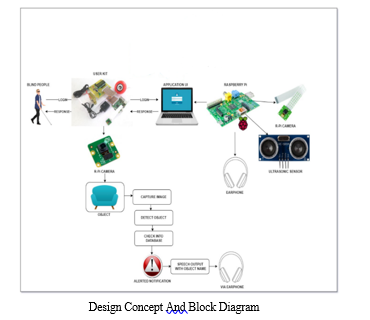
The proposed system is to build an customized application for blind people. This application acts as a voice assistant. This application is used to help the blind people to access most important features of the text to speech. The System will have custom Object Detection This system will speak out all the object detected. This system in all is a voice assistant for blin people. The proposing system uses Raspberry pi, it is a small processing device which works as computer at relatively low cost. Blind and visually impaired people find difficulties in detecting obstacles during walking in the street. The system is intended to provide artificial vision and object detection, real time assistance via making use of Raspberry Pi. The system consists of pi camera module, ultrasonic sensors, and Earphone to receive the instruction through audio, Voice output works through TTS (text to speech).The proposed system is equipped with pi camera module, ultrasonic sensors. This system detects an object around them and finds the type of the object sends feedback in the form of speech that is warning messages via earphone. The aim of the overall system is to provide a low cost, efficient navigation and obstacle detection aid for blind which gives a sense of artificial vision by providing information about the natural scenario of static and dynamic object around them, so that they can walk independently. The proposed system helps us to deal with the limitations of the existing system. The proposed system can view and detect object form different angles. It will also help us to identify the correct number of objects present in front of Pi-camera. The same class of the objects can be detected and recognized incorrectly which will the visually impaired person to know the accurate type of object.
V. SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
The framework of the proposed project is the raspberry pi board. The system consists of a webcam interfaced with raspberry pi. The webcam captures image from a given picture and the text from the captured image is converted into an audio output using Raspberry Pi. The quality of the image captured will be high so as to have fast and clear recognition due to the high-resolution camera. And also we measure the distance of the object using the ultrasonic sensor. Both outputs are heard in an audio. The output device can be a headset connected to the raspberry pi which can spell out the text document loud. The proposed system detects the obstacle images which are present in outdoor and indoor with the help of a camera. when any objects or obstacles come in range of an ultrasonic sensor and it make notify Speech warning messages activated when any obstacle is detected via earphone this is voice for the alert for blind person.
VI. PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
A. Raspberry Pi
Raspberry Pi is a low cost (35 dollar), credit card sized, computer that performs various applications. Some of its main features include 1GB of RAM, 4 USB Ports, General Purpose Input Output pins, Linux support. These features gives programmers a wide range for diverse applications. The Raspberry Pi is a series of small single-board computers developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation to promote the teaching of basic computer science in schools and in developing countries. The original model became far more popular than anticipated, selling outside of its target market for uses such as robotics. Peripherals(including keyboards, mice and cases) are not included with the Raspberry Pi. But can be connected to the chip using USB ports. The various functionalities of the components are given below The various components of Raspberry- Pi are:
- SD Card Slot is used to install OS/booting/long term storage .The total memory of the SD card is about 8GB.
- Micro USB Power Port provides 700mA at 5A.
- RCA Video Out is connected to display if HDMI output is not used. It is mainly used to carry audio and video signals. They are otherwise called as A/V jacks.
- Audio Out Digital audio is obtained if HDMI is used to obtain stereo audio. Here analogue RCA connection is used.
- Ethernet Port is used to connect to the Internet. It also plays a role in updating, getting new software easier.
- HDMI OUT(High Definition Multimedia Interface) is used with HDTVs and monitors with HDMI input. Also HDMI-HDMI is used here.
- BROADCOM BCM 2835: It is otherwise defined as System on chip .It is a 700 MHz Processor. It has a Video core IV GPU.
- GPIO allows us to control and interact with real world.

