Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Experimental Study of Mix Design of Concrete by Mixing Sand with Plastic Waste
Authors: Vikash Ranjan, Dr. Kapil Soni
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2022.42895
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
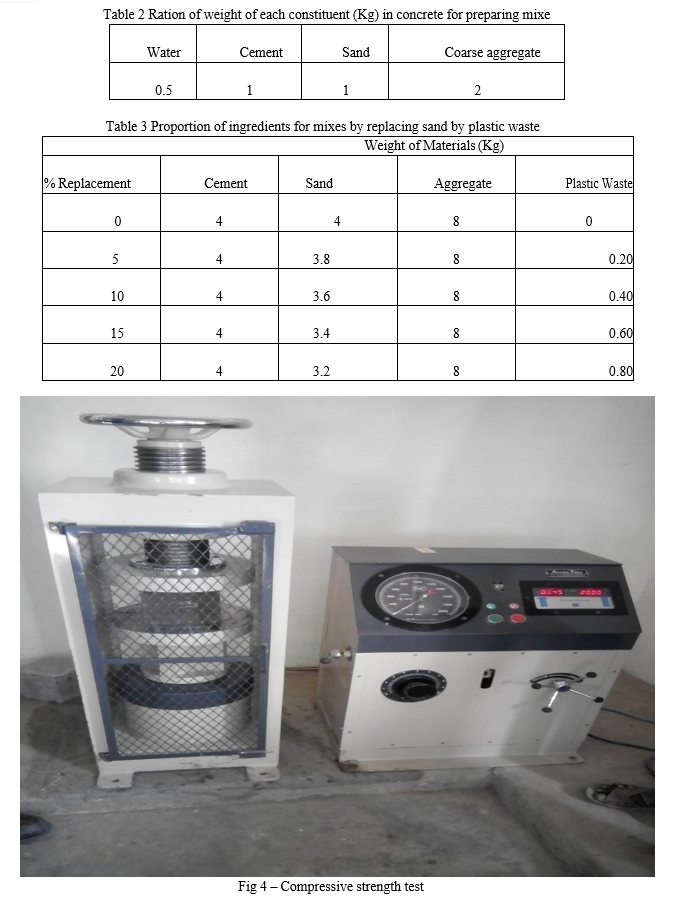
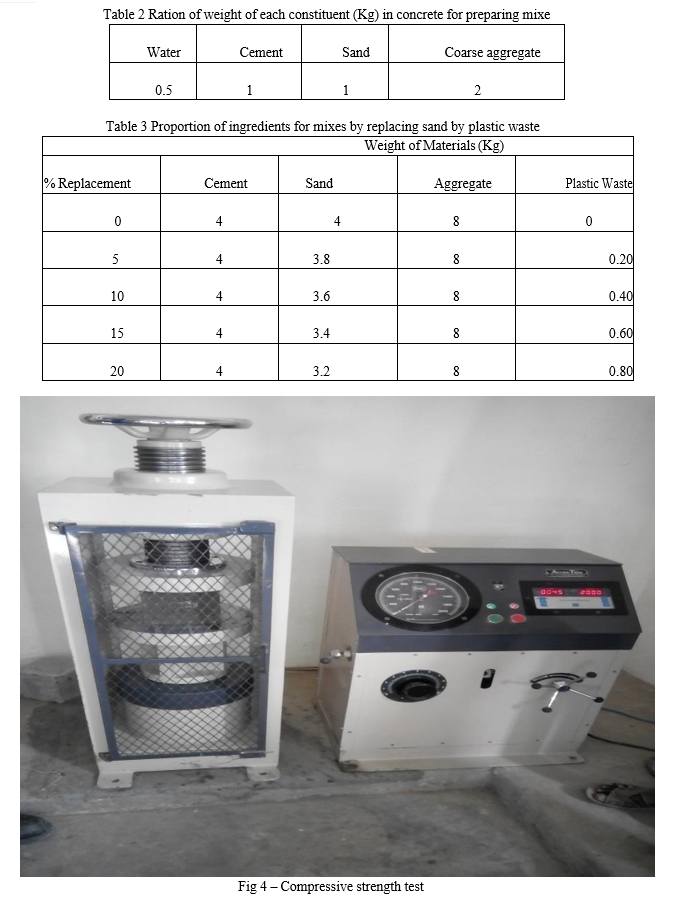
Cement concrete are designed to resist the disastrous surrounding effects such as high temperature variations, high humid environments, coastal areas, industrial areas and other pollutant types. Engineers are continuously studying its properties and performance by blending several waste and modern materials in cement or other aggregates. The major advantage of these materials is the replacement of cement or other ingredients partially in concrete and presenting the comparable cementations property. The use of waste material can consume these materials and also saves the principal ingredients of concrete. This can also improve the properties of concrete in fresh and hydrated states or may presents the properties comparable to the basic properties of concrete. In the current study a set of experiments had been performed to Compare the use of one type of mixes formed by replacing sand with Plastic waste. Sand was replaced in different proportions such as 5 %, 10 %, 15% And 20 % by these materials. The properties of concrete are studied for 7days, 14days, 21days and 28days.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Utilization of plastic waste or other waste materials in preparing concrete for various civil engineering projects is a subject of high significance. Integration of extra materials in concrete or mortar affects its several characteristics such as strength, compaction factor and other relative performances.
