Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Review On Cross-Platform Mobile Application Development
Authors: Pranjali Ravindra Hiwale, Anand Arun Kalsait, Kishori Yadavrao Choukade, Aishwarya Sanjay Puri, Prof. Priyanka Vikrant Shirbhate
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.40004
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
In this modern day and age, using mobile technologies is growing at an alarming scale. Because of this, greater effective and efficient mobile applications are wished so that you can maintain up with this trend. Due to the fact there exist several mobile systems (iOS, Android, and many others.), every one with distinct SDK (software program development kit) tools and specific improvement abilities, software development will become more complicated and steeply-priced. The project is to provide you with a solution that permits us to deploy in one of a kind platforms using a one kind of SDK device and maintain the same performance because of the local software. A suitable solution is cross-platform. In this paper, we present a survey of cross-platform creation techniques with focus on the MDA (model driven structure) approach as it\'s far one of the most promising move-platform strategies. We also picked out and discussed requirements of any cross-platform technology.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Mobile applications are becoming increasingly common today, especially in the business world. Mobile App Software Development refers to the process of developing software for mobile devices such as smartphones and the personal assistant. Through the use of mobile applications the user is provided with various features and services that will enable him to fulfill all his needs and much more than that. Apps must interact with users. Apps can be downloaded from various platforms such as Google Play Store and iOS App Store. There are free apps and paid apps. Some apps can be used for free for a while before you sign up for a premium membership. For priced apps, about 20% -30% goes to the distribution provider (for example iTunes) and the rest to the app manufacturer. With the development of applications, the limitations and features of mobile devices must be considered. Mobile devices have low processing power, are battery-operated but have many features such as location detection. The wide range of screen sizes and hardware specifications also need to be considered while developing the applications. For developing applications, specialized integrated development sites such as Android Studio or Eclipse or any Application Development Environment are required. The app is first tested using devices called emulators that simulate real hardware device software and then perform a field test [1]. Mobile User interface (UI) design is another important component in application development. The UI includes configuration considerations, screen and user input and output flow. The user cheats the system by installing and then the expected results are displayed exit. There are limits to the mobile UI as the screen size is limited. The mobile UI is considered as the front and rear of the background to support access to business systems. Background services such as data routing, security and authorization and alerts are provided with middleware components such as Mobile Backend as a service (MBAaS). The paper begins by examining the challenges of mobile application development.
II. FUNDAMENTALS OF APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT
A. Master the Language
Java and XML are the two main programming languages used in Android development. Mastery over these programming languages is a necessity to developing an Android app. Some of the fundamentals of the Java programming language include:
- Packages
- Objects & classes
- Inheritance & interfaces
- Strings & numbers, generics,
- Collections
- Concurrency
A good understanding of Java and XML will help you build / improve a strong and excellent android app. [5]
B. Familiarity with Application Development Tools and Environment
To get into the development of the Android app, it is very important that you familiarize yourself with the flexible build tools and IDE before you start upgrading your app. You can use Android studio IDE or Eclipse with tools; they will help you learn the basics and help improve your code. It is also important that you familiarize yourself with the resource management tools and concepts. Learn Git and create a Git source repository (by creating an account on GitHub). To understand the basic concepts and principles of how a forum works, you can use the Git Pocket Guide.
C. Application Component Information
App components are important building blocks for Android Application Development. Every component is a separate point where the system can install your app. While each one exists as its own business and plays a desirable role, not all are real entry points and some are interdependent.
There are five different types of components for each application that serve a different purpose that explains how the application is created and destroyed. They include:
- Tasks: The part representing one screen that can be used visually. These functions collectively create a shared user experience in the app. However, each one is independent.
- Services: The part that works in the background to perform long-term tasks. It does not provide a user interface.
- Content Providers: The part that holds the shared set of app data. Data you store on file systems, on the web, SQLite website may be query or modified as long as the content provider approves it. This section is also useful for writing and reading private data in your application.
