Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Pipe Inspection Robot
Authors: Firoz Patel, Aaftab Pathan, Ayaz Ranasariya, Asad Shailkh, Harshal Ahire
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.41365
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
The engineer is constantly conformed with the challenges of bringing ideas and design into reality. New machines and techniques are being developed continuously to manufacture various products at cheaper rates and high quality. The pipe inspection robot with active pipe-diameter adaptability and automatic tractive force adjusting is developed for long-distance inspection of main gas pipelines with different diameter series. Its physical design employs the scheme that three sets of parallelogram wheeled leg mechanism are circumferentially spaced out 120° apart symmetrically. This structural design makes it possible to realize the adaptation to pipe diameter and tractive force adjusting together. On the basis of analyzing the mechanical actions of the adaptation to pipe diameter and tractive force adjusting, the related mechanical models are established, and their control system structure and control strategy are discussed. To verify the pipe-diameter adaptability and tractive force adjusting of the robot, related field experiments are implemented in actual underground gas pipeline. The experimental results show that the theoretical analysis in this paper is valid and the prototype of this robot can work well in actual underground gas pipelines. Compared with other similar robots, this robot, which employs active mode for its adaptability to pipe diameter, can be adaptable to the wide range of gas pipeline diameters from ?300 mm to ?500 mm and automatically provide a stable and reliable tractive force with strong capacity of tractive force adjusting. As a mobile carrier for visual inspection wireless camera is mounted to see corrosion, crack, defect, and holes of main gas pipelines, spring is also mounted in middle for making it flexible to take turn.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
There are a wide variety of pipelines such as urban gas, sewage, chemical plant, nuclear power plant etc., which are indispensable in our life. Also, pipelines are the major tools for transportation of oils and gases and a number of countries employ pipelines as the main facilities for transportation. In our country, the urban gas pipelines currently go up to 13,000 Km long but since most of them have been constructed in 1980's, there happen a lot of troubles caused by aging, corrosion, cracks, and mechanical damages from third parties. Continuous activities for inspection, maintenance and repair should be performed from now on. However, those activities need enormous budgets that may not be easily handled by gas companies as they are mostly small and medium in size. Efficient equipment’s for inspection and integrated maintenance program are required in gas industries an in-pipe inspection robot for the inspection of pipe with pipe diameter adaptability is introduced here. There were various models developed for the pipe inspection; however, this robot excludes various dis-advantages associated with them.
A. Aim of Project
In-pipe inspection robot with automatic adaptability to various pipe diameters and to monitor the defect, cracks, corrosion, block etc.
- Why this topic is chosen?
Often, robots are used to do jobs that could be done by humans. However, there are many reasons why robots may be better than humans in performing certain tasks.
a. Speed: Robots may be used because they are FASTER than people at carrying out tasks. This is because a robot is really a mechanism which is controlled by a computer - and we know that computers can do calculations and process data very quickly. Some robots actually MOVE more quickly than we can, so they can carry out a task, such as picking up and inserting items, more quickly than a human can.
b. Accuracy: Accuracy is all about carrying out tasks very precisely. In a factory manufacturing items, each item has to be made identically. When items are being assembled, a robot can position parts within fractions of a millimeter.
c. Hazardous (dangerous) Environments: Robots may be used because they can work in places where a human would be in danger. For example, robots can be designed to withstand greater amounts ofHeat, Radiation, Chemical fumesthan humans could.
d. Repetitive Tasks: Sometimes robots are not really much faster than humans, but they are good at simply doing the same job over and over again. This is easy for a robot, because once the robot has been programmed to do a job once; the same program can be run many times to carry out the job many times. And the robot will not get bored as a human would.
e. Efficiency: Efficiency is all about carrying out tasks without waste. This could mean not wasting timenot wasting materials.
B. Problem Definition.
The inspection of pipes may be relevant for improving security and efficiency in industrial plants. These specific operations as inspection, maintenance, cleaning etc. are expensive, thus the application of the robots appears to be one of the most attractive solutions. The pipelines are the major tools for the transportation of drinkable water, effluent water, fuel oils and gas. A lot of troubles caused by piping networks aging, corrosion, cracks, and mechanical damages are possible. So, continuous activities for inspection, maintenance and repair are strongly demanded. The robots with a flexible (adaptable) structure may boast adaptability to the environment, especially to the pipe diameter, with enhanced dexterity, maneuverability, capability to operate under hostile conditions.