There are various purposes of applying additional materials as substitute to cement and other components in concrete – first is the financial saving obtained by replacing a considerable part of the aggregates with these materials and second is saving of materials. The ecological aspects of cement are now receiving more concern of researchers, as cement developing is liable for about large amount of total worldwide waste emissions from manufacturing sources. The trend of mixing several kinds of additional materials in building engineering is now growing. This has double advantage -
- To reduce the quantity of deposited waste.
- To conserve natural resources.
Partial substitution of sand or cement in concrete minimizes the energy consumption and thus, decreases the global warming. Current practice may permit up to a certain limit of reduction in the content of sand in the concrete mix.
A. Additives Used In The Presentstudy
Cement and sand are the main materials needed for fulfilling the modern infrastructure needs. As an outcome, the construction and concrete industry worldwide is facing growing challenges in conserving material and energy resources, as well as reducing its CO2 emissions. According to the International Energy Agency, the main concern for cement producers is the increase in energy efficiency and the use of substitute wastes or other waste materials. Consequently, it is converting into employ the substitute material in cement concrete.
Plastic waste is a significant material utilized in the building production. During the last decade, considerable attention has been given to the use of plastic waste as a partial replacement of plastic waste to produce high-strength concrete. Plastic waste is added to element concrete to improve its properties, in particular its compressive strength, and other resistance. Plastic waste consists of fine particles with particles very small to the size of the average cement particle size. Because of its extreme fineness and plastics content, plastic waste is a very effective material particle.
Plastic waste is formed from plastic factories during the breaking of plastic parts, and almost 10 – 15 % of the processed plastic is converted into the waste. Deletion of the plastic waste from the plastic places is a noteworthy environmental trouble today. Though, waste material from plastic industry can be used to enlarge several properties of concrete. It has been analyzed that typically compressive strength increased with accumulation of this waste in place of sand. Thereby fore, employment of the plastic dust in a variety of industrial sectors particularly the civil engineering projects, would aid to defend the surroundings.
Reprocess of these waste materials in construction industry is an inventive run towards sustainable and ecological construction. Utilization of waste materials in construction has been considered as ecological, however, this thought has been not accepted widely between the researchers as these materials imposes severe deleterious effects on the concrete. But, through proper concrete mix design the reprocessed concrete can achieve target strength and is appropriate for broad variety of applications in Civil engineering.
To estimate the efficiency of plastic waste as substitute Construction material,
Following properties of concrete were requisite to be tested.