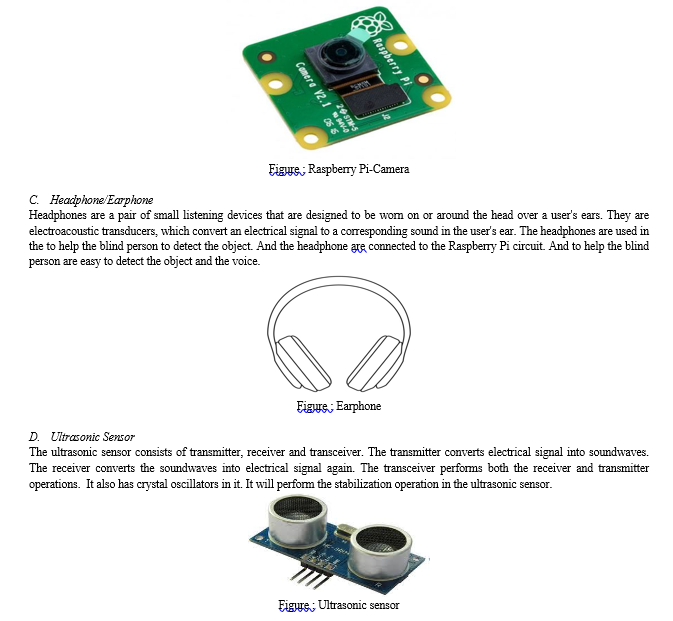
B. Raspberry Pi-Camera
Raspberry Pi-Camera module is a 8MP camera with full HD recording capability. This provides a perfect solution for face recognition. Pi Camera component is a camera which could be used to take pictures and high definition video. Raspberry Pi Board has CSI (Camera Serial Interface) interface to which we can attach Pi Camera module directly. This Pi Camera component can unite to the Raspberry Pi’s CSI port using 15-pin ribbon cable. The Raspberry Pi camera component could be used to take high-definition video, as well as stills photographs. The module has a five Mega pixel fixed-focus camera that supports 1080p30, 720p60 and VGA90 video modes, along with stills capture. The Pi Camera Module Interface with Raspberry Pi using Python. It captures the real time images through a tiny grid of light-detectors, known as charge-coupled device (CCD) from the location where it is place. The CCD novices the image into digital format so that computer can path this data. Pi cams do not have the internal memory to store the images so it transmits the data immediately to the host device through the USB or other analog cable.
E. Python (Programming Language)
This programming language also requires user to implement lower quantity of code lines to execute coding concepts compared to languages such as C++ and Java. Python supports object oriented, imperative, functional programming and procedural styles, together with automatic memory management as well.
This makes Python is suitable to be used to develop the proposed Raspberry Pi Surveillance System. The developer of Python programming language is the Python Software Foundation and the license is also provided by the same foundation.
The Python Software Foundation is an independent non-profit organization that holds the copyright on Python versions 2.1 and newer. The creation of Python is mainly influenced and inspired from other programming languages like C, C++, Java, Perl, and Lisp.
F. OpenCV
OpenCV (Open Computer Vision) is a library mainly aimed at real-time computer vision. It provides great support for face detection and face-recognition techniques using Python.
VII. MODULES
- Object Detection: This system capture object from the camera and extracts the object from the object with clear perception. With help of Text-to-Speech engine the text will be read for the user then it normally converts a normal text into speech. Object detection is a computer technology related to computer vision and image processing that deals with detecting the presence of objects with a limitative box and types or classes of objects located in an image in digital images and videos. By Using object detection, blind peoples can understand their surrounding environment without any challenges and remain independent of others.
- Object Recognition: Technology in the field of computer vision for finding and identifying objects in an image or video sequence. Humans recognize a multitude of objects in images with little effort, despite the fact that the image of the objects may vary somewhat in different viewpoints, in many different sizes and scales or even when they are translated or rotated. Objects can even be recognized when they are partially obstructed from view. This task is still a challenge for computer vision systems. Many approaches to the task have been implemented over multiple decades.
VIII. MODULE ANALYSIS
- Module Name: Object Detection
- Purpose of the Module: The purpose of the module is to capture object from the camera and to extract the object with clear perception. With help of Text-to-Speech engine the text will be read for the user. It will convert normal text into speech. Object detection is a computer technology related to computer vision and image processing that deals with detecting the presence of objects with a limitative box and types or classes of objects located in an image in digital images and videos.
By Using object detection, blind peoples can understand their surrounding environment without any challenges and remain independent of others.
2. Inputs and Outputs for Module:
3. Input: Object
4. Output: Object will be detected
5. Files Used: Detection
6. Algorithm:
a. Start
b. Camera will get switched on.
c. Object will be placed in front of camera.
d. Object will get detected.
e. Audio sound will be read for the user.
f. Surrounding environment will get known to the user.
g. Stop
B. Module Name: Object Recognition
- Purpose of the Module: The purpose of the module is to recognize the type of object from the camera and to extract the object with clear perception. It is the technology in the field of computer vision for finding and identifying objects in an image or video sequence. It finds the instances of the object. Humans recognize a multitude of objects in images with little effort, despite the fact that the image of the objects may vary somewhat in different viewpoints, in many different sizes and scales or even when they are translated or rotated. Objects can even be recognized when they are partially obstructed from view. This task is still a challenge for computer vision systems. Many approaches to the task have been implemented over multiple decades.