- Broadcast Recipients: Part of which responds to broadcast announcements. Most broadcast receivers from the system can create a notification to users when the broadcast event is in progress. Usually, the gateway to the other parts and does only a small amount of work.
- Opening Sections: The synchronization message called objective activates 3 of the 4 components namely services and functions. Objectives also bind individual segments during operation whether the component belongs to your application or not.
D. Awareness over Fragmentations, Android Application, Threads, Loaders, and Tasks
Android is a different market with different devices and operating systems. Consider, if the app supports multiple devices and or versions it will require additional maintenance and testing and related costs. Vice-versa is also true. Engineers also need appropriate fonts, assets, and structures that will help ensure the best possible understanding of the various screen ratings provided. You should also consider a list of sensors supported by android or UI resources. All android apps have an application class, one or more functions, and one or more clips.
Most of the time, engineers may have background services that should work continuously but sometimes may not work. If an Engineer wants to deliver a good and smooth user interaction, always make sure the series is not blocked. That is why, long calculations should all be done in the background.
E. Making the Right Choice Over Needed Tools
The simple tools the developers need for Android app development are Mac or Windows PC, any Linux version, and Eclipse, ADT Plugin, and Android SDK — all open source. Engineers can go through the installation guide on relevant sites to learn how to set up your development site; it provides documentation of everything you need. Android has some unique features that developers should consider when designing an Android app. Some of these include:
- Performance and Responsiveness: Application should always respond to user input within five seconds otherwise the operating system will ANR you. (ANR-application not responding.)
- Lags of More Than 100ms: As mentioned above, the UI thread should never be blocked because it is only one and can be noticed by users.
- Limited Resources: Wake-locks (the mechanism that forces the device to do a certain task despite the recommendation to put the device to sleep by the battery manager) should be reserved. Do not unnecessarily reserve hardware because it will quickly run down the battery.
III. NATIVE APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT VS. CROSS-PLATFORM APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT
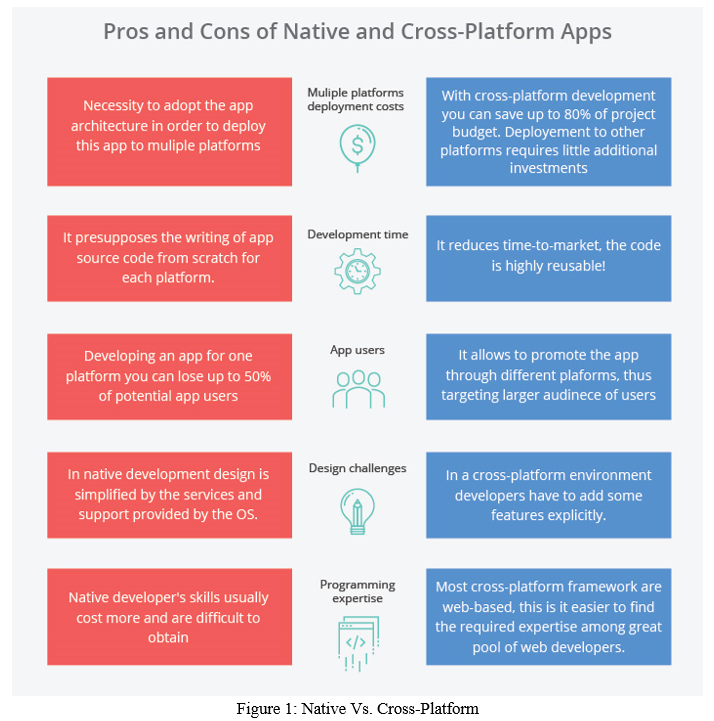
A. Development Time
Indigenous applications have a high development time as codes are written from scratch on each platform. Cross-platform applications, on the other hand, operate with the principle of 'write once, run anywhere'. Since the engineers here do not have to start everything from scratch and can use single codes on many bases.
B. Performance and Speed
Application performance and speed play an important role in determining the future of an application. With native applications, an IT business owner does not have to worry about application performance. This is because these apps are responsive, fast, and less likely to be infected. But in Cross-platform applications, these applications often suffer from operational problems and are slower compared to native applications as they can deal with interoperability issues.
