Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Resume Screening using NLP
Authors: Astitva Aggarwal, Samyak Jain, Shalini Jha, Ved Prakash Singh
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.43037
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Presently, we have seen the technology reaching new heights than ever ahead. But each association has a different way of working but for this they need people who have a specific skill set. Selection of the candidate is done on the base of seeing the skill set mentioned in the person\'s capsule who is applying at the organization. Generally, resumes are sorted manually but, going through the resumes of these people manually is extremely time- consuming and lower effective as there are chances of human intervention error. Hence, we have proposed a design which will sort all the resumes according to the demand of the company and reduce the working time for further recruitment process. In this design we are going to use the technology of Artificial Intelligence and Natural Language Processing. We are going to train the model for recognizing the words which actually define the skill set of the person and demanded by the association by rendering in Python language. The algorithm will work in such a way that when a resume is to be scanned it will search only for the words according to the demand by the company and sort it accordingly. The required resume is shortlisted and the rest are auto rejected by the model. This will give high effectiveness compared to the manual sorting and give produce good results. This will lots of time and work of recruiters.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Many large firms' recruitment processes have changed in recent years. Recruiters can attract a various range of applicants for his or her opportunities by using online job postings on numerous employment portals and websites. Talent acquisition is a vital, complex, and time-consuming function within Human Resources (HR). Applicants come from a spread of professions and are available from a spread of backgrounds. Each of them has had various kinds of education, has worked on various projects, and thus incorporates a distinct way of presenting his or her credentials within the resume. Resumes are unstructured documents that may be saved in a very form of file formats and are not produced using conventional forms or templates. As a result, reading resumes is difficult, and recruiters must devote a major amount of your time to sifting through resumes to pick out the most effective applicants. Effective screening of resumes requires domain knowledge, to be able to understand the relevance and applicability of a profile for the work role. With many various job roles existing today together with the typically sizable amount of applications received, shortlisting poses a challenge for the human resource department. Which is simply further worsened by the dearth of diverse skill and domain knowledge within the HR department, required for effective screening. Having the ability to comb out non-relevant profiles as early as possible within the pipeline leads to cost savings, both in terms of your time also as money. Today the industry face three major challenges:
- Separating Right Candidates from the Pack: India being an enormous job market and with millions seeking jobs; it's humanly impossible to screen the CVs and find the proper match. This makes the full hiring process slow and inefficient costing resources to the businesses.
- Making Sense of Candidate CVs: Second challenges are posed by the actual fact that the CVs within the market don't seem to be standard practically every resume within the market has different structure and format. HR needs to manually bear the CVs to search out the correct match to the duty description. This is often resource intensive and susceptible to error whereby a right candidate for the task might get missed within the process.
- Knowing that Candidates can do the task Before you Hire Them: The third and therefore the major challenge is mapping the CV to the duty description to grasp if the candidate would be ready to do the work that she is being hired.
To overcome the mentioned issues within the resume shortlisting process, during this synopsis we present an NLP based Algorithm. It takes the features extracted from the candidate’s resume as input and finds their categories, further supported the desired verbal description the categorized resume mapped and recommend the foremost suitable candidate’s profile to HR.
To overcome the mentioned issues in the resume short-listing process, in this synopsis we present an NLP based Algorithm. It takes the features extracted from the candidate’s resume as input and finds their categories, further based on the required job description the categorised resume mapped and recommend the most suitable candidate’s profile to HR.
Our main contributions are listed below:
a. We developed an automated resume recommendation system.
b. Natural Language Processing based Algorithm with similarity functions are used to find most relevant resume.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
Literature surveys are mainly carried out in order to analyse the background of the current project, which helps to find out flaws in the existing system and guides on which unsolved problems we can work out. So, the following topics not only illustrate the background of the project but also uncover the problems and flaws which motivated us to propose solutions and work on this project.