Pipe inspection robots have been studied for a long time, and many original locomotion concepts have been proposed to solve the numerous technical difficulties associated with the change in pipe diameter, curves and energy supply. Although an exhaustive review of the literature is impossible due to the limited space available, a few broad categories can be identified:
(i) For small size, many projects follow the earthworm principle consisting of a central part moving axially while the two end parts are provided with blocking devices connected temporarily to the pipe. Pneumatic versions of this concept have been proposed but they require an umbilical for power. For smaller diameter (10 mm or less), a piezoelectric actuation has been considered, according to the inchworm principle, or according to an inertial locomotion driven by a saw-tooth wave voltage, or using vibrating fins with differential friction coefficients.
(ii)For medium size piping, classical electromechanical systems have been proposed with various architectures involving wheels and tracks, with more or less complicated kinematical structures, depending on the diameter adaptability and turning capability
(iii)For large pipes, walking tube crawlers have also been proposed.
C. Scope of the Project
The main scope of our FINAL YEAR MECHANICAL project is to locate defects due to corrosion and obstacle at the inner side of the pipe line. Nevertheless, damage still occurs, which reduces the strength of the pipe. If it goes undetected and becomes severe, the pipe can leak and, in rare cases, fail catastrophically. So, extensive efforts are made to mitigate defects. So we proposed a new design in inspecting pipelines.
II. METHODOLOGY
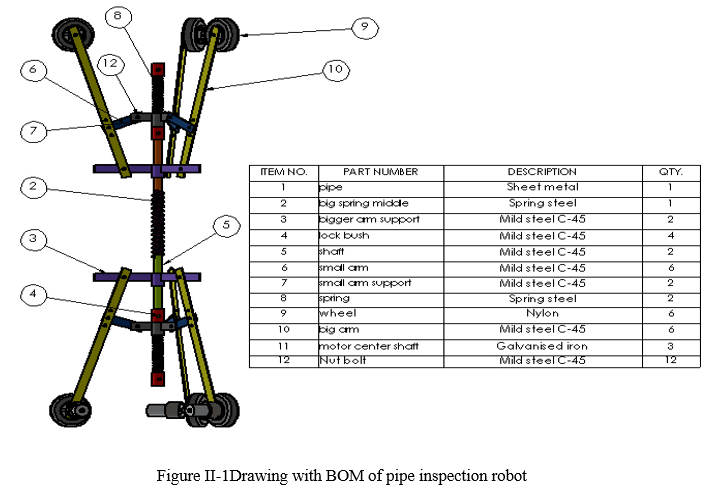
A. Main Component and it Working in Project
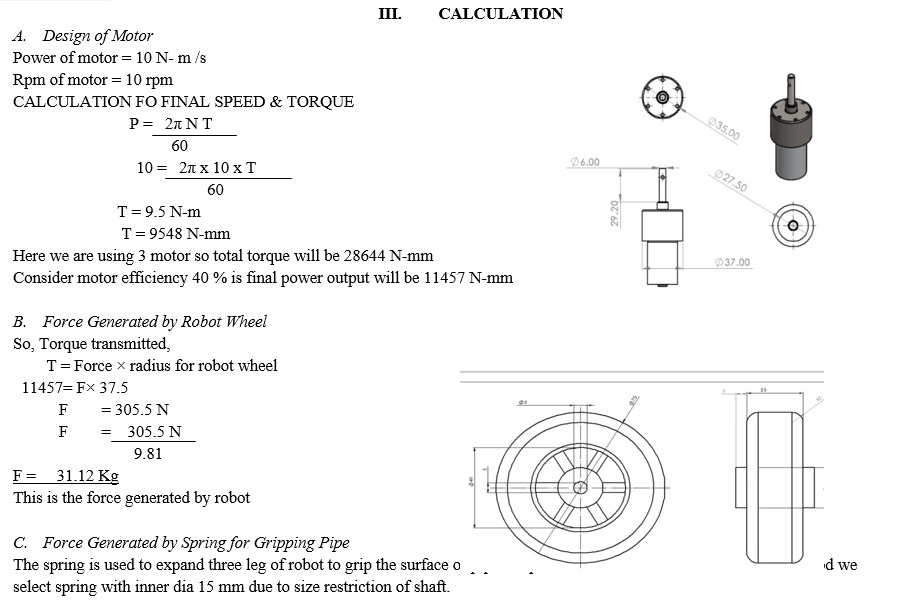
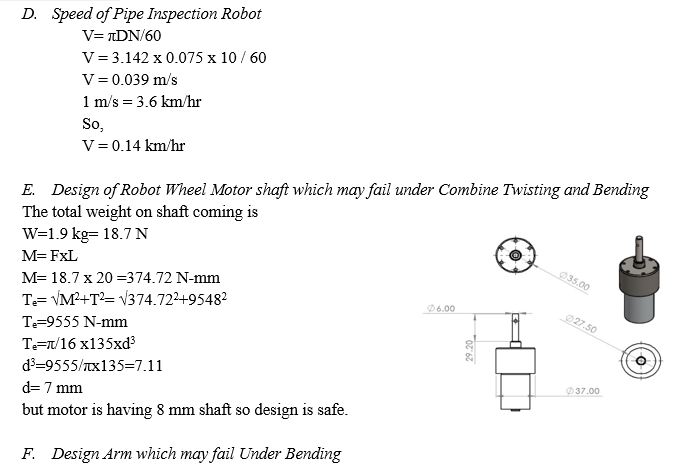
- Dc Motor: The project is powered by using three permanent magnets direct current motor, The DC motor which we are using in our project consumes 12v and 10-watt powerand in output it gives us 10 RPM. The gear box is attached with DC motor. On the shaft of DC motor nut is provided for mounting it on link. Wheel is directly nut bolt on the shaft of motor.
