Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Experimental Study of the Physical Properties of Concrete Prepared by Partial Replacement of Cement with Alccofine, Metakaolite and GGBS
Authors: Nayyer Ansari, Deepak Kumar Bandewar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.46417
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
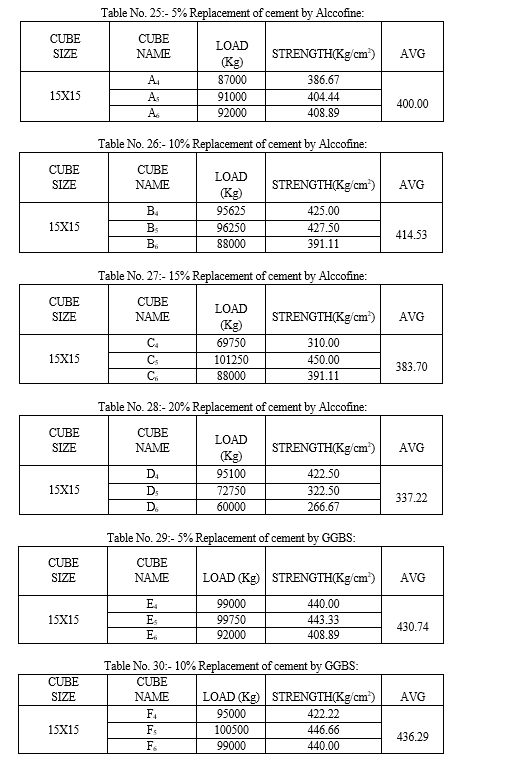
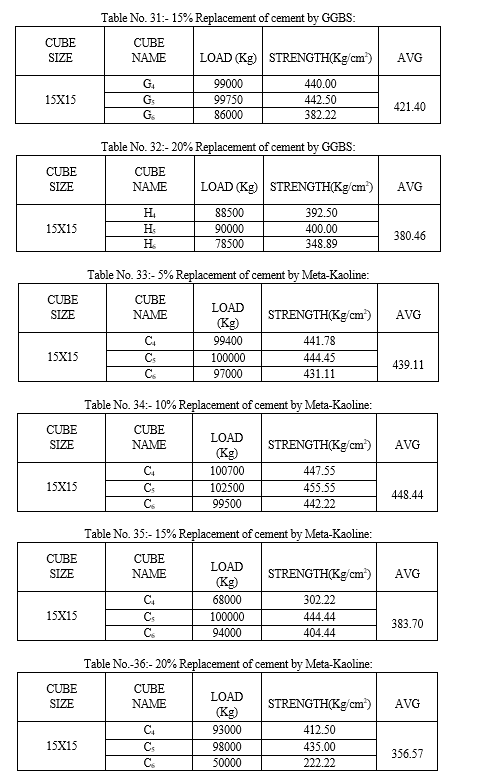
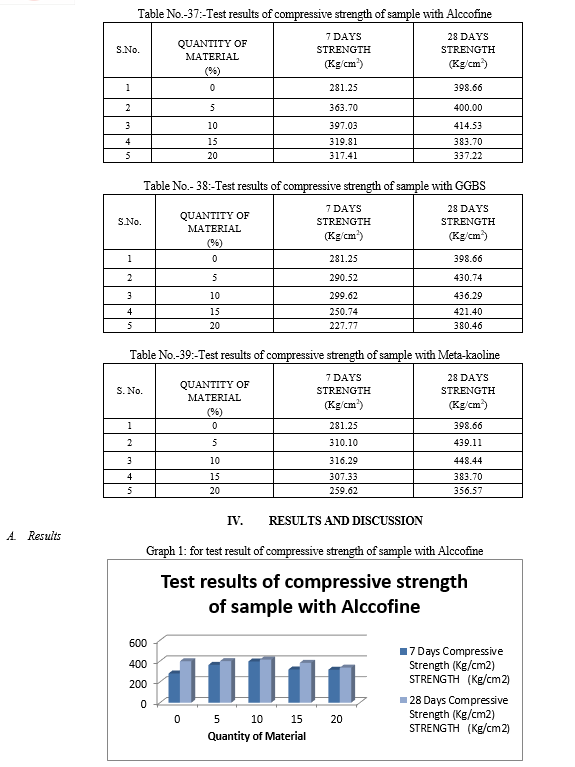
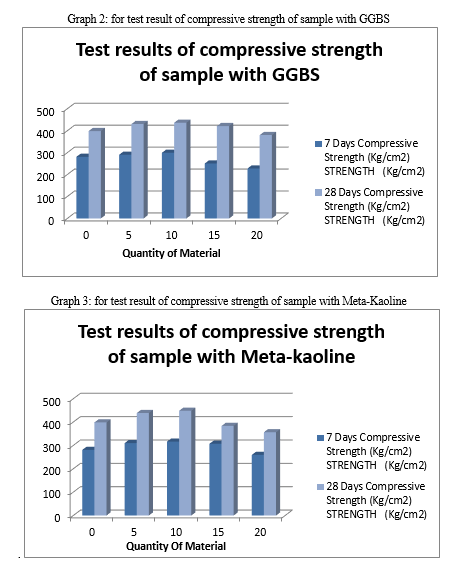
Cement concrete is the most broadly used construction material in the world. Maintenance and repair work of concrete structures is an increasing problem involving the significant expenditure. As a result of study carried out worldwide, it has been made possible to process the material to satisfy more strong performance requirements, especially durability. To reduce the expenditure for making of concrete we should consider the industrial waste materials for partial replacement of cement with supplementary cementitious materials like alccofine, GGBS and meta-kaoline. We consider these materials because these are available at very low cost. For this purpose we prepared number of samples by the various mixes with variable percentage of these materials in the mix. After the selection of the mix on these prepared specimens we perform workability and compressive strength test in the laboratory. By these tests we come to know that when we replace cement by Alcofine up to 10% the compressive strength increases 414.53 but after this range of addition it starts reducing the strength. when we replace cement by GGBS up to 15% the compressive strength increases 421.40 but after this range of addition it starts reducing the strength and same when we replace cement by Meta-kaoline up to 10% the compressive strength increases 448.44 but after this range of addition it starts reducing the strength
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Conventional Concrete