- Inputs and Outputs for Module:
- Input: Object, image or video
- Output: Object will be recognized
- Files Used: Detection
- Algorithm:
a. Start
b. Camera will get switched on.
c. Object will be placed in front of camera.
d. Object will get detected.
e. Object will be recognized.
f. Instance of the object will be recognized.
g. Type of the object will get recognized.
h. Audio sound will be read for the user.
i. Stop
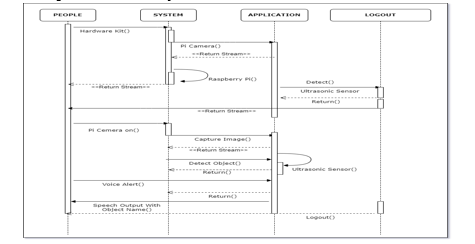
IX. SEQUENCE DIAGRAM
A Sequence Diagram is an interaction diagram that emphasis the time ordering of messages; a collaboration diagram is an interaction diagram that emphasizes the structural organization of the objects that send and receive messages. Sequence diagrams and collaboration diagrams are isomorphic, meaning that you can take one and transform it into the other. Sequence diagram and collaboration diagram are called INTERACTION DIAGRAMS. An interaction diagram shows an interaction, consisting of set of objects and their relationship including the messages that may be dispatched among them. A sequence diagram is an introduction that empathizes the time ordering of messages. Graphically a sequence diagram is a table that shows objects arranged along the X-axis and messages ordered in increasing time along the Y-axis. A sequence diagram for Blind People Helping hand represent communication flow between People, System, Application. The system consists of a webcam interfaced with Raspberry-Pi , Pi Camera detects and find the type of object with the help of ultrasonic sensor. Ultrasonic sensor to detect the real time hurdles while walking on the roads. The ultrasonic sensor used in this project plays a vital role. It detects the object in front of this. When object is detected a indication sound is given to the user via earphone.
B. Functional Dependency Diagram
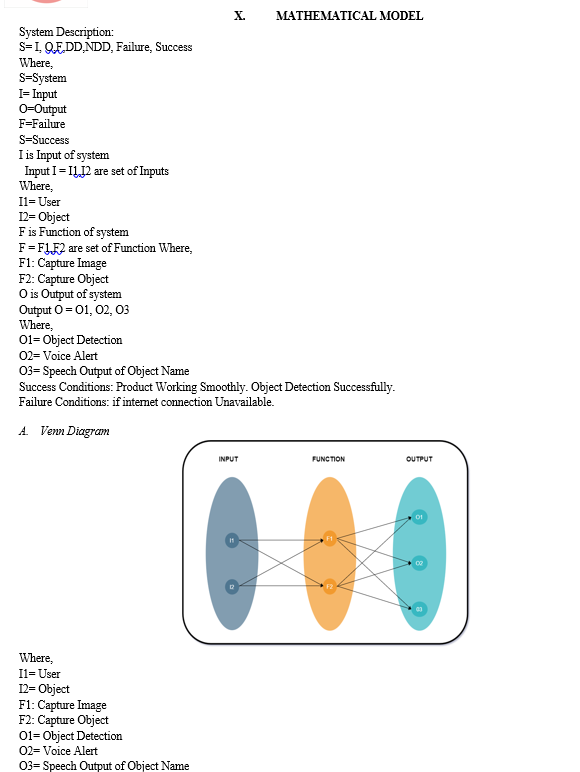
A set of Functional Dependencies for a data model can be documented in a Functional Dependency Diagram (also known as a Determinancy Diagram). In a Functional Dependency Diagram each attribute is shown in a rectangle with an arrow indicating the direction of the dependency.
|
|
F1 |
F2 |
|
F1 |
1 |
0 |
|
F2 |
0 |
1 |
F1: Capture Image
F2: Capture Object
C. Perspective Of The Proposed System
Blind People helping hand: It is a Hardware application. To make an efficient use of Raspberry Pi Technology. Provide solution with least hardware requirement. To develop an application that is cost efficient. Easy to use and accurate so that blind People can adopt the application quickly. The major challenge with visually impaired people is difficulty in recognizing of objects. There are various issues they have to deal with, while performing various daily tasks. They are unable to recognize objects while performing day-to-day activities, depriving them from normal social life. To Implement application for blind People.
