Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- Copyright
Skin Disease Detection Using Machine Learning
Authors: Harsh Ahir, Chandu D, Rohit Kumar, Harshvardhan karthik, Assistant Prof. Sunanda
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.49211
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Particularly dangerous and frequently contagious include melanoma, eczema, and impetigo. When found early enough, some skin conditions are curable. The main issue with it is that only a skilled dermatologist can identify and categorise such diseases. In several cases, medical professionals appropriately categorise the illness and consequently give the pa-tient the wrong drugs. Navies Bias Classifier has been contrasted. Real-time testing findings are displayed. Since our solu-tion is mobile-based, it can be used anywhere. In order for the programme to function, the patient must supply an image of the affected area. It is processed using deep learning techniques and produces the most accurate results. In this essay, we compare two distinct real-time skin disease detection algorithms based on accuracy in this presentation.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
The human skin is the largest organ in the body. Its surface area is around two square yards, and its weight is between six and nine pounds. Skin serves as a barrier between the inside body and the outside world. It defends against bacterial, viral, allergic, and fungal infections and regulates body temperature. Dermatitis, hives, and other skin issues can be brought on by allergies, irritants, certain diseases, genetics, and immune system-related issues. Numerous skin conditions, including eczema, ringworm, alopecia, and acne, also have an impact . Most image processing models start with input samples that are 2-D signals and then process those data using predetermined signal processing techniques. It is a technology that is commonly utilised nowadays and has many uses in the commercial world.
II. MOTIVATION
Melanoma is the most varied skin disorder, affecting more than 125 million individuals globally, and its prevalence has been rapidly increasing over the past few decades. Nevus incidence is significant, particularly in rural areas. Skin conditions may cause difficulties in the body, including the transmission of an infection from one person to another, if they are not treated at an early stage. Investigating the contaminated area early on might help to prevent skin problems. The characteristics of skin photographs vary widely, making it difficult to develop a reliable and effective algorithm for automatically identifying skin diseases and their severity. Skin tone and colour are key factors in identifying skin diseases. Visual differences exist between skin colour and coarseness. Such photos must be processed automatically for skin analysis, which calls for a quantitative discriminator to distinguish between the illnesses.
III. RELATED WORKS
- The Paper [1], The most prevalent disease in the world is skin disease. A computer-aided skin disease diagnostic model is recommended to provide a more objective and reliable response since identifying skin illnesses requires dermatologists to have a high level of expertise and precision. To aid in the diagnosis of skin disorders like skin cancer and skin tumours, numerous research have been carried out. However, correct diagnosis of the disorder is rather challenging due to factors like low contrast between lesions and skin, visual similarity between the infected and unaffected parts, etc. The goal of this project is to identify skin disorders from skin photos, analyse those images by removing noise and other unwanted features, and then convert the images to greyscale to speed up processing and collect pertinent data.
- The Paper [2], Skin conditions like melanoma and carcinoma are notoriously difficult to diagnose in their early stages and are even more challenging to categorise. Melanoma is now widely recognised as the most serious type of skin cancer among all others because, if detected and treated early, it has a significantly higher propensity to spread to other regions of the body. In this article, we suggest a technique for determining whether a particular sample has melanoma or not. The steps in this study include gathering labelled data from pre-processed images, flattening those images, and obtaining the pixel intensities of images into an array. Then, a database is appended with each of these arrays. The SVM is subsequently trained using labelled data and a suitable kernel, and the samples are successfully classified using the trained data. According to the results, a 90% categorization accuracy was achieved.' The Paper'
- The Paper [3], As one of the most common human diseases, skin disease, intelligent classification systems for skin disorders have become a new topic of deep learning study that is extremely important for both patients and medical professionals. Several datasets on skin diseases, such as the SD-198 dataset, which contains 6584 clinical skin disease pictures categorised into 198 categories, have already been made public. However, previous research has shown that because clinical dermatology is so diverse, deep visual features perform as poorly as or worse than hand-crafted features for diagnosing skin disorders. In order to improve the deep visual feature creation process. Our test shows that when positional information is included, deep visual features outperform hand-crafted features. We believe that this strategy outperforms even the most sophisticated clinical skin disease classification methods now in use.