Concrete is most widely used construction material in the world. Concrete is a composite material formed by the combination of (a) cement, (b) aggregate and (c) water in particular proportion in such way that concrete produce meets the need of the job on hand particularly as regards its workability, strength, durability and economy. In our country the concrete is generally prepared at the sites and therefore need to be carefully supervised and controlled in order that it performs the way its technically expected to perform. Lot of care is to be taken in every stage of manufacturing of concrete.
The various stages of manufacturing concrete are:
- Batching
- Mixing
- Transporting
- Placing
- Compacting
- Curing
- Finishing
B. Special Concrete
- Fibre Reinforced Concrete
Fibre reinforced concrete (FRC) is concrete containing fibrous material which increases its structural integrity. It contains short discrete fibres that are uniformly distributed and randomly oriented. Fibres include steel fibres, glass fibres, synthetic fibres and natural fibres. Within these different fibres that character of fibre reinforced concrete changes with varying concretes, fibre materials, geometries, distribution, orientation and densities.
The concept of using fibres as reinforcement is not new. Fibres have been used as reinforcement since ancient times. Historically, horsehair was used in mortar and straw in mud bricks. In the early 1900s, asbestos fibres were used in concrete, and in the 1950s the concept of composite materials came into being and fibre reinforced concrete was one of the topics of interest. There was a need to find a replacement for the asbestos used in concrete and other building materials once the health risks associated with the substance were discovered. By the 1960s, steel, glass (GFRC), and synthetic fibres such as polypropylene fibres were used in concrete, and research into new fibre reinforced concretes continues today.