C. Features
Indigenous applications have operating SDKs that ensure access to the API device without any problem. Unlike Cross-platform applications, native apps allow offline features as well. In Cross-platform applications, there is no guaranteed shot access to the device API and other resources.
D. Customer Access
Customer access to traditional apps is low as they are designed for a specific platform or operating system. However, identifying large audiences is easy with Cross-platform applications as it allows you to promote a single application through different platforms or operating systems.
E. Language Compatibility
The language compatibility of Indigenous applications is high as they are developed with a specific language. That is to say, Java and Kotlin are used for Android and Swift and Objective C are used for iOS app development. Cross-platform applications are developed in JavaScript compatible with multiple devices and can be distributed across a variety of platforms.
IV. TECHNOLOGY
A. Frontend Development
The front of the web- or mobile app is the part the user interacts directly with. It is usually called the "client side" of the application. The front area contains everything the user sees when interacting with a website or app, such as text colors and styles, images, graphs and tables, buttons, colors, navigation menu, and much more. [1]Front End engineers provide the layout, look, behavior, and content of everything from the browser that is displayed when websites, online applications, or mobile applications are opened. Key points to focus on improving frontend response and performance. The previous developer should ensure that the site is responsive, which means that it works well on devices of all sizes. Application performance must be stable at all times, regardless of the device used to access the app.
Front languages:
- Hypertext Markup Language (HTML): HTML stands for Markup Hypertext Language. The language used to design the front of the web pages. HTML is a simple language that combines hypertext with punctuation. The word "hypertext" means a link between web pages. The language of the text is used to construct the architecture of the text under the mark. In this way, the content on the page is structured in the form of headings, headings, subtitles, basic text, images, etc.
- Cascading Style Sheets (CSS): CSS is a simple language designed to simplify the process of changing the content of a web page. A piece of CSS code can be easily linked to HTML code, which automatically renders certain styles and is formatted on web pages. CSS allows you to do so without having to worry about the HTML code that forms each web page. Although there is a way to assign styles directly to HTML code, having a separate code on the CSS writing side ensures you do not accidentally waste existing HTML code. Additionally, you can make a format change on a single CSS style sheet, and it will automatically apply to all areas where that particular style is applied across the site. This makes it very easy to maintain a consistent style across all your web pages.
- JavaScript: JavaScript is a well-known programming language used to integrate interactive features into websites to make the interface more attractive to users. It is used to improve website performance and run games and web-based software.
- Front Panels: Frames or libraries in application development provide developers with the right tools to assist them in the development process. The most popular libraries in frontend development are ReactJS, AngularJS, and jQuery.
- ReactJS: ReactJS is a JavaScript library for creating fast, easy-to-use and flexible user links. ReactJS is an open source, front-end library based solely responsible for application overview. Facebook manages to keep it up to date.
- AngularJS1: AngularJS is a front-end JavaScript framework that is widely used to build single-page web applications (SPAs). It is an ever-changing framework that provides better ways to improve online applications. Stable HTML is replaced by dynamic HTML. An open source project that can be downloaded for free. Add Directions to HTML attributes and uses HTML to compile data
- JQuery: jQuery is a free JavaScript framework that makes it easy to manage HTML / CSS documents. JQuery makes it easy to manipulate HTML texts
B. Backend Development
Backend is part of the website server. Maintains and organizes data, and ensures that everything around the website client works properly. It is part of a website that you can see and communicate with. It is part of the software that does not communicate directly with users. Features and features developed by backend designers are indirectly accessed by users through a pre-app. Tasks, such as writing APIs, creating libraries, and working with system components without user interaction or science program systems, are also included in the background.
Background languages:
- PHP: PHP is a server-side scripting language specifically designed for web development. Since PHP code is generated on the server side, it is also called server-side scripting language.
- C++: A common programming language that is common and widely used today in competitive systems. It is also used as a background language.