D. Features Of The Proposed System
The main objective of this is to provide an application for blind people to detect the obstacles in various directionsThe main objective is that, our proposed device with advanced embedded technology which will give the blind person an imaginary vision rather than being dependent on others. This project is designed keeping the view of visually impaired people, with this tool they can travel to their destination without the need of others. No additional devices need to be carried for object detection.
XI. PROJECT PLAN
A. Project Estimate
The Constructive Cost Model (COCOMO) is an algorithmic software cost estimation model developed by Barry Boehm. The model uses a basic regression formula, with parameters that are derived from historical project data and current project characteristics. It is a method for evaluating the cost of a software package. According to him software cost estimation should be done through three stages:
- Basic COCOMO: Computes software development effort and cost as a function of program size expressed in estimated DSIs.
There are three modes within Basic COCOMO:
a. Organic Mode
Development projects typically are uncomplicated and involve small experienced teams. The planned software is not considered innovative and requires a relatively small amount of DSIs (typically under 50,000).
b. Semidetached Mode
Development projects typically are more complicated than in Organic Mode and involve teams of people with mixed levels of experience. The software requires no more than 300,000 DSIs. The project has characteristics of both projects for Organic Mode and projects for Embedded Mode.
c. Embedded Mode
Development projects must fit into a rigid set of requirements because the software is to be embedded in a strongly joined complex of hardware, software, regulations and operating procedures.
The basic COCOMO estimation model is given by the following expressions:
Effort = a1 x (KLOC)a2PM
Tdev =b1 x(Effort)b2 Months
Where,
- KLOC is the estimated size of the software product expressed in Kilo Lines of Code,
- a1, a2, b1, b2 are constants for each category of software products,
- Tdev is the estimated time to develop the software, expressed in months,
- Effort is the total effort required to develop the software product, expressed in person months (PMs).
2. Intermediate COCOMO
An extension of the Basic model that computes software development effort by adding a set of "cost drivers," that will determine the effort and duration of the project, such as assessments of personnel and hardware.
3. Detailed COCOMO
An extension of the Intermediate model that adds effort multipliers for each phase of the project to determine the cost drivers impact on each step.
Example: A distributed Management Information System (MIS) product for an organization having offices at several places across the country can have the following sub-components:
- Database part
- Graphical User Interface (GUI) part
- Communication part
XII. RISK MANAGEMENT
NP-hard (non-deterministic polynomial-time hard), in computational complexity theory is a class of problems that are informally, quote ;at least as hard as the hardest problems in NP quote ;. A problem H is NP-hard if and only if there is an NP-complete problem L that is polynomial time Turing-reducible to H (i.e., LTH). In other words, L can be solved in polynomial time by an oracle machine with an oracle for H. Informally, we can think of an algorithm that can call such an oracle machine as a subroutine for solving H, and solves L in polynomial time, if the subroutine call takes only one step to compute. NP-hard problems may be of any type: decision problems, search problems, or optimization problems. If there is a polynomial algorithm for any NP-hard problem, then there are polynomial algorithms for all problems in NP and hence P = NP; If P NP, then NP-hard problems have no solutions in polynomial time, while P = NP does not resolve whether the NP-hard problems can be solved in polynomial time.
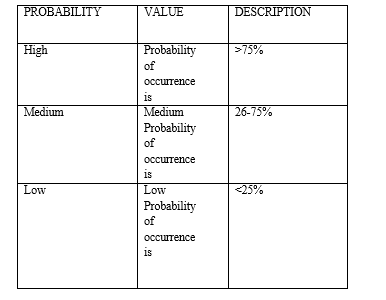
XIII. RISK ANALYSIS
There are quite different types of risk analysis that can be used. Basically, risk analysis is used to identify the high-risk elements of a project in software engineering. Also, it provides ways of detailing the impact of risk mitigation strategies. Risk analysis has also been found to be most important in the software design phase to evaluate criticality of the system, where risks are analyzed and necessary counter measures are introduced. The main purpose of risk analysis is to understand risks in better ways and to verify and correct attributes. A successful risk analysis includes important elements like problem definition, problem formulation, data collection.
Risk analysis is useful in many situations:
- When you're planning projects, to help you anticipate and neutralize possible problems.
- When you're deciding whether or not to move forward with a project
- When you're improving safety, and managing potential risks in the workplace.