2. Polymer Concrete
In the constructions industry new building materials with improved properties are required for satisfying the new utilization domains for modern construction or for repair works. The application of polymer on concrete has significantly progressed in the last 30 years. Polymers are either incorporated in a cement-aggregate mix or used as single binder. The composites made by using polymer along with cement and aggregates are called polymer-modified mortarorpolymer-modified concrete, while composites made with polymer and aggregates are called polymer mortar or polymer concrete, depending on the maximum size of aggregate granule.
In the composition of polymer concrete there is not cement: the aggregates are bonded by the resin. Function of the type of polymer it can obtain concretes with synthetic resin, concretes with plastic resin or simple concrete with resin. The composite does not contain hydrated cement paste. Polymer concrete presents some advantages compared to the cement Portland concrete such as: rapid hardening, high mechanical strengths, improved resistance to chemical attack, durability, etc. One of the most important disadvantages is the high cost of resin that limited the use domains of polymer concrete. The performances of polymeric concrete depend on the polymer properties, type of filler and aggregates, curing temperature, components dosage, etc. The aggregates can be silicates, quartz, crushed stone, gravel, limestone, calcareous, granite, clay, etc. Near the aggregate, the filler is very important. Different types of fine materials can be used such as fly ash, silica fume, phosphor-gypsum, cinder, etc.
The different ingredients used for casting the concrete are as follows:
a. Waste Material: Due to sustained pressure of industrial and developmental activities, there are appreciable disturbances in the ecological balance of nature. As with most large manufacturing industries, by-product materials are generated. These industrial by-product and waste materials must be managed responsibly to insure a clean and safe environment. The concept of environmental geo-techniques has emerged as an answer to the need to understand the ecological problems, connected with Fly ash, CKD, Quarry fines, Silica fines.
- Fly ash: Fly ash is one of the residues generated in combustion, and comprises the fine particles that rise with the gases. In an industrial context, fly ash usually refers to ash produced during combustion of coal. It is having a fineness of about 4000-8000 cm2 /g. Fly ash is generally captured by electrostatic precipitators or other particle filtration equipment’s before the flue gases reach the chimneys of coal-fired power plants Depending upon the source and makeup of the coal being burned, the components of fly ash vary considerably. It may include one or more of the following elements or substances in quantities from trace amounts to several percents arsenic, beryllium, boron, cadmium, chromium, chromium VI, cobalt, lead, manganese, mercury, molybdenum, selenium, strontium, thallium, and vanadium, along with dioxins.
- CKD: Cement manufacturing is a critically important industry in the world worldwide production accounted for about 2.5 billion metric tons. Over the past several years dramatic advances have been achieved in the management and use of cement kiln dust, thus reducing its dependency on landfill disposal. Sustainability is the cornerstone of the cement industry, not only in the products that use cement, but also in its manufacturing process. Many of the older, inefficient plants are being replaced by more modern plants or being renovated with new technologies to be more efficient as well as more environmentally friendly. The majority of CKD is recycled back into the cement kiln as raw feed. In addition, new technology has allowed the use of previously land filled CKD to be used as raw feed stock. Recycling this by-product back into the kiln not only reduces the amount of CKD to be managed outside the kiln, it also reduces the need for limestone and other raw materials, which saves natural resources and helps conserve energy.
- Quarry Fines: In 2005, 216 million tonnes of saleable aggregate was produced; corresponding 55 million tonnes of quarry fines and 24 Million tonnes of quarry waste were also produced. The need to minimize fines production is driven by the Aggregates Levy (which has priced quarry fines out of the market in favour of recycled aggregate) and the Landfill Tax (which has made it expensive to dispose of fines). Future developments are likely to be driven by the need to respond to climate change .New crusher designs will be more automated, offer improved energy efficiency, have a greater production capacity and improved reliability.
b. Supplementary Cementing Materials (S.C.M.): Supplementary cementing materials (SCMs) such as Meta-kaolin, Alccofine and GGBS are increasingly used in recent years as cement replacement material. They help to obtain both higher performance and economy. These materials increase the long term performance of the concrete through reduced permeability resulting in improved durability.