- Java: Java is one of the most popular and widely used editing languages ??and platforms. It sounds great. Parts of Java are easily accessible.
- Python: Python is a programming language that allows you to work quickly and integrate applications successfully.
- JavaScript: JavaScript can be used in both editing languages ??(front and back).
- Node.js: Node.js is an open source and cross-platform for using JavaScript code without a browser. You need to remember that NodeJS is not a framework, nor is it a programming language. Most people are confused and understand that it is a framework or language of planning. We often use Node.js to build background apps such as APIs such as the Web App or the Mobile App. It is used in the production of big companies like PayPal, Uber, Netflix, Walmart, and so on.
- Back End Frameworks: List of backgrounds are: Express, Django, Rails, Laravel, Spring, etc. Other background / writing languages ??are C #, Ruby, REST, GO, etc.
- IDE: Integrated development area is a combination of all the tools you need to write and test software. Engineers use many tools throughout their development cycle including text editors, code libraries, moderators, and test platforms. Now imagine that you have to select, extract, compile, and manage all of these tools separately. It's crowded, time-consuming, and frustrating. This is where these IDEs come in and bring many development tools to a single framework, application, or service - making coding, finding and removing bugs or errors easy. IDE can be open source or commercially available at a tag price. In addition, it can serve as a standalone application or as part of a comprehensive package
- Android Studio: Android Studio is the official IDE for Android. Android Studio is best known for its ability to speed up the development process while not losing any quality. If you are new to Android development, Android Studio has a lot of apps for building apps. You will easily capture android mobile conversations and business development
- Eclipse: Eclipse is one of the most widely used Java IDE applications that provides a customizable working environment and an expandable plug-in system. Written in Java, this Integrated Development site is very popular among Java development companies. The Eclipse Software Development Kit (SDK) includes a wide range of Java development tools to help Java developers build solid applications.
- Xcode: Xcode is Apple's integrated development platform (IDE). It is used to build applications for Apple products, such as the iPad, iPhone, Apple Watch, and Mac. It is a powerful tool that allows you to control the flow of your development work from start to finish; that is to create your app, test it, configure it, and send it to the Apple App Store.
V. ADVANTAGES OF CROSS-PLATFORM DEVELOPMENT
In the recent period of time, the concept of cross-platform mobile app development has taken a huge leap. It allows the developer to write the code once and deploy it across all platforms – Android, iOS or Windows.
Some of the advantages of developing Cross-Platform Applications are:
A. Reusable Codes
Instead of creating new applications for all platforms, developers can re-apply the same code across all platforms. This also saves from repetitive tasks, thus eliminating boredom. However, this is not a completely new concept. It has been used in software development for several years now and the benefits of reusing codes are seen here as well.
B. Cost Controls
Thanks to the development of various mobile applications, developers now need to invest just once to make their system more developed than before when they had to spend a lot of money on various tools and technologies. They no longer have to spend money on developing applications for the whole platform separately. For developers, the same team can be used to work in different forums.
C. Fast development time
Application development is very fast, where a single script can be installed in multiple forums. The increase in development speed, on the other hand, is causing the product to reach the market faster than before. Time can be spent working on new system codes. Winning status for all stakeholders - developers, advertisers and consumers.
D. Easy Implementation
There are many technologies these days, such as PhoneGap and Appcelerator, which provide a cross-platform solution that makes it easier for developers to make changes. For example, when using a tool like Appcelerator, codes can be easily written in HTML5 and converted to different platforms. In other words, the use of resources you already know and translate into different forums. This not only speeds up app development, but also makes it easier to sync updates to all mobile devices.
E. Similarities and similarities
Applying multi-platform app development ensures that the overall look of the app can be maintained in all forums as the same set of codes are used. Customers find the app difficult and inefficient when they need to use different methods to access the same app on different phones. They can choose to use the same look and feel on both devices.
What are the two main goals of a mobile application developer? The answer is simple: get as many customers as you can or aim at a target market and engage customers fully.