- The Paper [4], The exterior integument of the human body is its skin. The hue of human skin varies from person to person, and there are three different skin types: combination, dry, and oily. The human skin's diversity offers bacteria and other microbes a range of habitats. Melanocytes, which are found in human skin, produce melanin, which can absorb UV radiation from the sun that can damage skin and lead to skin cancer. In the majority of third world communities, the essential instruments required ,there are presently no methods for early illness detection. If you have signs of skin conditions such eczema, chicken pox, ringworm, psoriasis, dermatomyositis, candidiasis, cellulitis, or Scleroderma. Adaptive thresholding, edge detection, K-means clustering, and morphology-based picture segmentation were used in this study to identify skin illnesses from the provided image set.
- The Paper [5], As a result of their challenging and subjective human interpretation, dermatological diseases are one of the most pressing medical challenges of the twenty-first century. How important is early diagnosis in influencing the likelihood of recovery from deadly conditions like melanoma? When a batch of images contains a variety of diagnoses, we believe the adoption of automated methods will facilitate early diagnosis. As a result, we describe in this article a fully automated approach for identifying dermatological diseases from lesion photos. This machine intervention differs from traditional medical personnel-based identification. The three stages of our model's development are data collection and augmentation, model creation, and prediction. To construct a more precise structure, we combined image processing tools with a variety of AI techniques, such as Convolution Neural Network and Support Vector Machine.
- The Paper [6], Everybody gets skin problems frequently, and different kinds of infections are on the rise. You are aware that all of these illnesses can be quite dangerous if not treated quickly. Skin illnesses cause more than just skin harm. It can significantly impact a person's day-to-day activities, undermine self-confidence, impede movement, and lead to despair. On occasion, a lot of folks make an effort to treat these allergies employing their own therapies. However, the danger would be magnified if these treatments were ineffective for that kind of skin condition. Skin conditions can readily spread from person to person, so it's important to manage them when they're first discovered to stop them from getting worse. After taking a picture of the skin condition, several pre-processing procedures are used to reduce noise and improve the image. Thresholding segmentation, a segmentation technique, is used to divide up this image. In order to diagnose the skin illness and give consumers advice, data mining techniques are finally applied. This expert system has a melanoma recognition accuracy of 85%, impetigo recognition accuracy of 95%, and eczema recognition accuracy of 85%.
7. The Paper [7], In this model, skin illness images are assessed using the grey normalised symmetrical simultaneous occurrence stencils (GLCM) method to determine the state of the skin disease. The suggested approach is employed in a productive and cost-effective manner for the computerised evaluation of skin problems. This mechanism aids the skin in reducing the error in medical diagnosis. The initial checkup for people in distant areas without access to qualified doctors is another. In order to store the implied demand for textual skin images, the system uses relational databases. The same type of photos can also be used with this approach directly over feature vectors.
8. The Paper [8], The medical profession is a newer topic of research in artificial intelligence (AI). In this study, CBR and image processing are combined to construct a mobile-based medical support system for the diagnosis of skin diseases. This model was created to assist users in determining if they have a condition or not by helping them pre-examine their skin status. Additionally, it is important to raise awareness of skin illnesses so that we can find a remedy before they worsen and cause death or infection in other individuals. 90% accuracy is achieved in the suggested system's detection of 6 different skin disorders.15% of the symptoms are utilised for testing, 10% are used for validation, and 75% are used for testing. In comparison to unsupervised systems, which only detect diseases at a rate of 80%, our supervised system detects diseases at a rate of 90%. The following table shows the correlation between the sample disease and other associated diseases: Skin Cancer: 51%; Acne: 75%.