- Compressive strength after different curing periods
- Initial and final setting time
- Workability
II. TESTING METHODOLOGY
Table 1 parameters identified and testing techniques
|
PARAMETERS |
SIGNIFICANCE |
TESTING |
|
Compressive Strength (7 Days) |
In 7 days, concrete can gain almost 65 % of The28 days compressive strength. |
Compression testing Machine |
|
Compressive Strength (14 Days) |
In 14 days, concrete can gain almost 68 % of The28 days compressive strength. |
Compression testing Machine |
|
Compressive Strength (21 Days) |
21-day test may be help to detect potential problem with concrete or testing procedure at the lab. In 21 days, compressive strength
is almost 90 % of the 28 days strength. |
Compression testing Machine |
|
Compressive Strength (28 Days) |
To evaluate quality and characteristics of concrete. Concrete mixes are recognized by their respective 28 days strength. |
Compression testing Machine |
|
PARAMETERS |
SIGNIFICANCE |
TESTING |
|
Initial Setting Time |
Time period available for the transportation and placing of concrete after mixing. It marks roughly the end of the period when the wet mix can be moulded into shape. |
Vicat’s Apparatus |
|
Final Setting Time |
The final setting time is the point at which the set cement has acquired a sufficient firmness to resist a certain defined pressure. |
Vicat’s Apparatus |
|
Workability |
Workability represents the effort which is to be done to compact the concrete in a given module. |
Slump Test |
A. Compressive Strength
Out of many tests applied to the concrete, this is the utmost important which gives an idea about all the characteristics of concrete. By this single test one judge that whether Concreting has been done properly or not. For cube test two types of specimens either cubes of 15 cm x 15 cm x 15 cm or 10cm x 10 cm x 10 cm depending upon the size of aggregate are used. For most of the works cubical moulds of size 15 cm x 15cm x 15 cm are commonly used.
This concrete is poured in the mould and tempered properly so as not to have any voids. After 24 hours these moulds are removed and test specimens are put in water for curing. The top surface of these specimens should be made even and smooth. This is done by putting cement paste and spreading smoothly on whole area of specimen.
These specimens are tested by compression testing machine after 7, 21 days curing or 28 days curing. Load should be applied gradually at the rate of 140 kg/cm2 per minute till the specimens fails. Load at the failure divided by area of specimen gives the compressive strength of concrete.
Preparation: The proportion and material for making these test specimens are from the same concrete used in the field. Mix the cement and fine aggregate on a water tight none- absorbent platform until the mixture is thoroughly blended and is of uniform color. Add the coarse aggregate and mix with cement and fine aggregate until the coarse aggregate is uniformly distributed throughout the batch. Add water and mix it until the concrete.
The test specimens are stored in moist air for 24hours and after this period the specimens are marked and removed from the molds and kept submerged in clear fresh water until taken out prior to test.
Procedure
- Remove the specimen from water after specified curing time and wipe out excess water from the surface.
- Take the dimension of the specimen to the nearest 0.2m
- Clean the bearing surface of the testing machine
- Place the specimen in the machine in such a manner that the load shall be applied to the opposite sides of the cube cast.
- Align the specimen centrally on the base plate of the machine.
- Rotate the movable portion gently by hand so that it touches the top surface ofthe specimen.
- Apply the load gradually without shock and continuously at the rate of 140kg/cm2/minute till the specimen fails.
- Record the maximum load and note any unusual features in the type of failure.
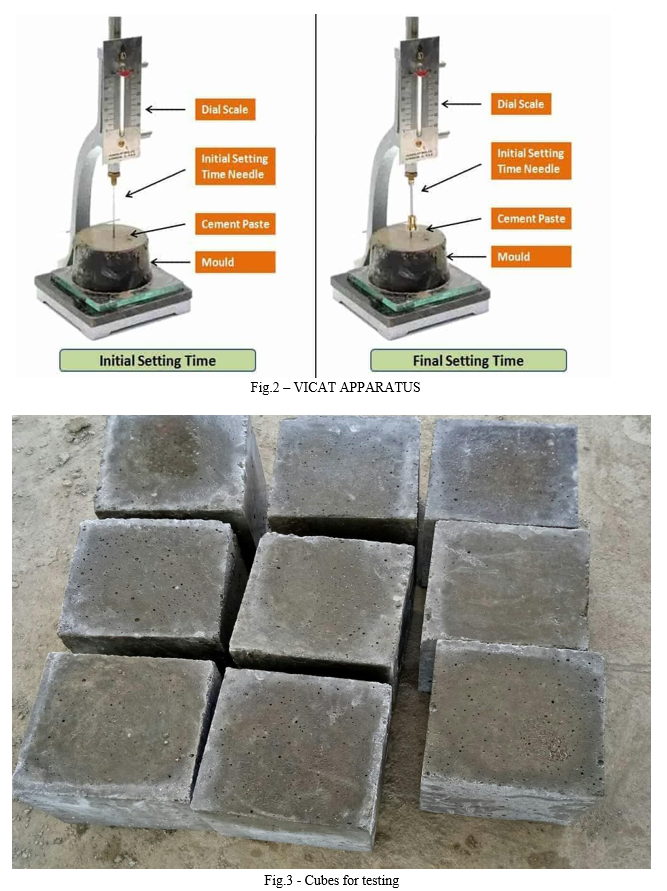
B. Initial And Final Setting Time
We need to calculate the initial and final setting time as per IS: 4031 (Part 5) – 1988. To do so we need Vicat’s apparatus conforming to IS: 5513 – 1976, Balance, whose permissible variation at a load of 1000g should be +1.0g, Gauging trowel conforming to IS: 10086 – 1982
Procedure to determine initial and final setting time of cement
- Prepare a cement paste by gauging the cement with 0.85 times the water required to give a paste of standard consistency.