So, first let’s talk about the importance of screening of resume in selection process as it excludes all the irrelevant and unqualified candidates. Ugbah and Majors in 1992 reported that when selecting a fresher for a job, recruiters believed that applicant have great paper credentials such as resume, relevant work experience and right education followed by applicant’s behaviour during interview and when using applicants’ resumes screening medium, recruiters thinks that information provided on the resume is linked to important, job-relevant attributes or personality characteristics. Because applicants typically mail or send their resumes electronically, if resume information were linked to these important applicant constructs, substantial savings could accrue to an organization before investing in more-expensive, time-consuming selection techniques requiring on-site applicant presence. [1]
The linkage between quality of hiring and organizational outcomes is well established (Boudreau & Ramstad, 1996; Erickson, Lamoureux, & Moulton, 2014, La2014. Lawler Organizations can reasonably expect that greater levels of hiring success will contribute to improved organization-level outcomes such as profitability (Erickson et al., 2014). A variety of approaches may be taken by employers in order to improve their hiring success including improvements in applicant sources, recruiting practices, selection methods, selection criteria, and onboarding (Adkins, 1995; Carr, Pearson, Vest, & Boyar, 2006; Rynes & Cable, 2003; Russell, 2007). Sackett and Lievens (2008) identified five strategies that may be utilized by organizations to improve hiring success through selection system enhancements (i.e., enhancements of criteria and methods): (a) measure the same construct (e.g., personality) with another selection method, (b) improve construct measurement, (c) improve contextualization of measurement (e.g., ensure that 15 scales are work-specific), (d) reduce response distortion when using self-report instruments, and (e) impose a greater level of structure in the use of existing selection methods. This study provides an initial examination of resume screening processes and criteria for managerial applicants that could be used to implement the strategies outlined by Sackett & Lievens (2008)[3]
The first resume parsers were born within the late '90s to produce an information structuring technology to HR software companies that are searching for a stand-alone packaged solution to concentrate on their core business. A number of these first-mover solutions are: Sovren (1996) TextKernel (2001) Daxtra (2002) How Daxtra , Sovren , Hireability, Textkernel and Segmentr (by Riminder ) do at this task? Building a general and reliable parser requires many building blocks. For instance, the system should be ready to handle: complex layouts (ex: multi-column resumes, pictures with backgrounds, etc.) ambiguous entities (ex: Facebook, as a former employer vs. a social media skill) different media formats (PDF, Word, Image, etc.) Multiple languages etc.[4]
This article examines research on learning related vocabulary, like lexical sets,
- Opposites, and synonyms, together. This research shows that learning related words at the same time makes learning them harder. This learning difficulty is avoided if related words are learned separately, as they are when learning from normal language use. Teachers can decrease the likelihood of interference
- By making the contexts, collocates,
- Visual representations of related words as different as possible. Intuitively, it seems a decent idea to present words of related meaning together so that learners can see the distinctions between them and gain a fairly complete coverage of an outlined area of meaning. We do not have to look very far in textbooks to determine that opposites (e.g., hot-cold, long-short, old young ) , free associates (e.g., table-chair), and lexical sets (e.g., banana-orange-applepear-plum) are often presented together.[5]
Sentence segmentation (also noted as sentence boundary detection, sentence boundary disambiguation or sentence boundary recognition) is that the process of determining how a text should divided into sentences (Dale, Moisl , & Somers , 2000). A straightforward approach to unravel this problem would be to introduce a brief list of sentence-final punctuation marks like "?", "." and "!", however such an approach starts to malfunction when abbreviations like "etc." or "e.g." appear within the text (Reynar & Ratnaparkhi, 1997). After all one could create an exception list that would contain words where the dot as a punctuation sign is disregarded, however such rule-based lists are never complete , moreover multiple rules might interact erroneously with one another. As an example, what happens when the sentence ends with an abbreviation like "Mr." or "Mrs."? In such cases the punctuation marks the top of the abbreviation yet because the end of the sentence. In conclusion rule-based systems (such because the one described above) has the advantage of simplicity, however they don’t learn nor use the advantage provided by annotated corpora (Kiss & Strunk , 2006).
III. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION & CHALLENGES
A recruiter must undergo every resume to seek out best resume as per the task description. This process isn't only tedious but exhausting also. Let’s take a glance how the backend process of resume screening works:
- A single job posting can get anywhere from hundreds to thousands resumes. From which only about 4-6 resumes are shortlisted.
- On an average every experienced resume is 2-3 pages, hence it's practically out of the question to go through all the resume for any recruiter.
- While browsing initial 50-100 resumes, if a recruiter finds 8-10 suitable resume, chances are that they do not screen the resumes further. This further reduces the prospect of getting a decent resume shortlisted.
- Wherever there's human intervention, it's very natural to own some amount of bias. As a result, it's difficult to get an unbiased resume score.
- It is incredibly time-consuming also.
