Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Parametric Studies for Concrete Sheet Pile Wall Using GE05FINE
Authors: Amit Kumar, Dr. Umesh Pendharkar
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.48822
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Based on the site conditions and lateral earth pressure of soil plays important role in the selection of sheet pile wall. In the present day different types of sheet pile wall present in the market like as steel sheet pile wall , concrete sheet pile wall and timber etc. Concrete sheet pile walls are common in use. Modification in the properties of the concrete sheet piles is easier making it more economical as the utility of the section can be considerably increased according to projects requirement. Sheet pile wall deformation is dependent on the materials properties. Consequently, it is essential to research how different material types and properties affect the deformation and stress distribution of cantilever concrete sheet pile walls. A parametric analysis was carried out numerically using a case study that makes use of a base model to determine how long a sheet pile wall should be at the bottom of an embankment with various material types for ditch with a depth of 3m, 5m and 7m.to safeguard and improve the stability of the embankment , a sheet pile wall was temporarily constructed near the toe of the embankment. Analysing simulation data was completed with the aid of GE05FINE. The analysis findings revealed that when subjected to the same loading situation, bending moment and shear force varies with the material properties. Therefore, it is wise to carefully select the sheet pile wall materials in accordance with the projects requirements.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Sheet pile walls, a type of retaining walls, are built to hold back - soil, water or other fill materials. As compared to masonry walls they are narrower in section. The following are typical applications for sheet piles walls:
- Buildings on the water edge, such as wharves, quays, and piers,
- Constructing cofferdams or other diversion dams,
- River bank defense,
- Maintaining the edges of earthen cuttings.
Steel and reinforced concrete can be used for sheet pile walls. The popularity of steel sheet pile structure in cities is due to their advantage over reinforced concrete pile wall. In the present time steel sheet pile wall available in different shape according to strength with easy in driving into the soil.
Steel sheet pile wall gives approximate same value in compressive and tension loading condition. Steel sheet pile wall durable as compare to reinforced concrete wall.
In this study examine the effect of material types on the bending moment and shear force distribution with depth of cantilever sheet pile wall. To clear the selection of pile in design process for economical and sustainable in nature. In this research study involves conditions of soil at sites , total stress and soil behavior for selection of material types of sheet piles can be proposed and accepted.
The sheet pile walls are preferred over retaining wall due to following reasons.
a. Available a wide range of lengths, size and steel options.
b. Can be used for temporary and permanent structures.
c. Can be installed using silent and vibration-free methods.
d. Quicker installation than masonary wall.
e. Cofferdams can be constructed in almost any desired shape
f. Provide a close-fittings joint to form an effective water seal.
g. Light in weight , making lifting and handling easy
h. A little maintenance is needed.
The objective of this work is to study the effect of different parametrs of a concrete sheet pile wall on its behaviour. The analysis is being carried out using software GE05FINE. The study is being carried out to see:-
- Effect of soil layers on behaviuor of concrete shet piles.
- Effect of properties and earth pressure on the sheet pile wall with varing depth of ditch.
- Effect of grade of concrete & steel on behavior of concrete sheet pile wall.
- To understand the behavior of steel sheet pile wall and reinforced sheet pile wall.
II. SHEET PILE WALL
Here we defined used member of reinforced concrete wall component.
- Reinforced concrete pile wall
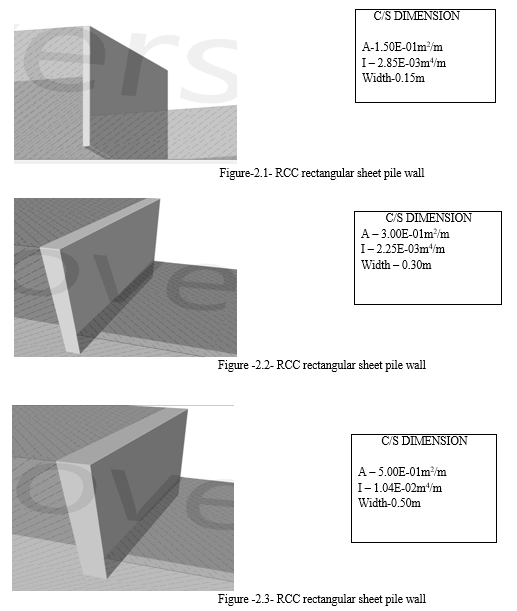
III. MODELLING AND ANALYSIS
The concrete sheet pile walls are being modeled, analysed using software GE05FINE. The code for steel and concrete member is consider in design procedure. The calculation of bending moment and shear force on different model is mentioned here.