- Meta-kaolin: The necessity of high strength high performance concrete is increasing because of demands in the construction industry. Efforts for improving the characteristics of concrete over the past few years suggest that cement replacement materials along with chemical admixtures can improve the durability and corrosion characteristics of concrete. High Reactive Meta-kaolin (HRM), is a pozzolanic material that can be utilized to produce highly durable concrete composites. However, information to understand the behaviour of this mineral additive in concrete is insufficient. Some of the recent information is discussed in this paper highlighting the role of meta-kaolin in high strength high performance concrete.
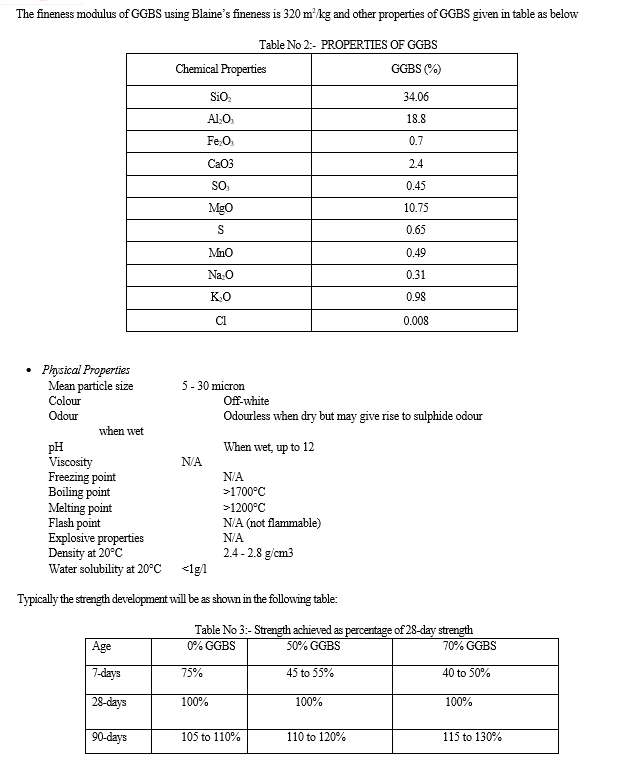
- GGBS: GGBS is non-metallic product consist of silicates and aluminates of calcium and other bases. The molten slag is rapidly chilled by quenching in water to form glassy sand like grains, further these grains ground to fineness less than 45µ. IS146:2000 suggest, GGBS obtained by grinding granulated blast furnace slag conforming to IS 12089 may be used as part replacement of OPC provided uniform blending with cement is ensured. When the GGBS is use as a replacement of cement the water requirement reduces to obtain the same slump. It also reduces the heat of hydration the main advantage of use of GGBS is reduction in permeability and increase resistance to chemical attack. Therefore GGBS is best applicable in the marine structure or concreting in the saline environment. This slag suitable for the use in combination with Portland cement in concrete, particular uses include concrete containing reactive aggregates, Large pours to reduce the risk of early-age thermal cracking, Concrete exposed to sulphates or aggressive ground & Concrete exposed to chlorides.