9. The Paper [9], The concept of "skin detection" the classification of the pixels in an image into two groups—skin and non-skin—is referred to as from an image. Numerous algorithms extract features for pixel categorization using multiple colour spaces, yet the bulk of these methods fail to correctly identify different skin tones. The color-based image retrieval (CBIR) technique is used to implement the current methodology in this work. In this method, a set of feature vectors are first created by using the CBIR method, picture tiling, and establishing the association between a pixel and its neighbours. Then, during the test stage, training is employed for skin detection. The suggested model is highly accurate in differentiating between skin types, according to experimental results, and it is not sensitive to changes in lighting or facial movement. The two steps in the suggested method are training and testing. In the testing stage, skin area was discriminated from non-skin areas after pure skin images were first trained in the training stage.
10. The Paper [10], This model, which is used to recognise skin diseases, is implemented using rule-based and forward chaining inference engine techniques. By using this approach, users are able to diagnose paediatric skin conditions online and promptly offer pertinent medical recommendations or counsel. This system is composed of the diagnosis module, login module, info module, report module, and management module. The diagnosis and management modules are the two main ones. Children's symptoms and conditions are recognised in the diagnose module based on questions the user is asked and their responses. In response to queries concerning the signs and symptoms and the state of children's skin, this approach might be an option for parents to recognise skin illnesses in kids.
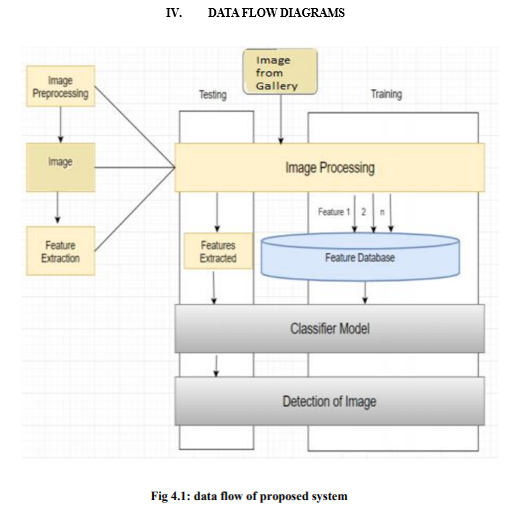
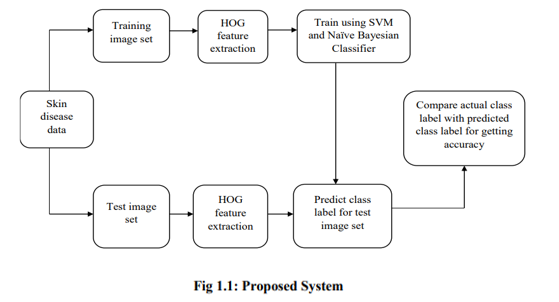
V. LIMITATIONS
Eczema, impetigo, and melanoma are the only three skin conditions for which this treatment is used. Because it has only been built for Windows applications, it has not yet been created for smart phones running on Android, iOS, etc.
It is necessary to capture the image for this application without any lighting effects. It only supports English; it doesn't support common languages like Sinhala or Tamil.
Conclusion
Skin illness detection is a crucial step in lowering mortality rates, disease transmission, and skin disease progression. Skin disease diagnosis requires lengthy and expensive clinical procedures. In the early stages of developing an automated derma-tology screening system, image processing techniques are helpful. The identification of characteristics is crucial in the claci-fication of skin disorders. In this study, pre-trained SVM and naive bayes were used to build the detection algorithm. In conclusion, it is important to keep in mind that because Saudi Arabia has extremely hot weather and the presence of humidity, skin illnesses are more like-ly to spread there.
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Harsh Ahir, Chandu D, Rohit Kumar, Harshvardhan karthik, Assistant Prof. Sunanda. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET49211
Publish Date : 2023-02-22
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