- Model 1: RCC rectangular wall for 3m depth of ditch in 1 layer soil
- Model 2: RCC rectangular wall for 5m depth of ditch in 1 layer soil
- Model 3: RCC rectangular wall for 7m depth of ditch in 1 layer soil
- Model 4: RCC rectangular wall for 3m depth of ditch in 2 layer soil
- Model 5: RCC rectangular wall for 5m depth of ditch in 2 layer soil
- Model 6: RCC rectangular wall for 7m depth of ditch in 2 layer soil
A. Optimization
The process of finding the best economic structural outcomes with maximum benefit at minimum material or cost is called optimization. Due to recent advances in structural design, it is very easy to obtain a safe design, but difficult to find an economical design, so optimization techniques are needed to obtain most economically efficient design. This is beneficial in many ways such as saving materials, reducing concrete usage. Therefore, optimization has gained momentum in structural engineering. In this work, optimized reinforced concrete rectangular sheet pile wall are considered as bench mark for studying the effect of different parameters on behavior of sheet pile walls.
B. Step of Section Optimization
- First define depth of required ditch both for concrete rectangular sheet pile wall
- Start assigning width of RCC rectangular wall as per needed.
- After analyses check for design if design check meets the demand capacity ratio, then section is safe for structure.
- If not then increase the section and repeat the process till design check satisfy the demand capacity ratio
- After satisfy the demand capacity ratio for section, then shear and bending moment values are obtained.
- According to shear force and bending moment variation in RCC sheet pile, the section come out by this iterative process is now optimized section for structure.
C. Material properties
In analyzing RCC concrete sheet pile walls, three models have been considered with soil to be retained is of only one type. The models have been named as models with 1- layer of soil. Similarly three models have been considered with two layers of soil to be retained and the models have been named as models with 2- layer of soil. The properties of the soil considered in the modeling are given in the following table
Table 3.1: Soil properties used in GE05FINE software
|
Soil type
Unit weight
Stress state
Angle of internal friction
Cohesion of soil
Angle of friction-struc. |
Silt
21 KN/m3
Effective
300
75 kPa
200 |
Clay
18 KN/m3
Effective
270
100kPa
180
|
The grade of concrete and steel being considered in the for modeling RCC concrete sheet pile walls are M20, M25 and Fe500 respectively.
D. Optimized RCC Concrete sheet pile wall section and Moment and pressure distribution
For the six models of concrete sheet pile wall the optimize sections obtained are given in the table Table 3.2.
Table 3.2: Optimsed width for RCC Sheet pile walls.