- When you're preparing for events such as equipment or technology failure, theft, staff sickness, or natural disasters.
- When you're planning for changes in your environment, such as new competitors coming into the market, or changes to government policy.
XIV. RISK MANAGEMENT ANALYSIS
If there is a possibility that the achievement of a goal is harmed, prevented from occurring or suffers negatively due to the occurrence of uncertain events, we call it the risk.These so-called uncertain events can be caused by different factors. An efficient risk management analysis should be able to attend to every one of them to be able to identify them promptly in each of the listed cases:
A. Personnel Risks
Caused by a lack of Knowledge about technology and training to perform functions. There is a possibility that errors are intentional, this is the result of the dubious conduct.
The main risks from personal issues are:
- Unintentional; resulting in omission or negligence.
- Cannot perform task because lack of ability.
- Lack of time management.
B. Process Risks
The occurrence of internal process deficiencies like inadequate performance indicators, inefficient controls, modeling failures and an inability to abide by the current laws.
C Systems Risks
Arising from inadequate, poorly structured or defective IT systems. Some examples:
- Intermittent networks
- Server crash
- Physical damage to data storage components
- System obsolescence
- Improper maintenance
- Power outage from internal causes
- System slowdown
- Security holes
D. Risk Management wrt. NP Hard Analysis
- In rural area most of the time Internet will not be available so our system may not work.
- If reviews not available and false review are there then systems results will fail.
- If provide wrong input then system will show wrong output or it may fail.
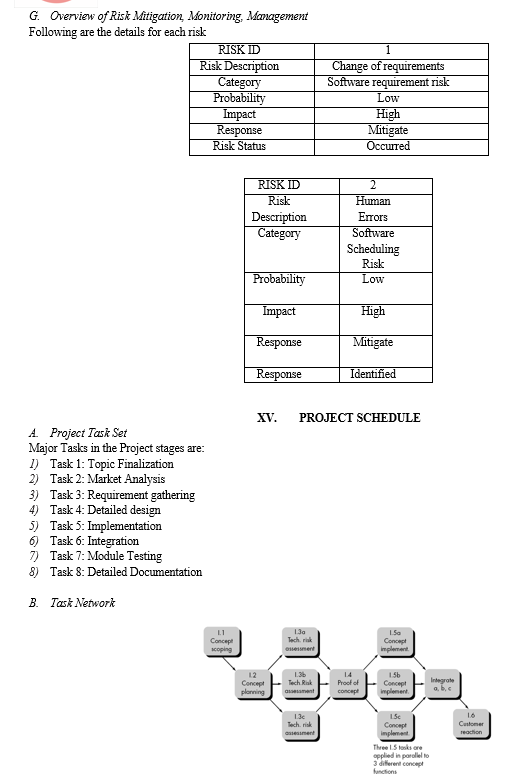
E. Risk Identification
- System may get fail during review database.
- Results may get fail.
F.
Risk Analysis
The risks for the Project can be analyzed within the constraints of time and quality
XVI. ADVANTAGES OF THE PROPOSED SYSTEM
- Access to authorized personnel only.
- No additional devices need to be carried for object detection.
- The system is used in the real time object detection.
- It helps to Blind person to prevent from dangerous location.
- This project is to provide cost effective way to allow path planning for blind people.
- Reducing the bulkiness and making the system portable for the application to come into picture in real life.
- Modifying speed, accuracy, and reliability of the system
- Making the Raspberry Pi speak and respond to instructions given by blind person (eg. Navigation)
XVII. DISADVANTAGES OF THE PROPOSED SYSTEM
- Slow Internet Connection.
- Low Light Intensity affects accuracy of model
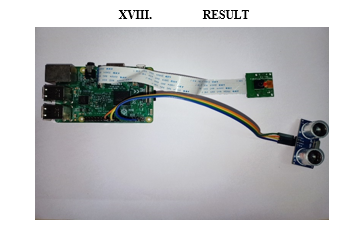
The hardware kit as shown in the above picture consists of Raspberry-Pi which has a pi-camera and ultrasonic sensor connected to it. The proposed system will detect and recognize the object which comes in front of camera. We have imported ‘imutils’ package in the python program for the proposed system. The proposed system will give a speech output when earphones will be connected to it. The type of the object and the distance between the blind person and the object will be read by the system for the blind person.
XIX. FEATURES OF THE PROPOSED SYSTEM
- The system can be used in the real time object detection.