- Wheels: The wheels used in pipe inspection robot is of 75 mm diameter and 25 mm width. This wheels made of nylon material.here we have used 6 number of wheels. The circumference of wheel a provided with rubber grip so that it should not sleep inside pipe. Three wheels are idle and other three wheels are powered by using DC gear motor. This wheels are used to grip pull and push the robot inside pipe.
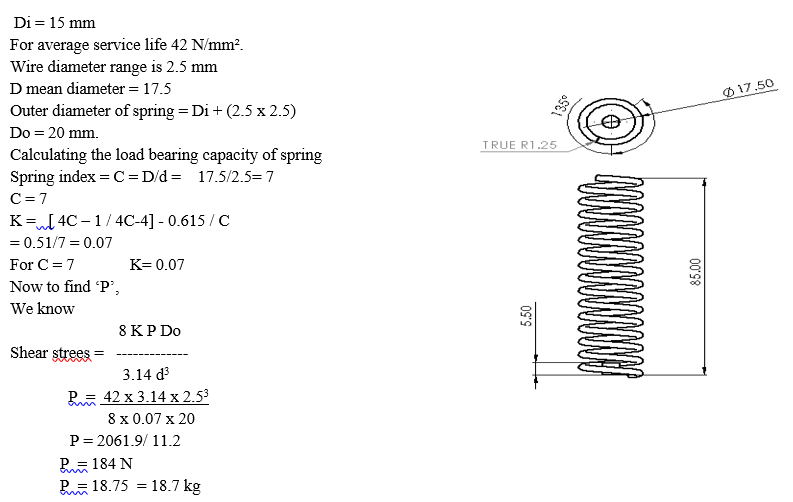
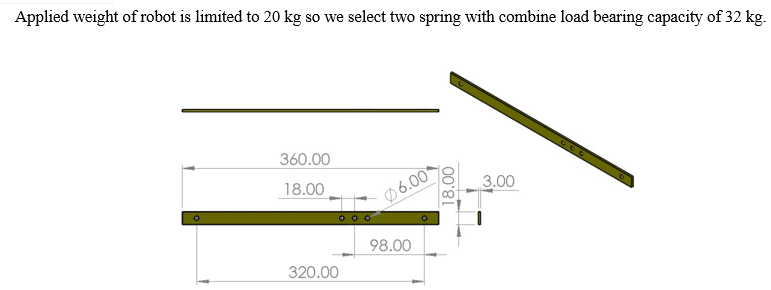
- Spring Arrangement: Springs are flexible machine elements used for controlled application of force (or torque) or for storing and release of mechanical energy. Flexibility (elastic deformation) is enabled due to cleverly designed geometry or by using of flexible material. The springs used in pipe inspection robot is for providing grip of robot inside pipe. By using spring compression, we can compress the robot and will put it inside variable size of pipe diameter. in our project we are using three number of spring, two spring are used for gripping the wheels at front and back of robot and middle spring is used for making the robot flexible while turning.
- Toggle Switch: The toggle switch is used to move the project in forward and reverse direction. These switches are fitted inside switch box and are connected by using wire with DC motors and battery. This is spring loaded toggle switches; it will automatic comes in its center position when you release the forward or backward button. Electric toggle switches control the current to power equipment.