|
MEMBER |
WIDTH |
GRADE OF STEEL |
GRADE OF CONCRETE |
DEPTH |
SOIL LAYER |
|
|
RCC RECT. |
0.15M |
B500 |
M20 |
3M |
1 LAYER |
|
|
RCC RECT. |
0.30M |
B500 |
M20 |
5M |
1 LAYER |
|
|
RCC RECT. |
0.50M |
B550 |
M25 |
7M |
1 LAYER |
|
|
RCC RECT. |
0.15M |
B500 |
M20 |
3M |
2 LAYER |
|
|
RCC RECT. |
0.30M |
B500 |
M20 |
5M |
2 LAYER |
|
|
RCC RECT. |
0.50M |
B550 |
M25 |
7M |
2 LAYER |
|
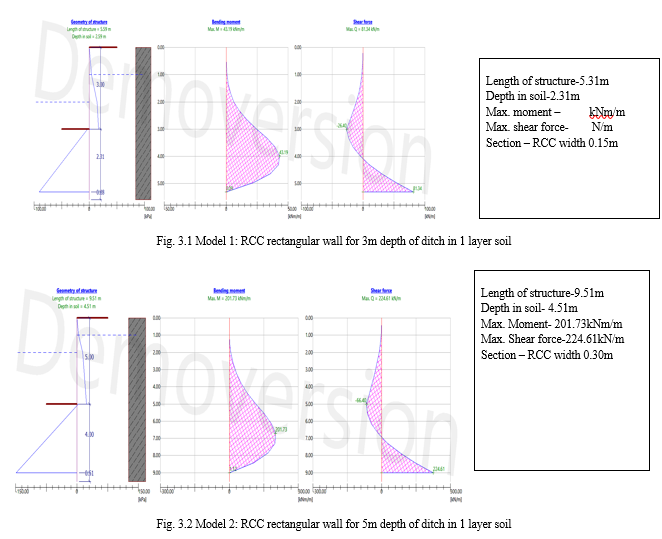
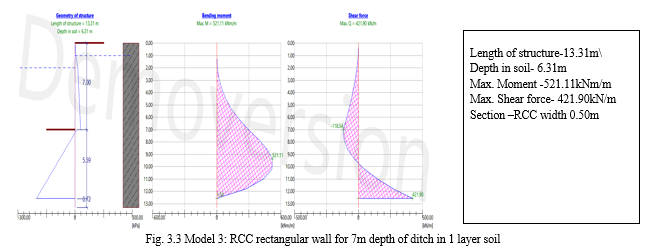
IV. RESULT
The Analysis is conducted on three different section using GE05FINE software , several values of model were found out from RCC rectangular wall. The all recommended code is used for the analysis for the all model. After analysing, optimized section is selected for design.
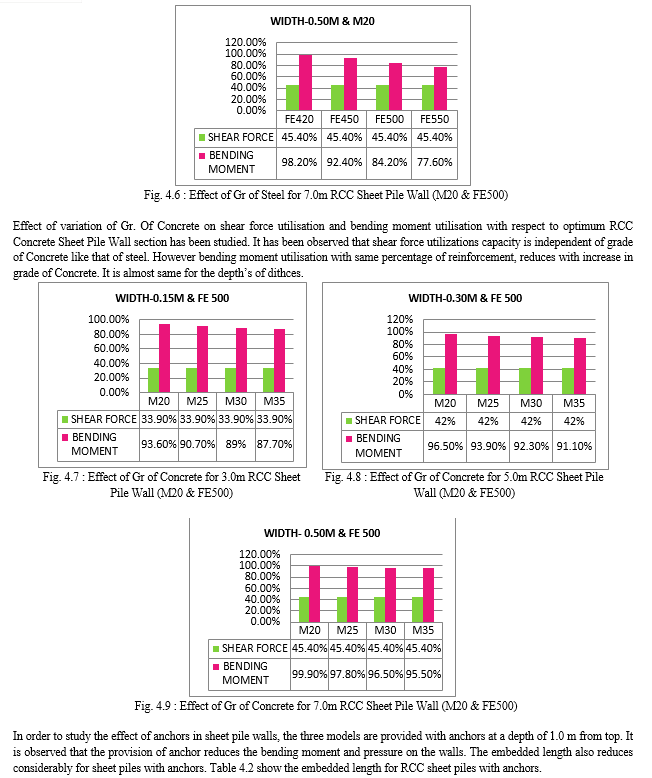
Therefore, total 6 model are used for analysing the response of soil behavior , effective stress and active earth pressure of soil. The impact of grade of steel, grade of concrete, thickness of RCC member, layer of soil and anchor are mentioned here.
Utility results of member are in form of shear force and bending moment
Table 4.1 shows the sheer force and bending moment utilization of the optimum sections for three different depth of ditches and for two types of backfill considered. From the table it is very clear that embedded length does not depends on the no of layers of the different soils to be retained. With every 2 m increase in depth of ditch; embedded length increases by almost same amount. Shear force utlisation for all the depths of sheet pile walls considered is almost same at optimum section. Bending moment marginally varies with no of layers of soil for optimised section.