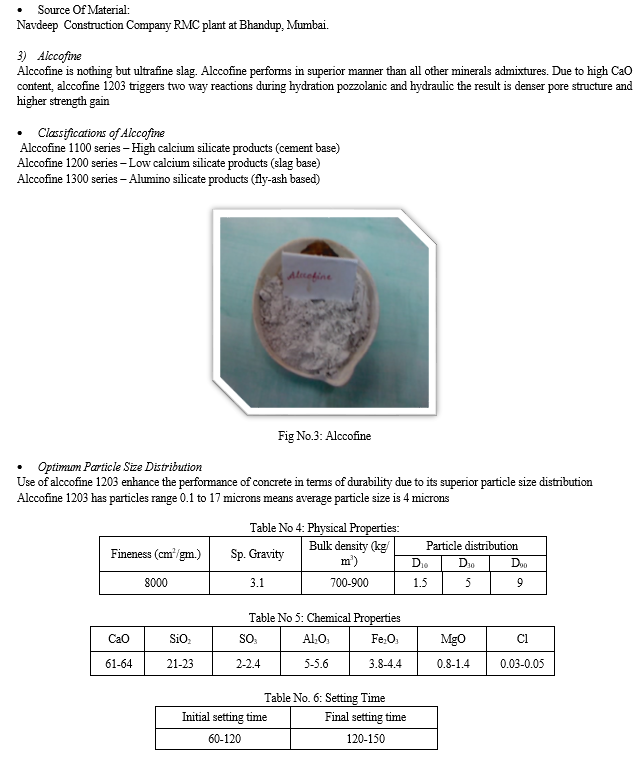
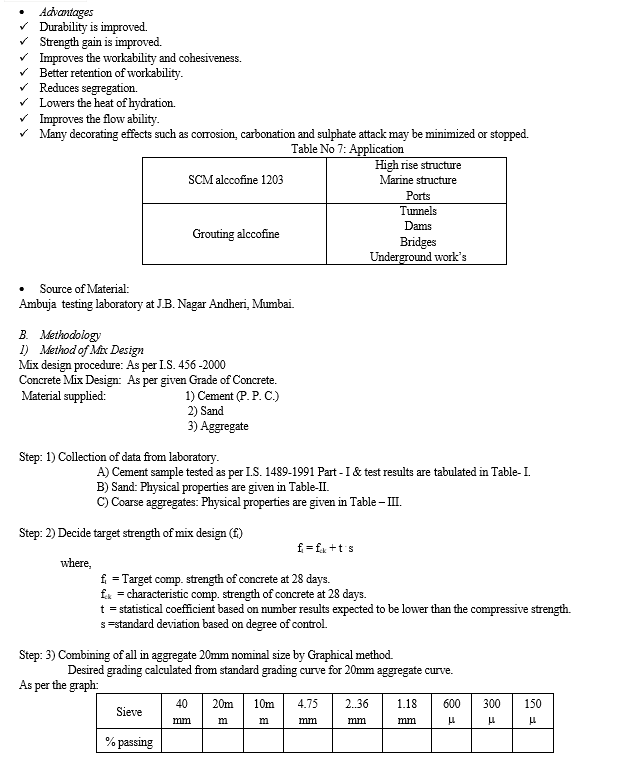
- Alccofine: ALCCOFINE 1203 is a specially processed product based on slag of high glass content with high reactivity obtained through the process of controlled granulation. The raw materials are composed primary of low calcium silicates. The processing with other select ingredients results in controlled particle size distribution (PSD). The computed blain value based on PSD is around 12000cm2/gm and is truly ultrafine. Due to its unique chemistry and ultrafine particle size, ALCCOFINE1203 provides reduced water demand for a given workability, even up to 70% replacement level as per requirement of concrete performance. ALCCOFINE 1203 can also be used as a high range water reducer to improve compressive strength or as a super workability aid to improve flow.
II. MATERIAL AND METHODOLOGY
A. Materials
- Meta-kaoline
Meta Cem grades of Calcined clays are reactive aluminous silicate pozzolanformed by calcining very pure hydrous China clay. Chemically Meta Cem combines with Calcium Hydroxide to form Calcium Silicate and Calcium Alluminate Hydrates. Unlike other natural pozzolan MetaCem is water processed to remove uncreative impurities producing an almost 100 percent reactive material. The particle size of MetaCem is significantly smaller than cement particles. IS 456:2000 recommends use of Meta-kaolin as Mineral admixture.

