Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Artificial Intelligence
Authors: Anant Manish Singh, Wasif Bilal Haju
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.44306
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (A.I.) is a multidisciplinary field aimed at automating tasks that currently need human intelligence. Despite its lack of general familiarity, artificial intelligence (AI) is a technology that is revolutionizing every aspect of life. This article aims to educate laypeople about AI and encourage them to utilize it as a tool in many disciplines to rethink how we combine data, analyze it, and make choices. We quickly covered what artificial intelligence (AI) is, how it works, and how it may be applied in our daily lives in this article.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Artificial intelligence (AI) is defined as the ability of an artificial entity to solve complicated problems using its own intelligence. Computer science and physiology are combined in Artificial Intelligence. In layman's terms, intelligence is the computational component of one's capacity to attain goals in the real world. Intelligence is defined as the capacity to think, envision, memorize, and comprehend, see patterns, make decisions, adapt to change, and learn from experience. Artificial intelligence is focused with making computers behave more human-like and in a fraction of the time it takes a person to do it. As a result, it is known as Artificial Intelligence. Artificial intelligence is also concerned with pushing the boundaries of practical computer science in the direction of systems that are adaptable, flexible, and capable of forming their own analyses and solution techniques by applying general knowledge to specific situations.
II. OVERVIEW OF AI
Machine or software intelligence is referred to as artificial intelligence. Perceive + Analyze + React = Intelligence. Artificial intelligence is a subject of computer science that is rapidly gaining popularity since it has improved human existence in a variety of ways. Artificial intelligence has substantially enhanced the performance of manufacturing and service systems during the previous two decades. Expert systems are a fast emerging technology that originated from artificial intelligence research. Intelligent machines will replace or augment human capabilities in many sectors in the future.
III. WORKING OF AI
AI is frequently misplaced on an island with robots and self-driving cars, according to popular belief. This method, however, overlooks one of artificial intelligence's most important practical applications: analyzing the massive volumes of data created every day. Insight gathering and job automation may be done at a previously inconceivable velocity and scale by carefully applying AI to particular activities. AI systems execute sophisticated searches through the mountains of data generated by people, deciphering both text and pictures to detect patterns in complicated data and then acting on their findings. Computer systems that can grasp the meaning of human language, learn from experience, and make predictions, thanks to cutting-edge technologies. Following are a few subfields of AI.
A. Machine Learning | Learning from experience
Machine learning, or ML, is an AI application that allows computers to automatically learn and grow from their experiences without having to be explicitly programmed. The goal of machine learning is to create algorithms that can analyze data and generate predictions. Machine learning is being utilized in the healthcare, pharma, and life sciences sectors to improve illness detection, medical picture interpretation, and medication acceleration, in addition to predicting what Netflix movies you would like.
B. Deep Learning | Self-educating machines
Artificial neural networks that learn by analyzing data are used in deep learning, which is a subset of machine learning. Artificial neural networks are designed to look like organic neural networks in the brain. Several layers of artificial neural networks collaborate to produce a single output from a large number of inputs, such as detecting a facial picture from a mosaic of tiles. The machines learn by receiving positive and negative reinforcement for the tasks they perform, which necessitates ongoing processing and reinforcement in order for them to advance.
C. Cognitive Computing | Making inferences from context
Cognitive computing is another essential component of AI. Its purpose is to imitate and improve interaction between humans and machines. Cognitive computing seeks to recreate the human thought process in a computer model, in this case, by understanding human language and the meaning of images. Together, cognitive computing and artificial intelligence strive to endow machines with human-like behaviors and information processing abilities. Another form of deep learning is speech recognition, which enables the voice assistant in phones to understand questions like, “Hey Siri, how does artificial intelligence work?”

D. Computer Vision | Understanding images
Computer vision is a method of interpreting image material, such as graphs, tables, and photographs within PDF documents, as well as other text and video, using deep learning and pattern recognition. Computer vision is a branch of artificial intelligence that allows computers to recognize, analyze, and interpret visual input. This technology's applications have already begun to transform areas such as research and development and healthcare. Computer Vision and machine learning are being used to analyze patients' x-ray images in order to diagnose patients faster.