Table 4.1: Optimsed width for RCC Sheet pile walls.
|
Total Length |
Depth of Ditch |
Embedded Length |
Shear Force Utilsation |
Bending Moment Utilisation |
||
|
1 - Layer |
2- Layer |
1 - Layer |
2- Layer |
|||
|
5.31 m |
3.0 m |
2.31 m |
33.90 kN |
33.90 kN |
80.50 kN-m |
80.50 kN-m |
|
9.31 m |
5.0 m |
4.31 m |
42.42 kN |
42.90 kN |
96.50 kN-m |
86.40 kN-m |
|
13.31 m |
7.0 m |
6.31 m |
45.90 kN |
45.90 kN |
95.50 kN-m |
99.10 kN-m |
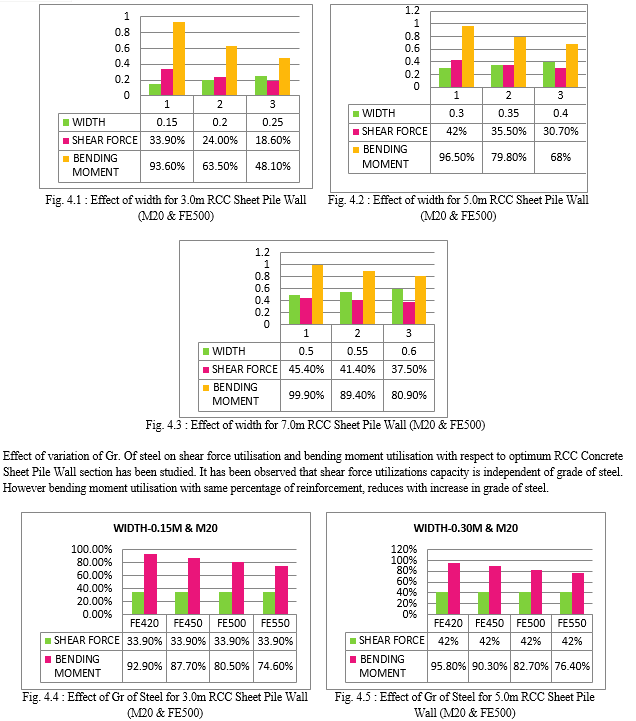
The effect of variation of width of the pile for the three depths’ has been studied. Figure 4.1 to 4.3 shows the variation of shear force utilisation and variation of bending moment utilsation of sheet pills for different ditch depths’. For smaller ditch depths, variation with width signifcantly affect the shear force and bending moment utilisation.
Conclusion
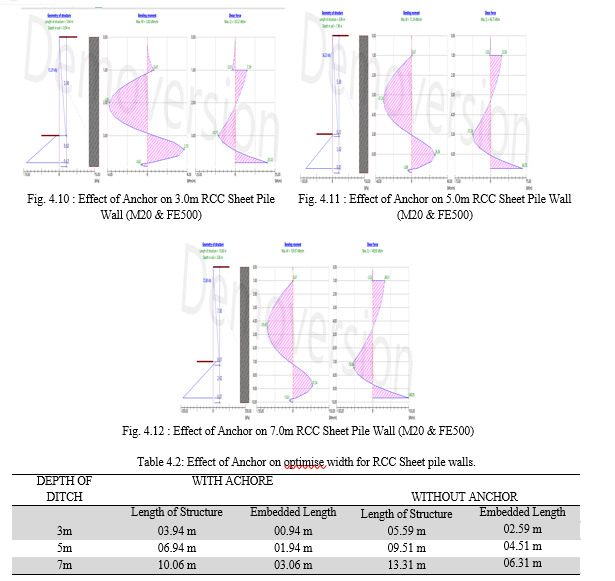
In the study concrete sheet pile walls of three different ditch depths have been considered. The concrete sheet piles have been subjected to two types of embankment system. In first only one type of soil mass has been considered where as in other the soil mass considered consist of two layers of different soil mass. Properties pertaining to optimsed sections of the concrete sheet pile wall have been considered as datum for the study. On the basis of study following conclusion have been drawn. 1) Embedded length does not depends on the no of layers of the different soils to be retained. 2) Embedded length increase with depth of ditch by almost same amount as depth of the ditch over 3.0m height. 3) Shear force utlisation for all the depths of sheet pile walls considered is almost same at optimum section. 4) Bending moment utilistion marginally varies with no of layers of soil for optimised section. 5) For smaller ditch depths, variation in width significantly affects the shear force and bending moment utilisation. 6) Shear force utilizations capacity is independent of grade of steel. However bending moment utilisation with same percentage of reinforcement, reduces with increase in grade of steel. 7) Shear force utilizations capacity is independent of grade of Concrete like that of steel. However bending moment utilisation with same percentage of reinforcement, reduces with increase in grade of Concrete. 8) The embedded length reduces considerably for sheet piles with anchors. Furthers studies could be carried to investigate the effect of anchor on embedded length of the piles.. The location of anchors, inclination of anchors could be studied to have a deep knowledge about effect of anchors on behavior of concrete sheet pile walls.