- Start a stop-watch, the moment water is added to the cement.
- Fill the Vicat’s mould completely with the cement paste gauged as above, the mould resting on a non-porous plate and smooth off the surface of the paste making it level with the top of the mould. The cement block thus prepared in the mould is the test block.
a. Initial Setting Time: Place the test block under the rod bearing the needle. Lower the needle gently in order to make contact with the surface of the cement paste and release quickly, allowing it to penetrate the test block. Repeat the procedure till the needle fails to pierce the test block to a point 5.0 ± 0.5mm measured from the bottom of the mould. The time period elapsing between the time, water is added to the cement and the time, the needle fails to pierce the test block by 5.0 ± 0.5mm measured from the bottom of the mould, is the initial setting time.
b. Final Setting Time: Replace the above needle by the one with an annular attachment. The cement should be considered as finally set when, upon applying the needle gently to the surface of the test block, the needle makes an impression therein, while the attachment fails to do so. The period elapsing between the time, water is added to the cement and the time, the needle makes an impression on the surface of the test block, while the attachment fails todo so, is the final setting time.
C. Workability
The behavior of fresh concrete from mixing up to compaction depends mainly on the property called “workability of concrete”. Workability of concrete is a term which consists of the following four partial properties of concrete namely, Mixability, Transportability, Mouldability and Compatibility. The slump is a measure indicating the consistency or workability of cement concrete. It gives an idea of water content needed for concrete to be used for different works. Slump cone apparatus is required to evaluate workability of concrete.
Procedure: Four mixes are to be prepared with water-cement ratio (by mass) of 0.50, 0.60, 0.70 and 0.80, respectively, and for each mix take 10 kg of coarse aggregates, 5kg of sand and 2.5kg of cement with each mix proceed as follows:
- Mix the dry constituents thoroughly to get a uniform color and then add water.
- Place the mixed concrete in the cleaned slump cone mould in 4 layers, each approximately ¼ of the height of the mould. Tamp each layer 25 times with tamping rod distributing the strokes in a uniform manner over the cross-section of the mould. For the second and subsequent layers the tamping rod should penetrate in to the underlying layer.
- Strike off the top with a trowel or tamping rod so that the mould is exactly filled.
- Remove the cone immediately, raising it slowly and carefully in the vertical direction.
- As soon as the concrete settlement comes to a stop, measure the subsidence of concrete in mm which will give the slump.


V. FUTURE SCOPE
- This work can be extended for high grade of concrete.
- Mix design of concrete by using other waste materials.
