Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
A Review on Development of Municipal Solid Waste Re-Derived Fuel Pellets from Mixed Municipal Solid Waste Using Smart Machine
Authors: Nikita Singh, Sanjay Sharma, Narsi Visharad
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.45874
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Municipal Solid Waste Management (MSW) and devise cost effective system which may ensure adequate level of MSW services to cities, segregation, treatment and disposal of Solid waste in an environmentally acceptable manner The wastes generated are either dumped in lands or find their way to the water bodies. This results in severe land, waste and air pollution. Our country generates thousand tons of municipal solid waste daily. So we have huge potential of energy generation from waste. Many countries are suffering from waste disposal problems and fuel shortages. To solve both waste and energy problems simultaneously, the refuse derived fuel (RDF) approach has been utilized in many countries. The purpose of study is to evaluate the energy potential of the RDF obtained from utilizing processed solid waste generated from the smart Dross Machine.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The Municipal Solid Waste or garbage is the unavoidable consequence of human civilization. Its production has been increased many folds with increasing population, urbanization, economic activities, income and their demand.
The increase of the quality of human life as well as rapid economic development and industry have created a huge volume of solid waste (SW), which has become one of the most critical current environmental problems. Many methods have successfully been used to dispose of different types of solid waste. Each disposal method has its advantages and disadvantages. Land filling is a long-standing disposal option; however, it is not a very suitable disposal method because of leachate problems and scarce available space. Bioremediation is an approach which decomposes waste; however, it is only suitable for biodegradable waste. Dumping into the ocean is one of the cheapest disposal methods but also the most harmful to the marine environment. Therefore, dumping is no longer allowed in many countries. Thermal treatment by using incineration technology has been proven to be an attractive method of waste disposal for many years. Incineration has been widely used because it is capable of reducing approximately 90% of the original volume and 75% of original weight of SW and can provide energy recovery. However, incineration has the drawbacks of producing ash and hazardous air pollutants such as dioxins and furans. Much of the solid waste can be transformed into useful products, and thus the proportion of solid waste that is being recycled, reused and recovered is increasing. Many countries are suffering from waste disposal problems and fuel shortages. To solve both waste and energy problems simultaneously, the refuse derived fuel (RDF) approach has been utilized in many countries. Before being incinerated, solid waste is classified based on combustible capacity and then materials with a high calorific content are used to produce RDF. The major advantages of the RDF approach are a large reduction of the volume and an effective utilization of SW available for a reusable energy form.
Type of Solid Waste:
Biodegradable Waste
Biodegradable wastes are the waste materials that are and can be easily degraded by natural factors like microbes (e.g. bacteria, fungi and a few others), abiotic components like temperature, UV, oxygen, etc. few examples of such wastes are kitchen wastes, food materials, and other natural wastes.
Non Biodegradable Waste
Waste that cannot be decomposed or degraded by the biological process is known as “Non- biodegradable wastes”. Most of them include the inorganic waste that is non-biodegradable cannot be decomposed or degraded by natural agents.
They remain on earth for thousands of years without any degradation or decomposition.
Waste Problems:
Improper handling and disposal of solid waste has multi-dimensional impact on human and environmental well-being. Improper dumping can lead to:
- Pollution of air, soil, and water,
- Contamination of surface and ground water supplies,
- Clogging of drains,
- Creation of stagnant water for insect breeding,
- Floods in the plains and
- Landslides in the hilly areas during rainy seasons.
Refuse Derived Fuel (RDF)
It is made from a common practice of segregation of solid waste to separate the combustible fraction from the non- combustibles, such as metal glass and cinders in MSW. RDF is predominantly composed of paper, plastic, wood, and yard wastes and has slightly higher energy content than untreated MSW, with gross calorific value typically in the range of 1800 to 2500 Kcal/kg. But RDF is slightly costlier in handling and transportation and can be used in cement plants kiln, the use of RDF for general purposes is negligible. Hence it is not considered a self-sustainable product.