IV. TYPES OF AI
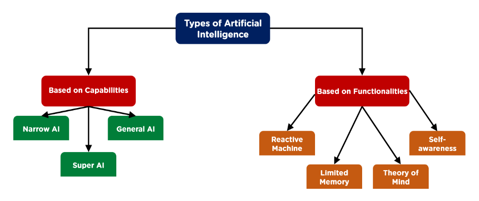
A. AI type-1: Based on Capabilities
- Narrow AI: Narrow AI is a sort of AI that is capable of doing a certain task intelligently. In the area of artificial intelligence, narrow AI is the most frequent and currently accessible AI. Because narrow AI is exclusively educated for one single activity, it cannot perform outside its field or boundaries. As a result, it's also known as "weak AI." When narrow AI reaches its boundaries, it might fail in unexpected ways. Apple Siri is an excellent example of Narrow AI, yet it only performs a restricted set of duties. Playing chess, purchasing suggestions on an e-commerce site, self-driving automobiles, speech recognition, and picture identification are all examples of narrow AI.
- General AI: General AI is a sort of intelligence that is capable of doing any intellectual work as well as a human. The goal of general AI is to create a system that can learn and reason like a person on its own. Currently, no system exists that can be classified as general AI and execute any work as well as a person. Researchers from all across the world are now concentrating their efforts on creating robots that can do general AI tasks. Because generic AI systems are still being researched, developing such systems will take a lot of work and time.
- Super AI: Super AI is a degree of system intelligence at which machines may outsmart humans and execute any task better than humans with cognitive qualities. It's a result of AI in general. Some fundamental properties of powerful AI are the capacity to understand, reason, solve puzzles, make judgements, plan, learn, and communicate independently. Super AI is still a futuristic Artificial Intelligence idea. The creation of such systems in the actual world is still a world changing effort.
B. AI type-2 Based on Functionality
- Reactive Machines: The most basic kinds of Artificial Intelligence are pure reactive robots. Such AI systems do not keep track of memories or previous experiences in order to make decisions in the future. These robots just consider current circumstances and respond in the best way feasible. Reactive machines, such as IBM's Deep Blue system, are one example. AlphaGo, developed by Google, is another example of reactive machines.
- Limited Memory: This sort of AI, like Reactive Machines, has memory capabilities, allowing it to leverage prior data and experience to make better judgments in the future. This category encompasses the majority of the commonly used apps in our daily lives. These AI applications may be taught using a huge amount of training data stored in a reference model in their memory. Example: Many self-driving automobiles have limited memory technology. They save data like as GPS position, neighboring automobile speeds, the size/nature of barriers, and a hundred other types of data in order to drive like a person.
- Limited Memory: While the first two categories of AI have been and continue to be abundant, the next two types of AI exist only as an idea or a work in progress for the time being. The next level of AI systems that researchers are actively working on is theory of mind AI. A theory of mind level AI will be able to identify the needs, emotions, beliefs, and mental processes of the creatures with whom it interacts. While artificial emotional intelligence is now a burgeoning business and a focus for prominent AI researchers, reaching the level of Theory of Mind AI would need advancements in other AI areas as well. Because AI computers will have to view humans as individuals whose brains may be changed by a variety of elements in order to genuinely grasp human needs, they will have to "understand" humans.
- Self-Awareness: This is the last step of AI development, which exists only in theory at the moment. Self-aware AI is an AI that has matured to the point where it is so similar to the human brain that it has gained self-awareness. The ultimate goal of all AI research is and will always be to create this form of AI, which is decades, if not centuries, away from becoming a reality. This form of AI will not only be able to recognize and generate emotions in individuals with whom it interacts, but will also have its own emotions, wants, beliefs, and maybe goals. And this is the kind of AI that sceptics of the technology are concerned about. Although the growth of self-awareness has the potential to accelerate our progress as a civilization, it also has the potential to lead to disaster. This is because, once self-aware, AI may have ideals like self-preservation, which could either directly or indirectly mark the end of mankind, since such an entity could easily outmaneuver any human brain and create sophisticated schemes to take over humanity. The categorization of technology into Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) is an alternative method of classification that is more commonly used in tech jargon (ASI).