Conclusion
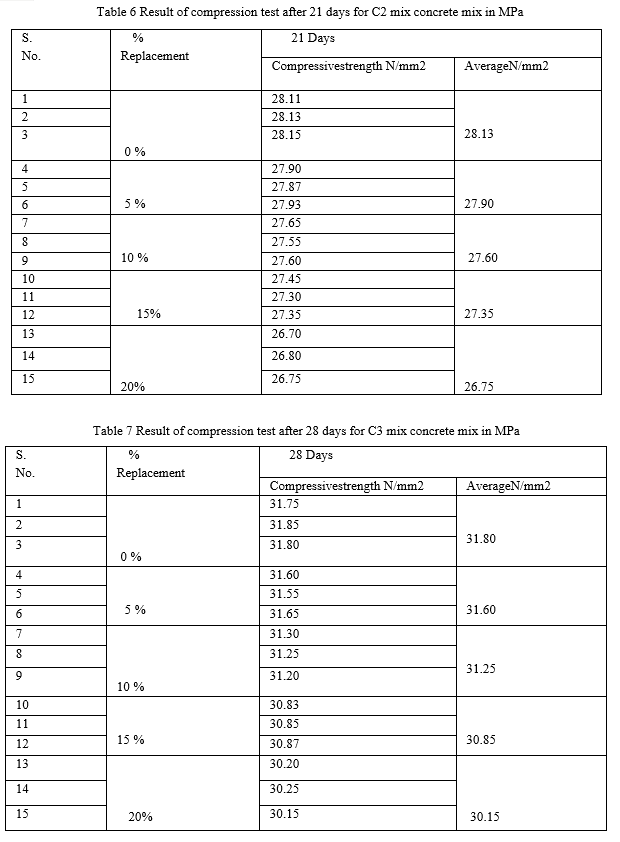
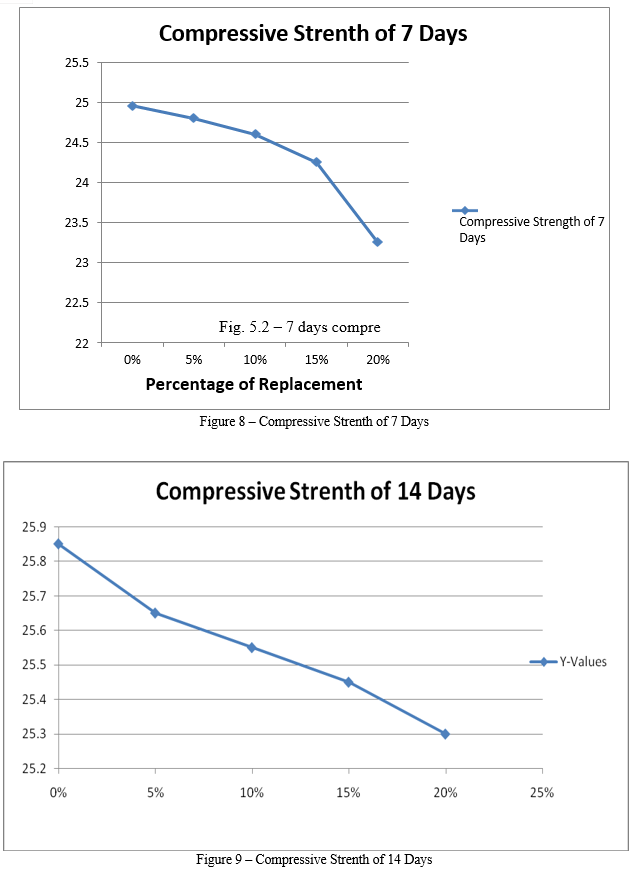
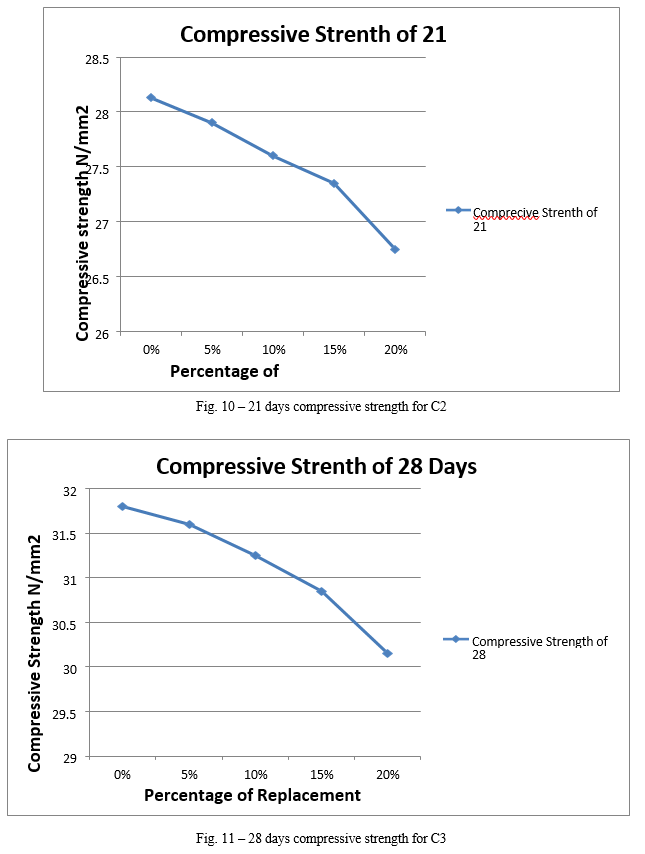
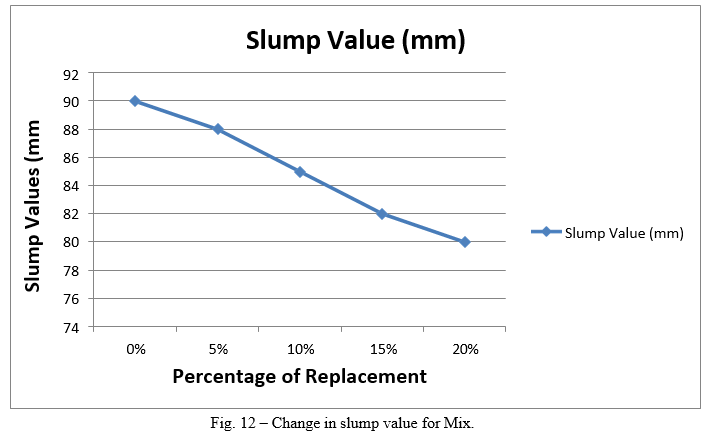
Following are the conclusions of the present work 1) It is observed that when the percent replacement increases compressive strength decreases. 2) Slump value is found to be decreasing by increasing the percentage of plastic waste. 3) The slump value for sand replacement with plastic waste up to 20% shows a decrease of about 11%. 4) Reduction in compressive strength for sand replacement with plastic waste in concrete is only 1%, 2%, 3% and 5% at the age of 28 days after replacement of 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% respectively. 5) Hence, from above results it has been recommended to replace sand upto20% with Plastic waste for good compressive strength and optimum workability. 6) Test on plastic waste replaced concrete shows that the properties of this concrete are satisfactory.
References
[1] An Experimental Study on Partial Replacement of Sand with Crushed Plastic in Concrete. (M. Usha Rani and J.Martina ,2016). [2] High Performance Concrete Using M Sand. (Magudeaswaran. P, Dr. Eswaramoorthi. P i. ,2016). [3] Study on performance of concrete with over-burnt plastics aggregates and micro- silica admixture.