References
[1] Roslan A, Ling, Felix N.L. ,“Comparative study of the steel sheet pile wall with concrete and polymer sheet pile wall, “Civil Engineering and Built Environment vol. 3No. 1(2022) 1656-1664. [2] L. Eskandari and B. Kalantari, “Basic types of sheet pile walls and their application in the construction industry-a review,’’ Electron. J. Geotech. Eng., vol. 16 L, no. August, pp. 1533-1541,2011. [3] Shinji TAENAKA,Kazuhide TODA, Kazutaka OTSUSHI, Ryuta TANAKA,Atsushi KATO,Noriyoshi HARATA,Hiroaki NAKAYAMA, “Development of new steel sheet pile foundation method,’’Nippon steel & Sumitomo metal technical report no.113 december 2016. [4] N. Fadilah, C. Y. Ong, and K. K. Choong, “Precast concrete sheet pile for the stabilization of road embankment on soft ground adjacent to river,” Appl. Mech. Mater., vol. 567, pp. 451– 456, 2014, doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.567.451. [5] Omer Bilgion and M.Bahadir Erten, “Analysis and anchored sheet pile wall deformations,”International foundation congress and equipment expo 2009,doi: 10.1061/41023(337)18. [6] D. Sobala and J. Rybak, “Steel Sheet Piles - Applications and Elementary Design Issues,” IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., vol. 245, no. 2, 2017, doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/245/2/022072. [7] J. Wang, W. Liu, R. Liang, and H. Gangarao, “reinforced polymer sheet piles Analytical and experimental study on flexural behavior of pultruded fibre reinforced polymer sheet piles,” no. December, 2015, doi: 10.1177/0021998315621369. [8] N. Atalla, H. Æ. Abdallah, I. H. Malkawi, and M. M. A. Yamin, “Stability analysis of slopes using the finite element method and limiting equilibrium approach Stability analysis of slopes using the finite element method and limiting equilibrium approach,” no. November, 2008, doi: 10.1007/s10064-008-0156-z. [9] F. N. L. Ling, “Simulation analysis of slope stability: A case study on slope failure at new laboratory of faculty of mechanical engineering utm” Master dissertation, Dept. Civ. Eng., Teknologi Mara Univ., Malaysia, 2003. [10] R. C. Mamat, A. Kasa, and S. F. M. Razali, “Performance prediction of road embankment on soft soil stabilized with prefabricated vertical drains using numerical method,” Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng., vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 1601–1608, 2019, doi: 10.30534/ijatcse/2019/85842019. [11] Abhijith Kamath,Wolfgang Gard,Jan-Wallem Van de Kuilen, “Biodynamic timber sheet pile walls:vegetation retaining structure,”sep 2020,https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-020-01598-7. [12] Xuzheng Chai, Arpad Rozas , Arthure Slobbe , Ana Teixeira, “Probabilistic parameter estimation and reliability assessment of a simulated sheet pile wall system,’’volume 142, February 2022,104567, https://doi.org/10.1016?j.compgeo.2021.104567 [13] Wenhu Zhao,Chengbin Du,Liguo Sun,Xiaocui Chen, “field measurements and numerical studies of the behavior of anchored sheet pile walls cinstructed with excavating and backfilling procedures” volume 259,4 september 2019,105165.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105165.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Amit Kumar, Dr. Umesh Pendharkar. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET48822
Publish Date : 2023-01-24
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