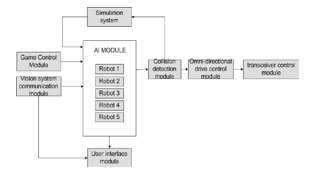
V. AI SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
A main thread runs through the artificial intelligence system, looping and calling each of the several modules. To determine the position and orientation of robots, the main system thread first connects with the visual system. Aside from the ball's location. The system then checks the referee's control of the game state. After that, the system invokes the AI module function, which provides the required robot movement position as well as extra actions to take. Following the specification of motions, the system calculates collision avoidance trajectories to prevent colliding with other robots. The algorithm then estimates the speed of each of the robots' four wheels. Finally, the system broadcasts communication packets corresponding to orders to take action via the transceiver.
The following is a full description of each of the modules depicted in the above diagram:
A. Vision System Communication Module
This module offers vision system commands for the game scenario, which correlate to robot and ball coordinates, as well as robot angles, through packets.
B. Game Control Module
Through a serial interface, this module takes referee orders and returns the game's current status.
C. AI Module
This module gets the locations of the robots and the ball, as well as the orientations of the robots, the game state, the roles of the robots, the firing direction, and the field setup. The system uses all of this data to calculate each robot's future position and actions. The chosen approach is determined by the configuration of a tree containing all feasible actions. The activities are categorized based on their significance. One or more evaluations are utilized for each node in the tree. Each evaluation has a set of possible outcomes linked to a certain score. The tree is assessed during the program's loop. The path to travel from root to leaf (final action) is determined by the highest score of each level's assessment result using the Best First Search technique. The robot movement vector, its linear and rotational velocity, and the employment of the kicker and dribbler devices are determined after the system has achieved a final action such as passing, shooting, or blocking. The robots also include a roll motion to help them coordinate joint operations. Different roles are used to coordinate the robots: goalkeeper, defense, first, second, and third forward. The goalie's job is to keep the ball out of the net. When the ball is far away, it takes a block path; when the ball is close, it kicks it. The region around the goal is the only place where you may move. The defense is responsible for assisting the goalkeeper in defending the goal from long-range shots, as well as developing collaborative plans with the three strikers. When near to their own area, defenders clear the ball out and follow opposite robots to prevent a pass and goal. The three forwards have a shared goal, but their priorities differ. They travel over the entire field, coordinating various forms of passing and shooting. When necessary, they may migrate in groups.
D. User Interface Module
Positions, orientations, motor speeds, intended positions, ids, actions, game status, and referee instructions are all shown in real time for each robot in this module. Robot positions, orientations, desired locations, and actions are visually shown in an OpenGL-based GUI.
E. Simulation System
This module simulates the functioning of an artificial intelligence system without requiring the use of a real vision system or robotics. The artificial intelligence module may be used to debug and test activities. The construction of things that think using decision logic is referred to as intelligent object-based simulation. Simio, for example, selects jobs or resources using intelligent objects packed with decision logic. As a result, the item has intelligent behaviour that can predict future performances. The usage of intelligent objects in the context of AI in simulation emphasizes the integration of rule-based AI into simulation models. Manually developing complicated rule-based reasoning is a time-consuming operation, and the rule's performance is also determined by the creator's expertise level. AI, with a focus on the use of neural networks, eliminates the need for manual construction. Manually developing complicated rule-based reasoning is a time-consuming operation, and the rule's performance is also determined by the creator's expertise level.
F. Collision Detection Module
This module simulates the functioning of an artificial intelligence system without requiring the use of a real vision system or robotics. The artificial intelligence module may be used to debug and test activities. An infrared obstacle avoidance sensor with customizable detection distance is created for wheeled robot obstacle avoidance. One infrared transmitter and one detector make up the module. When an obstacle is in front of the sensor, the emitter's infrared light is reflected back to the receiver. A comparator squares the signal to generate a digital signal. The production is high when there are no obstacles. The output is low when an obstruction is within range. A potentiometer knob can be used to change the sensitivity.
G. Transceiver Communication Module
This module gets the speed of each robot motor as well as the activities to be performed. This module creates the packets that our transceiver sends out. It also ensures that communication is always active.
H. Omni-Directional Drive Control Module
This module takes the movement vector, which includes linear and angular velocities, and calculates the speed of each of the four robot motors. This module calculates the speed of each motor for the robot's four omnidirectional wheels in order to travel in the correct direction.