With this manual resume screening process, many a time a deserving resume is lost and doesn’t reach interview round. [3]
IV. PROBLEM SOLUTION
We are developing a web application using Django, HTML and CSS through which we will integrate various module.
A. Module Such As
- Applicants’ side
- Recruiters’ side
B. Software Requirements Are
- Operating System: Any
- Python3 : it need python to be installed in your system to run this successfully.
C. Packages in Python
- SpaCy
- Matplotlib
Hardware Requirements are- In terms of hardware requirements there is not much required at all but still below requirements are must: Working PC or Laptop or Smartphone capable of running a browser and a strong & fast internet connection.
- Recruiters’ Side: Recruiter have to first login into the application and then they have to create a job posting and have to set their requirements as keywords.
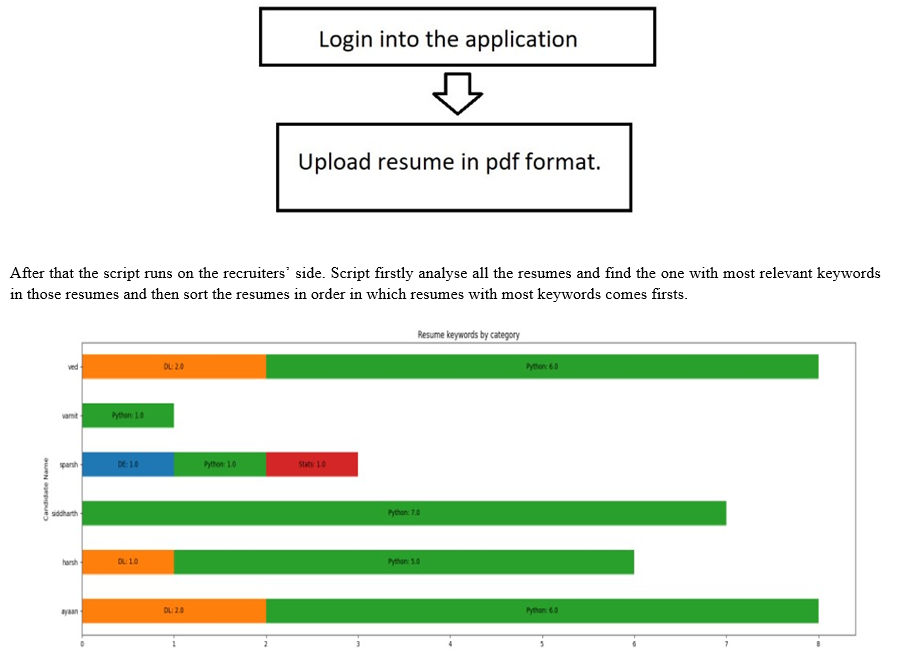
2. Applicants’ Side: Job seeker have to login to the web portal first then they’ll have to upload their resumes. The resumes should have to be in .pdf format which will then get stored in database.
Conclusion
The proposed system is currently under implementation and we are working on making as accurate as possible. This system will definitely aid the recruiters to filter out the most prospective candidates based on their resumes for further rounds in the hiring process. It will ease the burden of the recruiters and they will not have to manually view each and every resume of the large pool of candidates.
References
[1] Michael S. Cole University of St. Gallen Hubert S. Feild & William F. Giles Auburn University “What Can We Uncover about Applicants Based on Their Resumes? A Field Study” Applied HRM Research, 2003, Volume 8, Number 2, 51-62 [2] Workonic “challenges in manual resume screening” June 2019 [3] Gregory E. Higgins University of Southern Mississippi “Screening the Managerial Applicant: A Descriptive Phenomenological Study of Résumé Review and Evaluation” The Aquila Digital Community The University of Southern Mississippi Spring 2019 [4] Seiv, M., HR software companies? Why structuring your data is crucial for your business?, https://medium.riminder.net/hr-software-companies-why-structuring-your-data-is-crucial-for-your-business-f749ecf3255a. Accessed on 25 Jan 2020 [5] Nation, P.: Learning vocabulary in lexical sets: dangers and guidelines. TESOL J. 9(2), 6–10 (2000) [6] Neumer, T., Efficient Natural Language Processing for Automated Recruiting on the Example of a Software Engineering Talent-Pool 88 (2018)
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Astitva Aggarwal, Samyak Jain, Shalini Jha, Ved Prakash Singh. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET43037
Publish Date : 2022-05-21
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