It is not a difficult prospect when the majority of targeted audiences use the same platform. Then it is easy to choose which platform to improve the app. But if the goal is to target a large audience that can use an iPhone, Android, Windows Phone and others, the app will have to be tailored to different platforms.
VI. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We'd like to extend our deepest appreciation to everyone who helped with the research for this project; without their active participation, the project would not have been completed in the time period given. Prof. Priyanka Vikrant Shirbhate, our esteemed professor has inspired and directed us to accomplish this assignment with total focus and attention.We are also grateful to my project guide Lecturer, who has been really supportive and patient with us during this project and has assisted us in completing it.
Conclusion
Mobile applications have become an integral part of our daily lives because of the variety of functions they offer. Building a successful, trouble-free and easy-to-use application is essential due to the rapid increase in the number of applications. The developer should consider the challenges he faces and try to overcome them by following the appropriate steps. Also, it is important for the developer to be open-minded and well-informed about current technologies, needs and events in the field of mobile application. In order to build success, all guidelines must be properly considered and properly followed to avoid the risk of losing users due to crashing / crashing applications [12]. Developing new and innovative applications will lead to greater profit potential. There are also a few research studies conducted that could serve as a platform for future research sites. In its face, Android seems to be the most successful platform. An operating system that enables 85 percent of new smartphones shipped, and, along with iOS, completely eliminates competition. Android is also resisting the problems that Google.Inc does not seem to be solving. Developers must develop software that will work reliably on many different devices from various manufacturers. Sure, developers can focus on devices from major companies, but that defeats the purpose of having a platform in the first place. Then there is the problem with the update. Google has an annual release plan for Android, but it takes a new version for a good part of the year to break the 10 percent usage mark. And it takes about four years for the release to fully enter the ecosystem. While Google is quick to discover new releases on its Nexus Hardware, it can take months for owners of Android devices from other manufacturers to see the update. And many do not see the revision. Without buying a Nexus device, the easiest way to get your hands on a new Android release is to buy a new device that is fresh in the market.
References
[1] Zigurd Mednieks, Laird Dornin, G. Blake Meike and Masumi Nakamura, “Programming Android” ,O? Reilly [2] Venkata N Inukollu, Divya D keshamoni, Taeghyun Kang and Manikanta Inukollu, “Factors Influencing Quality Of Mobile Apps: Role Of Mobile App Development Life Cycle”, International Journal of Software Engineering & Applications(IJSEA), Vol.5, No.5, September 2014 [3] Ian Darwin, “Android Cookbook -Problems and Solutions for Android Developers”, O?Reilly Media, May 2017 [4] Performance of App, https://www.safaribooksonline.com/library/view/high-performance-android/9781491913994/ch03.html [5] Mobile App Design, https://www.noupe.com/imho/the-importance-creative-design-for-mobile-app-user-experience.html [6] Ryan Cohen, Tao Wang,” GUI Design for Android Apps”, apress.open [7] UI and UX design, http://colure.co/the-importance-of-ux-and-ui-in-mobile-app-design/ [8] Get App Noticed, https://www.forbes.com/sites/karstenstrauss/2014/09/23/how-to-get-your-app-noticed-wisdom-from-app-annie/#316e98cd3675 [9] Prasant Kumar Pattnaik, Rajib Mall, “Fundamentals of Mobile Computing”, PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd, New Delhi-2012 [10] Prof. K.D. Tamhane, Mr. Wsim T. Khan, Mr. Sagar R. Tribhuvan, Mr. Akshay P. Burke, Mr. Sachin B. Take,” Mobile Learning Application”, International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 5, Issue 3, March 2015 [11] Ryan Cohen, Tao Wang, “Android Application Development for the Intel Platform”, apress.open [12] Mobile App, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mobile_app
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Pranjali Ravindra Hiwale, Anand Arun Kalsait, Kishori Yadavrao Choukade, Aishwarya Sanjay Puri, Prof. Priyanka Vikrant Shirbhate. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET40004
Publish Date : 2022-01-19
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