VI. APPLICATIONS OF AI
There are many ways in which the average technology consumer interacts with artificial intelligence technologies in their daily lives, but most people don’t realize what technologies actually use AI. Here are a few examples of artificial intelligence technologies that many people encounter in their lives.
A. Chat bots
If you’ve ever come across a chat bot on a website or social media messenger, it is powered by AI. Chat bots are one of the more simple examples of AI, since they are simply coded to send messages based on rules about how they should interact with users. Sort of an “if this, then that” type of programming.
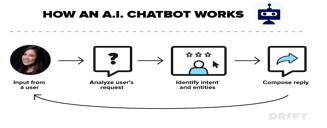
B. Smart Assistants
Siri, Alexa, and all the other smart assistants are examples of artificial intelligence. They understand what users say to them and can follow directions and respond accordingly. These are like the next level of chat bots, since they use speech recognition and are connected to larger databases of information such as search engines.

???????C. Disease Mapping and Prediction
Epidemiologists have always worked to try to understand how diseases spread in order to be able to predict and hopefully avoid them. Artificial intelligence is making this easier. This is an example where it’s easy to see how artificial intelligence simply allows for quicker progress on data analysis and prediction modelling than humans could do alone.
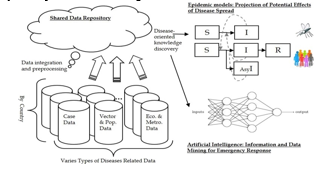
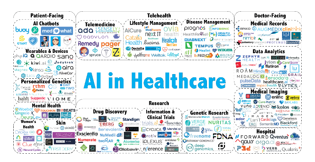
???????D. Healthcare
Because of its crucial role in a productive, healthy society, healthcare is one of the most important areas in the larger landscape of big data. The use of AI in healthcare data can actually mean the difference between life and death. Doctors, nurses, and other healthcare personnel can benefit from artificial intelligence in their regular job. AI in healthcare may improve patient outcomes through improving preventative care and quality of life, as well as producing more accurate diagnosis and treatment regimens. By analyzing data from the government, healthcare, and other sources, AI can help anticipate and track the spread of contagious illnesses. As a result, AI has the potential to be a critical instrument in the fight against diseases and pandemics in global public health.
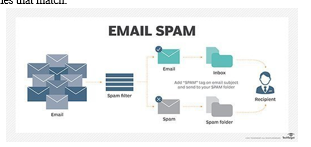
???????E. Spam Filters
Everyone who uses email knows about spam filters. Email inboxes are equipped with filters that send spam emails to a separate folder so they don’t clutter users’ inbox with useless messages. Spam filters also exist for phone calls, to filter out scammers and other spam phone calls. AI powers these spam filters by using previous knowledge of what spam emails or phone calls look like from a data perspective, and filtering out the ones that match.
???????F. Recommendation Engines
The recommendation engines on Netflix and Spotify are some of the most well-known. They use data about which shows you’ve previously watched or songs you’ve previously listened to in order to recommend other shows you should watch or songs you should listen to. These are only a couple examples. Recommendation engines also exist in social media platforms to recommend people you should connect to or to show you content you might like.
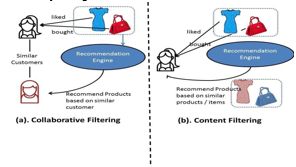
???????G. Search Engines
Search engines have such huge databases that the only way they are able to sort through all of their potential results to show you the best results for your search is with AI. Search engine algorithms are some of the best examples of robust algorithms out there. For example, Google is said to use something like 200 data points to determine where each result ranks on each results page. With billions of pages in their database, that is a lot of data running through their algorithm with every query.

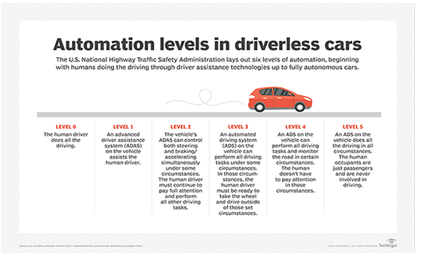
???????H. Self-driving cars
Although fully self-driving cars aren’t widely available yet, they are well in the works with multiple companies, and some self-driving features are already available in cars today. Companies like Google and Uber are vying to be the first to develop a consumer-ready self-driving car, but you can already buy cars with sensors that alert you to close objects, break automatically, and can parallel park themselves. Just like how AI can detect cancer better than the human eye, self-driving cars can probably drive better than a lot of humans too.