MSWDFP MADE FROM MIXED MUNICIPAL SOLID WASTE USING SMART MACHINE”
Municipal Solid Waste Re-Derived Fuel Pellets (MSWDFP) are made from mixed municipal solid wastes, inclusive of biodegradable and non-biodegradable along with sanitary and baby napkins using Dross Magic instant & mixed multiple wastes disposals an indigenous innovative machines. MSWDFP is predominantly composed of multiple mixed municipal solid wastes inclusive of biodegradable and non-biodegradable along with sanitary and baby napkins and has considerably higher energy content than RDF, with gross calorific value typically in the range of 4500 to 5000 Kcal/kg. Although heating values are vary, depending upon the composition of waste and availability of higher fuel value materials like plastic and polythene, etc.
II. NEED AND SCOPE OF STUDY
The existing systems for the collection, transportation and disposal of solid waste are in chaos. The problem is more acute as rapidly growing populations generate increasingly larger quantities of solid waste that urban governing bodies are unable to manage effectively. Continuous supply of energy and proper waste disposal has always been the global challenges that require continual research and development. Proper waste disposal and the security of public wellbeing should be strengthened and increased human reproduction frequency, upgraded living quality, and extensive industrialization have indisputably increased the generated waste volume and demand of energy.
III. OBJECTIVES OF STUDY
The following are the objectives of the study:
- To study the performance of waste processing by Dross Machine.
- To carry out the analysis of machine generated processed waste and its composition.
- To develop the pellets to use as energy.
- To carry out Calorific values of Pellets.
IV. LITERATURE REVIEW
This section briefly reviews about the energy potential of Refuse Derived Fuel obtained from the solid waste as a fuel resource. Various study articles and reputed journals have been scanned on this topic based on which this explains the use of solid waste management techniques to convert the waste into energy by various methods. The review describes, summaries, evaluates and clarifies the literature.
Trang T.T. Dong, Byeong-Kyu Lee(2008):The purpose of this study is to evaluate the energy potential of the RDF obtained from utilizing combustible solid waste as a fuel resource. Potential RDF resources based on combustible solid wastes including wastepaper, wood, rubber, plastic, synthetic resins and industrial sludge were identified. The total obtainable energy value from the RDF resources in the industrial city was more than 2,240,000 106 kcal/yr.
R.P. Singh, V.V. Tyagi, Tanu Allen, M. Hakimi Ibrahim, Richa Kothari(2011): In this paper an attempt has been made to provide a comprehensive review of MSW management to evaluate the current status of waste to energy facilities for sustainable management, which will be helpful in tackling this huge quantity of waste and the problem of energy crisis.
It shows that waste to energy facility is not only possible but necessary in order to meet the demands of growing population and to improve environmental crisis in both developed and developing countries.
JeongInGug, David Cacciola et al (2014): This study aims to investigate the effects of processing conditions and added recyclable plastics on the properties of MSW solid fuels. A well-sorted waste stream high in paper and fiber content was combined with controlled levels of recyclable plastics PE, PP, PET and PS and formed into briquettes using a compression molding technique. The effect of added plastics and moisture content on binding attraction and energy efficiency were investigated.
Yan Yang,et al (2015):Dwindling fossil fuels and improper waste management are major challenges in the context of increasing population and industrialization, calling for new waste-to- energy sources. The production cost of energy via refuse-derived fuel gasification is estimated at 0.05 USD/kWh.
K. K. Ummatin, Q. A. M. O. Arifianti, A. Hani and Y. Annissa,(2019): This study is to investigate the RDF quality standard that is in accordance with the needs of the cement industry and evaluate the RDF production process. Quality Function Development (QFD) method is used to determine the parameters of RDF quality standards that are suitable for the cement industry. The results of the QFD analysis show that there are six main characteristics in the RDF quality standard based on importance response, including RDF 3-5 cm, particulate 80 mg/Nm3, humidity level ≤20%, mercury 5 mg/Nm3, calorific value ≥ 2500 kcal/kg and low ash content.
Alisha Das, RoopaManjunatha et al (2021): This paper deals with Waste generation rates rising around the world as the result of rapid population growth and urbanization. . This paper focuses to segregate waste into dry and wet waste on the basis of the change in relative humidity in the presence of wet waste. The proposed model is cost effective and energy efficient.
Vinay Kumar Tyagi a,* , AparnaKapoor b et al(2021): This studies the long-term feasibility analysis of a 100 ton per day mechanical biological treatment (MBT) plant for municipal solid waste (MSW) valorization and material and energy recovery was carried out. . This study presents a cutting- edge scenario of all-inclusive recycling, recovery, and reuse loop of MSW direly required for accomplishing a circular economy.