- It helps Blind person which helps to prevent them from dangerous location.
- This project is to provide cost effective way to allow path planning for blind people.
- Speech output systems can be used to read screen text to computer users who are blind.
- Low cost.
- Huge processing power in a compact board.
- Supports Python (making it easy to build applications).
- We will use OpenCV (Open Computer Vision) algorithm for object recognition which will provide us with a huge libraries of datasets.
XX. APPLICATIONS OF THE PROPOSED SYSTEM
- This system is used to help the visually impaired to have access to the most important features of the phone enhancing the quality of the system making use of different custom layouts and using speech to text.
- Very affordable
- Reliable application for visually impaired users as deference’s between objects are easily detected
XXI. FUTURE SCOPE
In the domain of Artificial Intelligence, there was only the capturing the object using R-Pi in the existing system. At present, the work was successful to detect, recognize and track the object. And is used to avoids the user from touching the hot object. To further this project can be followed out with any other advanced devices by using simple coding language to get it less complicated. The complication can be reduced by a tiny gadget which could be more useful those people in this electronic world.
The future perspective of this project is to increase the object recognition to provide an exact distance measurement between the people and object. However, for developing an application that involves many objects that are fast-moving, you should instead consider faster hardwar
Conclusion
In this project, we have implemented an image to speech conversion technique using a raspberry pi. This system is much helpful Application for blind people. This system will be very easy to use. This Application is very helpful towards the blind people and makes very easy for them to use electronic gadgets with (text to speech) TTS technology, they will be able to interact more efficiently to the electronic system. This is an economical as well as an efficient device for the visually impaired people. The device is compact and helpful to the society. The proposed system is mobile, robust, and efficient. Also, it creates a virtual environment and this system provides a sense of assurance as it voices the name of the object recognized. The usage of Raspberry Pi has optimized the system and brought down the cost drastically compared to conventional systems. The proposed system is simple in design, easy to install and is reliable to a great extent. Blind person is able to detect and recognize the object in front (within a specific range) through audio output. In all, the developed system is able to develop a technical approach for solving a real- life problem in a time and cost-effective manner to a great extent
References
[1] Ayat A. Nada Department of Computers and Systems Electronics Research Institute, Giza, Egypt , “Assistive Infrared Sensor Based Smart Stick for Blind People” ayat@eri.sci.eg [2] Arnesh Sen Kaustav Sen Jayoti Das Jadavpur University: Dept. of Physics, “Ultrasonic Blind Stick For Completely Blind People To Avoid Any Kind Of Obstacles”, Kolkata, India senarnesh.elec@gmail.com. [3] “An Application of Infrared Sensors for Electronic White Stick” S. Innet 1, N. Ritnoom 21Department of Computer and Multimedia Engineering 2Department of Electrical Engineering University of the Thai Chamber of Commerce. [4] Sharang Sharma, Manind Gupta, Amit Kumar, Meenakshi Tripathi, Manoj Singh Gaur, “Multiple Distance Sensors Based Smart Stick for Visually Impaired People.”, 2017. [5] M.Micheal Priyanka, M.Michael Dharsana, “Navigational Aiding System For Visually Impaired\", Third International Conference On Science Technology Engineering And Management (ICONSTEM), 2017 [6] A. Aladrén, G. López-Nicolás, Luis Puig, and Josechu J. Guerrero, \"Navigation Assistance for the Visually Impaired Using RGB-D Sensor With Range Expansion.\" IEEE Systems Journal 2014. [7] Laviniu _epelea, Ioan Gavrilu_, Alexandru Gacsádi, “Smartphone Application to Assist Visually Impaired People”, 14th International Conference on Engineering of Modern Electric Systems (EMES), 2017. [8] Kabalan Chaccour and Georges Badr,\" Novel indoor navigation system for Visually Impaired and blind people\",2015. [9] Jinqiang Bai, Shiguo Lian, Zhaoxiang Liu, Kai Wang, and Dijun Liu, \"Smart Guiding Glasses for Visually Impaired People in Indoor Environment\", IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, Vol. 63, No. 3, August 2017,pp.258-266 [10] Zoran Zivkovic. Improved Adaptive Gaussian Mixture Model for Background Subtraction Pattern Recognition, 2004. ICPR 2004. Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on 20 Sep 2004
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Neve Sujal Rajesh, Khairnar Megha Himmat, Gamane Amrisha Gokul, Prof. Sangale Sunil Hiraman. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET51014
Publish Date : 2023-04-25
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