VII. ADVANTAGES OF AI
A. Reduction in Human Error
Because people make mistakes from time to time, the term "human error" was coined. Computers, on the other hand, do not make these errors if they are correctly programmed. Artificial intelligence makes choices based on previously obtained data and a set of algorithms. As a result, mistakes are decreased, and the prospect of achieving better precision and accuracy is increased.
- For Example: AI has removed the bulk of human mistake in weather forecasting.
B. Takes risks instead of Humans
One of the most significant advantages of artificial intelligence is this. By constructing an AI Robot that can do the dangerous tasks for us, we can transcend many of humanity's risky limits. It can be utilized efficiently in every type of natural or man-made disaster, whether it is travelling to Mars, defusing a bomb, exploring the deepest regions of the oceans, mining for coal and oil.
- For Example: Have you heard about the explosion at the Chernobyl nuclear power facility in Ukraine? There were no AI-powered robots available at the time to assist us in minimizing the effects of radiation by controlling the fire early on, since any human who came near to the core died in minutes. They ultimately used helicopters to drop sand and boron from a safe distance. AI Robots can be utilized in circumstances when human interaction is risky.

C. Available 24x7
Without breaks, an average human will labor for 4–6 hours every day. Humans are created in such a manner that they can take time off to replenish themselves and prepare for a new day at work, and they even have weekly off days to keep their professional and home lives separate. But, unlike humans, we can use AI to make robots work 24 hours a day, seven days a week with no breaks, and they don't grow bored.
- For Example: Educational institutions and helpline centres get a large number of requests and difficulties that AI can successfully address.

D. Digital Assistance
Digital assistants are used by some of the most modern enterprises to engage with people, reducing the requirement for human personnel. Many websites now utilize digital assistants to supply items that consumers seek. We can discuss what we're searching for with them. Some chatbots are created in such a manner that it's difficult to tell whether we're conversing with a machine or a person.
- For Example: We all know that businesses have a customer service staff that is responsible for answering customers' questions and concerns. Organizations may use AI to create a voice bot or a chatbot that can assist consumers with all of their questions. Many firms have already begun to use them on their websites and mobile applications.
VIII. DISADVANTAGES OF AI
A. High Cost of Implementation
Setting up AI-based machines, computers, etc. entails huge costs given the complexity of engineering that goes into building one. Further, the astronomical expense doesn’t stop there as repair and maintenance also run into thousands of dollars.
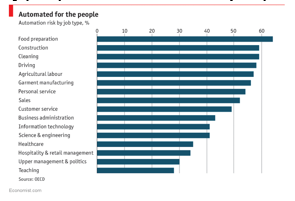
D. Risk Of Unemployment
With rapid development being made in the field of AI, the question that plagues our intuitive brain is that – will AI replace humans? Honestly, I am not sure whether AIs will lead to higher unemployment or not. But AIs are likely to take over the majority of the repetitive tasks, which are largely binary in nature and involve minimum subjectivity
 ???????
???????
Conclusion
While concluding, it can be analyzed that AI has benefited computer science because it is the artificial psychology that made the machines to focus on the philosophical arguments. AI performs tasks faster than human beings and the major goal of artificial intelligence is to create the technology in an intelligent manner. It is proved that artificial intelligence is the computer knowledge that has human traits, however, these computers and robots help the environment to grow, and they respond rationally to help human beings. AI has already impacted lives of people in various fields and will surely continue to do more in the future.
References
[1] https://idhjournal.com/article/S2468-0451(18)30144-5/fulltext [2] https://towardsdatascience.com/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-artificial-intelligence-182a5ef6588c [3] https://www.forbes.com/sites/cognitiveworld/2019/06/19/7-types-of-artificial-intelligence/?sh=453e91f0233e [4] https://www.indiatoday.in/education-today/news/story/robots-teachers-bengaluru-school-artificial-intelligence-ai-divd-1594366-2019-09-02 [5] https://www.exametc.com/magazine/details.php?id=521
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Anant Manish Singh, Wasif Bilal Haju. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET44306
Publish Date : 2022-06-15
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online