Fei, Fan; Wen, Zonguo; Huang, Shengbiao; De Clercq, Djavan (2018).According to this paper,Municipal solid waste (MSW) is treated mainly via landfill and incineration in most countries. The results showed that raw MSW landfill was the worst management option. Incineration had higher energy efficienc (20.5% energy recovery), but the large amounts of chemicals consumption for fly ash and exhaust treatment were also issues leading to relatively higher life cycle environmental impacts.
V. GAPS IN LITRATURE REVIEW
- Number of researchers have studied various techniques such as incineration aerobic digestion composting, etc to the conversion of solid waste to another form but all of them causes pollution in one way or another and is also time taking.
- Absence of proper waste management technique to convert waste into green coal.
- Most of the research work till date is focused on the particular type of solid waste reduction but not on the waste management technique which applied to the all type of waste.
- he moisture content property of the rdf produced by the various applied techniques in past needs to be taken care of as it affects the calorific value of the fuel.
VI. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
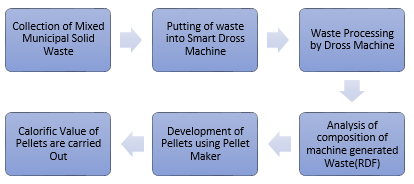
VII. EXPECTED OUTCOME
The expected outcome of this study is as given below: -
- The problem of solid waste disposal can be solved efficiently.
- The fuel derived from this machine can be used as a future alternative to the traditional coal fuel.
- It ensures the protection of environment through an effective waste management system.
- Briquettes made from this rdf is eco friendly and has high calorific value.
Conclusion
In the present situation, both Waste Management and energy generation is becoming key challenge in our country. Waste can become the source of energy and we can move towards a sustainable future. Huge study and research has been done and are still going onto make the processes easy. It is aimed to convert MMSW into fuel pellets and to test its calorific value. It can be used as an alternative fuel and is a cheaper alternative to the fossil fuel by providing them with a cleaner and sustainable solution.
References
[1] (Trang T.T. Dong, Byeong-Kyu Lee,(2008) Analysis of potential RDF resources from solid waste and their energy values in the largest industrial city of Korea. [2] R.P. Singh, V.V. Tyagi et al,(2011) Exploring the possibilities of energy generation solid waste [3] Gug, JeongIn; Cacciola, David; Sobkowicz, Margaret J. (2015). Processing and properties of a solid energy fuel from municipal solid waste (MSW) and recycled plastics. Waste Management, 35(),283–292. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2014.09.031 [4] (Yang, Y., Liew, R. K., Tamothran, A. M., Foong, S. Y., Yek, P. N. Y., Chia, P. W.,Lam, S. S. (2021). Gasification of refuse-derived fuel from municipal solid waste for energy production: a review. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 19(3), 2127–2140.doi:10.1007/s10311-020-01177-5 [5] K. K. Ummatin,et al, (2019) \"Quality Analysis of Refused-Derived Fuel as Alternative Fuels in the Cement Industry and Its Evaluation on Production,\" 2019 International Conference on Engineering, Science, and Industrial Applications (ICESI), 2019, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/ICESI.2019.8863000. [6] Tyagi, V. K., Kapoor, A., Arora, et al (2021). Mechanical-biological treatment of municipal solid waste: Case study of 100 TPD Goa plant, India. Journal of Environmental Management, 292,112741. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112741 [7] Fei, Fan; Wen, Zonguo; et al (2018). Mechanical biological treatment of municipal solid waste: Energy efficiency, environmental impact and economic feasibility analysis. Journal of Cleaner Production, (), S0959652618300684–. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.060 [8] Das A., ShuklaA,Manjunatha R and E. A. Lodhi,(2021), \"IoT based Solid Waste Segregation using Relative Humidity Values,\" 2021 Third International Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks (ICICV), 2021, pp. 312-319, doi:10.1109/ICICV50876.2021.9388611.
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Nikita Singh, Sanjay Sharma, Narsi Visharad. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET45874
Publish Date : 2022-07-21
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