Table No 1: - Properties of Meta-kaolin
|
PROPERTIES |
UNITS |
METACEM 85 |
TEST METHOD |
|
Physical Form |
- |
Off white powder |
- |
|
Specific Gravity |
- |
2.5 |
ISO 787 / 10 |
|
Bulk Density |
gm/ltr |
300 ± 30 |
DIN 468 |
|
Average Particle Size |
µ |
1.5 |
Sedigraph |
|
Residue 325 # |
% |
0.5 max |
- |
|
Pozzolan Reactivity - mg Ca(OH)2 |
- |
>1000 |
Chappel Test |
- Benefits
MetaCem is a thermally structured, ultrafine Pozzolan which replace industrial by products such as Silica fume / Micro silica. Commercial use of Meta-kaolin has already begun in several countries worldwide. Blending with Portland Cement MetaCem improves the properties of Concrete and Cement products considerably by:
- Increasing Compressive & Flexural Strength
- Providing resistance to chemical attack
- Reducing permeability substantially
- Preventing Alkali-Silica Reaction
- Reducing efflorescence & Shrinkage
- Chemical Composition - WT
SiO2+ Al2O3 + Fe2O3 > 96 %
Loss on Ignition <1%
2. GGBS
Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag (GGBS): GGBS is obtained by quenching molten iron slag (a by-product of iron and steel making) from a blast furnace in water or steam, to produce a glassy, granular product that is then dried and ground into a fine powder. GGBS is used to make durable concrete structures in combination with ordinary port land cement and/or other pozzolanic materials. GGBS has been widely used in Europe, and increasingly in the United States and in Asia (particularly in Japan and Singapore) for its superiority in concrete durability, extending the lifespan of buildings from fifty years to a hundred years. Use of GGBS significantly reduces the risk of damages caused by alkali-silica reaction, higher resistance to chloride, and provides higher resistance to attacks by sulphate and other chemicals. GGBS is procured from visage steel plant (VSP).

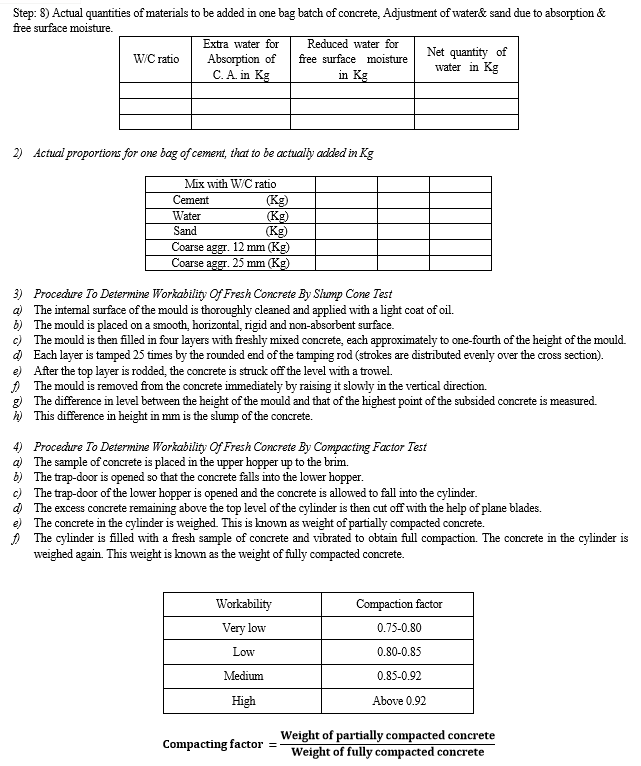


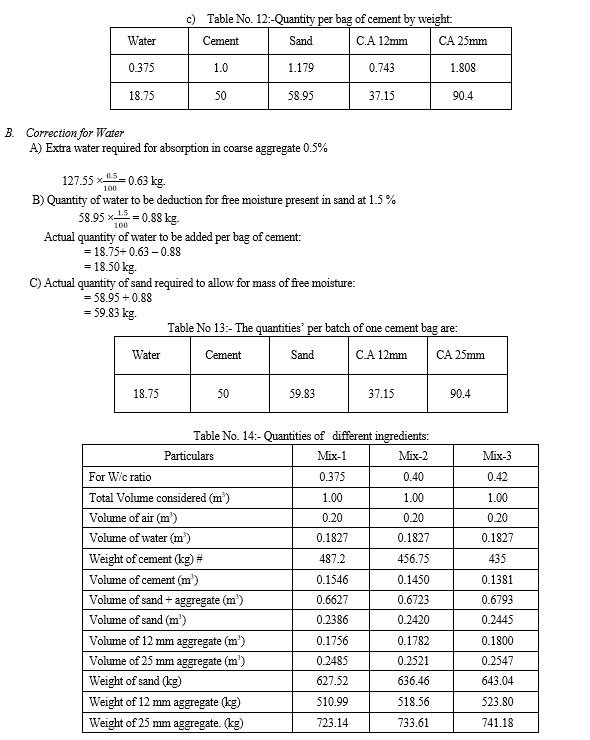
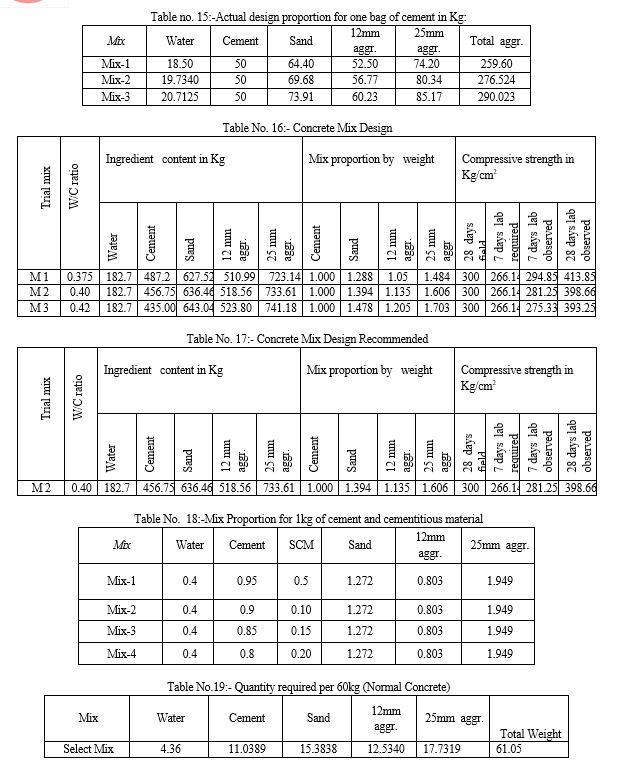
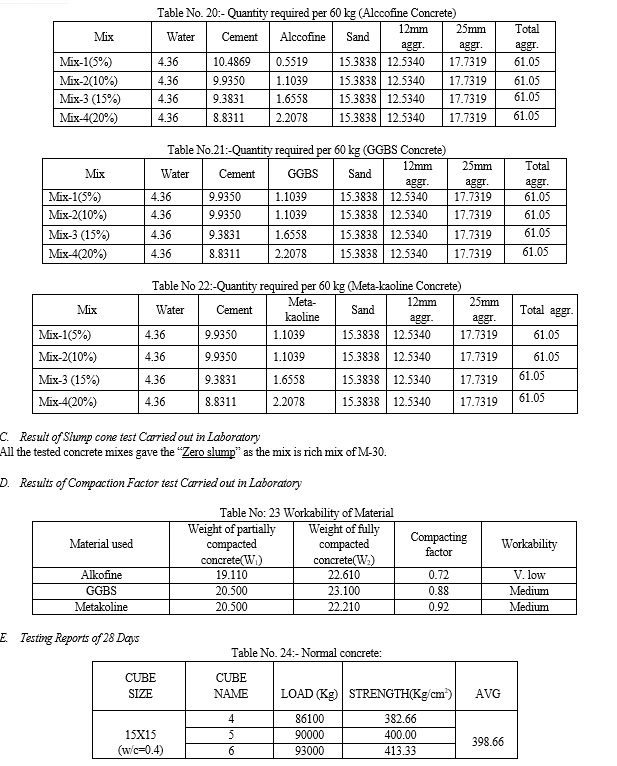