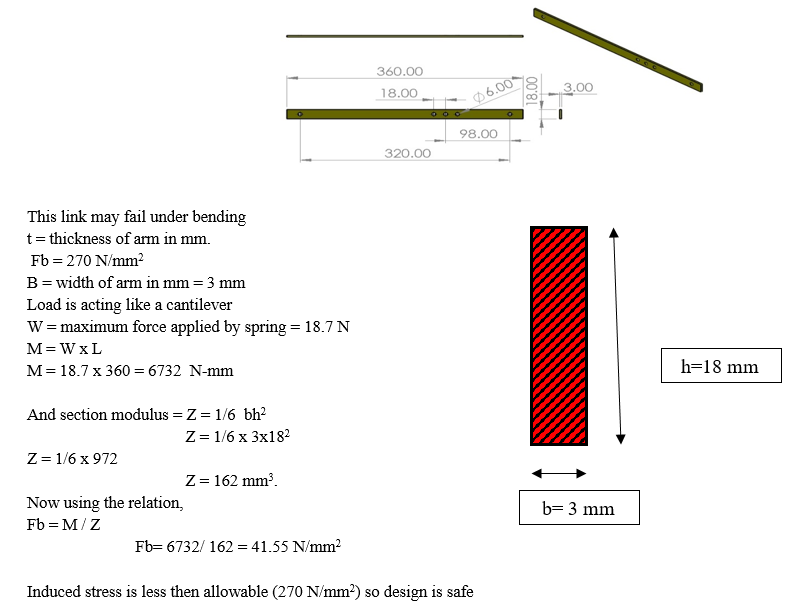
- Ms Flat: MS flat are used in our project for fabricating the arms of robot. the MS flat are used because they are light in weight compared to angle or square pipe and consumes less area for making mechanism. The ms flat used in our project is of 18 x 3 mm cross section. Flats is done by the Width (W) & the Thickness (T) of the Flat. The weight of flat bar is easily calculated. Simply multiply the appropriate alloy density by the length, width, and thickness of the required part
- Wireless Camera: Wireless cameras are wireless transmitters carrying a camera signal. The components are shown in Fig.15. The camera is wired to a wireless transmitter and the signal travels between the camera and the receiver. This works much like radio. Wireless cameras also have a channel. The receiver has channels to tune in and then the picture is obtained. The wireless camera picture is sent by the transmitter the receiver collects this signal and outputs it to a Computer or TV Monitor depending on the receiver type.
- Fasteners (Nut and Bolt): The nut bolt used for making pipe inspection robot is M6 size. The M6 size is selected because they are light in weight and it can easily take the load of our mechanism. Majorlythey are used in our project for pivoting the mechanism and for tightening of Bush on shaft.
- Battery: The battery is an electrochemical converting chemical energy into electrical energy. The main purpose of the battery is to provide a supply of current for operating the cranking motor and other electrical units. Its specifications are 12v and 3 amps.
- Pop Rivet: The 5 mm rivets are used in our project for making the robot. Therivet is used for joining powder coated sheet with MS flat for making external pipe. A rivet is a permanent mechanical fastener. Before being installed, a rivet consists of a smooth cylindrical shaft with a head on one end. The end opposite to the head is called the tail. On installation, the rivet is placed in a punched or drilled hole, and the tail is upset, or bucked (i.e., deformed), so that it expands to about 1.5 times the original shaft diameter, holding the rivet in place. In other words, pounding creates a new "head" on the other end by smashing the "tail" material flatter, resulting in a rivet that is roughly a dumbbell shape.
- Shaft: A shaft is rotating machine element which is used to transmit power from one place to another.But in pipe inspection robot shaft is used for assembling of whole mechanism here shaft is not transmitting any tangential power but it is acting as a chases for the whole project the material used for shaft is mild steel c45.
- Sheet Metal: Sheet metal is metal formed by an industrial process into thin, flat pieces. Sheet metal is one of the fundamental forms used in metalworking, and it can be cut and bent into a variety of shapes. The sheet metal is used in our project for making pipe. The Powder coated sheet metal we are using here use of 26-gauge size i.e. 0.5 mm thickness, the weight of sheet is 3.9 kg per square meter.