(K Praveen, Dhanya Sathyan, K M Mini ,2016). [4] Cement Replacement by Fly Ash in Concrete.(R. D. Padhye, N. S. Deo. ,2016). [5] Manufactured sand with silica fume, an alternative to river sand and in concrete industry. (Dr. T Suresh Babu, M Anveshkumar ,2016). [6] Experimental Investigation Of Using Concrete Waste And Plastic Waste As A Coarse Aggregate.(T. Subramani , S. Kumaran ,2015). [7] Properties of Concrete made with Waste Clay Plastic as Sand Incorporating Nano SiO2. (Davoud Tavakoli, Ali Heidari and Susan Hayati Pilehrood ,2014). [8] An Experimental Study On Properties Of Fly Ash Plastics.(Er. Rinku Kumar1, Er. Naveen Hooda,2014). [9] Effect of waste plastic kiln dust with partial replacement of cement with adding superplasticizer in construction of Paver Blocks.(Sharda Sharma, Ritesh Mall and Khalid Raza, 2014) [10] Partial Replacement of Sand with Quarry Dust in Concrete. (Chandana Sukesh, Katakam Bala Krishna, P. Sri Lakshmi Sai Teja, S. Kanakambara Rao ,2013).
Copyright
Copyright © 2022 Vikash Ranjan, Dr. Kapil Soni. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET42895
Publish Date : 2022-05-18
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