Conclusion
By conducting the study of 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% replacement of cement by different wastes and tested for workability and compressive strength we conclude that, 1) Using alccofine as a replacing material we get full design strength and workability for 5% and 10% of replacement. 2) Using GGBS as a replacing material we get full design strength and workability for 5%, 10% and 15% of replacement. 3) Using meta-kaoline as a replacing material we get full design strength and workability for 5%,10% and 15% of replacement. Thus we conclude that we can replace cement by: - Alccofine 10% - GGBS 15% - Meta-kaoline 10% Even for high strength mix such as M-30. A. Recommendation For Future Work Further research and investigation were highly recommended and should be carried out to understand more mechanical properties of prepared concrete. Some recommendation for future studies are mentioned below: 1) The effect of addition of fibre in our concrete mix can be checked by preparing the test samples with addition of different fibres. 2) More investigations and laboratory tests should be done to study on the mechanical properties of our concrete mix. Such application of prepared concrete was recommended in testing on concrete slabs, beam and walls or conducting more tests such as abrasion, shatter, shear, impact, blasting or creeping of concrete. 3) The addition of various different admixtures in variable % can be checked. 4) The addition of other supplementary cementitious material like Rice Husk ash, Sugar Cane ash, Fly ash and their combination in concrete mix can also be checked for compressive strength, Flexural strength and Split tensile strength.
References
[1] Alok Kumar et al(2016)- SSRG International Journal of Civil Engineering (SSRG-IJCE) – volume 3 Issue 5 – May 2016. http://www.internationaljournalssrg.org [2] Ansari U.S, Chaudhri I.M, Ghuge N.P, Phatangre R.R. “High Performance Concrete. with Partial Replacement of Cement by ALCCOFINE & Fly