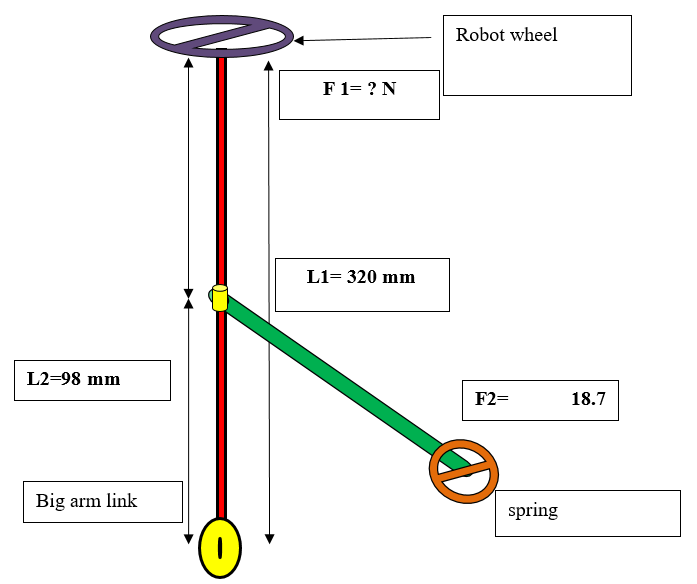
IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Pipe used for the demonstration is made of a powdered coated sheet plastic with 300 mm in diameter. The footpads are made of rubber grip just for the demonstration, but it may be need touse high friction footpads for real application. Both spring loaded arms are partially expanded at the initial position. The robot is subjected to the speed test. It is done bymeasuring time while the robot moves along the predetermined distance. It is shown that the average speed ranges 0.6~ 0.79 m/minand fifty percent decrease in speed while taking turn. By using lights and camera clear view of cracks and holes is shown on mobile and holes are visible on pipe from outside.
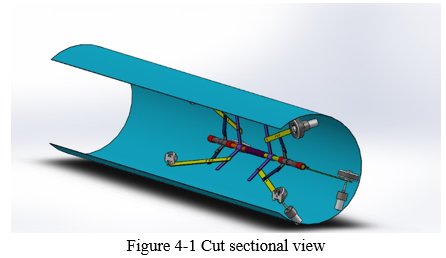
Conclusion
The design and fabrication of pipe inspection robot is successfully demonstrated. The camera installed for inspection purpose works well, the camera gives a clear view of crack, obstacle, damages, rust, holes.For non-insulated pipe LED light is installed on pipe inspection robot, if the pipe is cracked or holed somewhere, the ray of light comes out from that crack and we can easily identify the damagedspots.Three springs are mounted on robot which works very well. The two spring mounted on front and back of robot provide proper grip to all the six arms of the robot. This robot can travel in in pipe varying size from 300 mm to 500 mm. Because of spring the robot gets very good grip it does not slip inside pipe and middle spring provide flexibility to the robot so that it can take turn inside pipe. The robot is operated by using wired remote and wireless camera with power bank is provided on Robert so that clear view inside pipe is directly shown on mobile
References
[1] Okada, T., Sanemori, T. MOGRER-A Vehicle study and realization for in-pipe inspection tasks.-IEEE J. of Robotics and Automation, v. RA-3, No6, 1987, P.573- 582. [2] Suzumori, K., Miyagawa, T., Kimura, M., Hasegawa,Y. Micro inspection robot for 1-in pipes. -IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, v.4, No3, 1999, p.286-292. [3] A small mobile robot for security and inspection operations Control Engineering Practice, Volume 10, Issue 11, November 2002, Pages 1265-1270 Nicholas S Flann, Kevin L Moore, Lili M [4] H.T. Roman and B.A. Pellegrino, Pipe crawling inspection robotsan overview. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 8 3 (1993), pp. 576–583 [5] M. Beller, E. Holden and N. Uzelac, Cracks in pipelines and how to find them. Pipeand Pipelines International, 25 6 (2001), pp. 26–34 [6] Y. Kawguchi, 1. Yochida, H. Kurumatani, and T. Kikuta, \"Development of an In-pipe Inspection Robot for Iron Pipes,\" J. of the Robotics Society of Japan, Vol. 14, No.1, pp. 137-143, 1996. [7] S. Hirose, H. Ohno, T. Mitsui, and K. Suyama, \"Design of In-pipe Inspection Vehicles for <7\'>25,<7\'> 50,<7\'> 150 pipes\", Proc. of IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation, pp.2309-2314, 1999. [8] H. R.. Choi, S. M. Ryew, S. W. Cho, \"Development of Articulated Robot for Inspection of Underground Pipelines\", Trans. of the 15th Int. Conf. on Structural Mechanics in Reactor Technology(SMiRT-15), Vol. 3 , pp.407-414, 1999. [9] S. IvI. Ryew, S. H. Baik, S. W. Ryu, K. IvI. Jung, S. G. Roh, H. R. Choi, \"Inpipe Inspection Robot System with Active Steering Mechanism\" IEEE Int. Con/. on Intelligent Robot and Systems (IROS 2000), pp. 1652-1657,2000.
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Firoz Patel, Aaftab Pathan, Ayaz Ranasariya, Asad Shailkh, Harshal Ahire. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET41365
Publish Date : 2022-04-11
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