Ash” [3] M.S. Pawar- The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES) ||Volume||2 ||Issue|| 6 ||Pages|| 05-09||2013|| ISSN(e): 2319 – 1813 ISSN(p): 2319 – 1805 www.theijes.com The IJES Page 5 Effect of Alccofine on Self Com [4] Saurabh Gupta et al A Review on Alccofine : A supplementary cementitous material (IJMTER) Volume 02, Issue 08, [August– 2015] ISSN (Online):2349–9745 ; ISSN (Print):2393-8161 [5] Abhijitsinh Parmar, Dhaval M Patel “Experimental Study on High Performance Concrete by Using Alccofine and Fly Ash - Hard Concrete Properties”, International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT) Vol. 2 Issue 12, December – 2013 ISSN: 2278-0181 [6] Malvika Gautam, Dr. Hemant Sood Effect of Alccofine on strength characteristics of Concrete of different grades-A Review, International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) Volume: 04 Issue: 05 | May -2017 ISSN: 2395 -0056 [7] M.Narmatha, Dr.T.Felixkala IOSR “Meta kaolin –The Best Material for Replacement of Cement in Concrete”, Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) Volume 13, Issue 4 Ver. I (Jul. - Aug. 2016), e-ISSN: 2278-1684,p-ISSN: 2320-334X, PP 66-71 www.iosrjournals.org [8] Aiswarya, Prince Arulraj, Dilip “A REVIEW ON USE OF METAKAOLIN IN CONCRETE”, IRACST – Engineering Science and Technology: An International Journal (ESTIJ), ISSN: 2250-3498, Vol.3, No.3, June 2013 [9] Satyendra Dubey, Rajiv Chandak, R.K. Yadav “Effect of Metakaolin on Compressive Strength of Concrete”, Satyendra Dubey et al. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications,ISSN : 2248-9622, Vol. 5, Issue 6, ( Part -4) June 2015, pp.80-82 [10] CH Jyothi Nikhila and J D Chaitanya Kumar (2015) “Partial Replacement of Cement With Metakaolin in High Strength Concrete”, IJERST, ISSN 2319-5991 www.ijerst.com Vol. 4, No. 4, November 2015
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Nayyer Ansari, Deepak Kumar Bandewar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET46417
Publish Date : 2022-08-22
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

